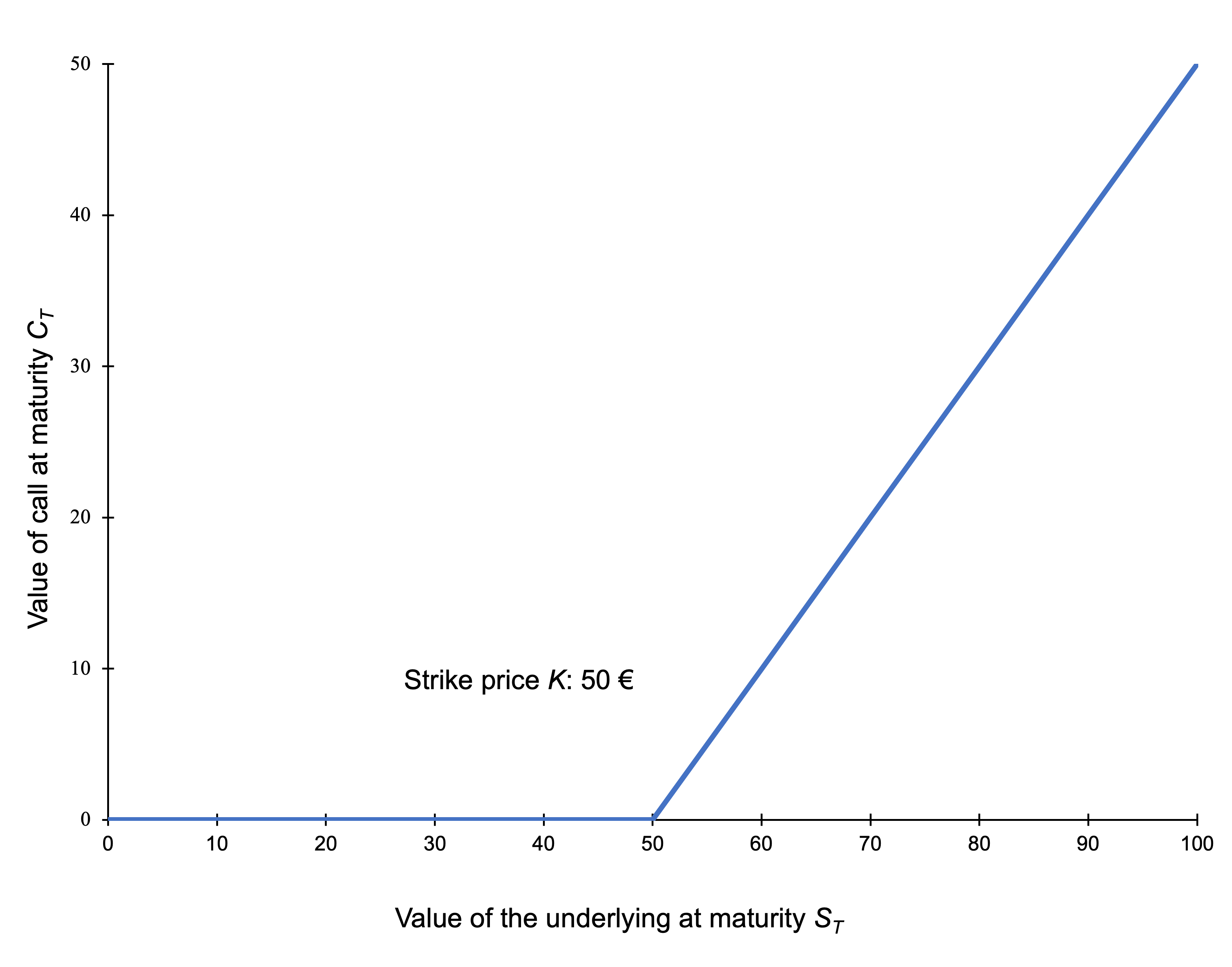
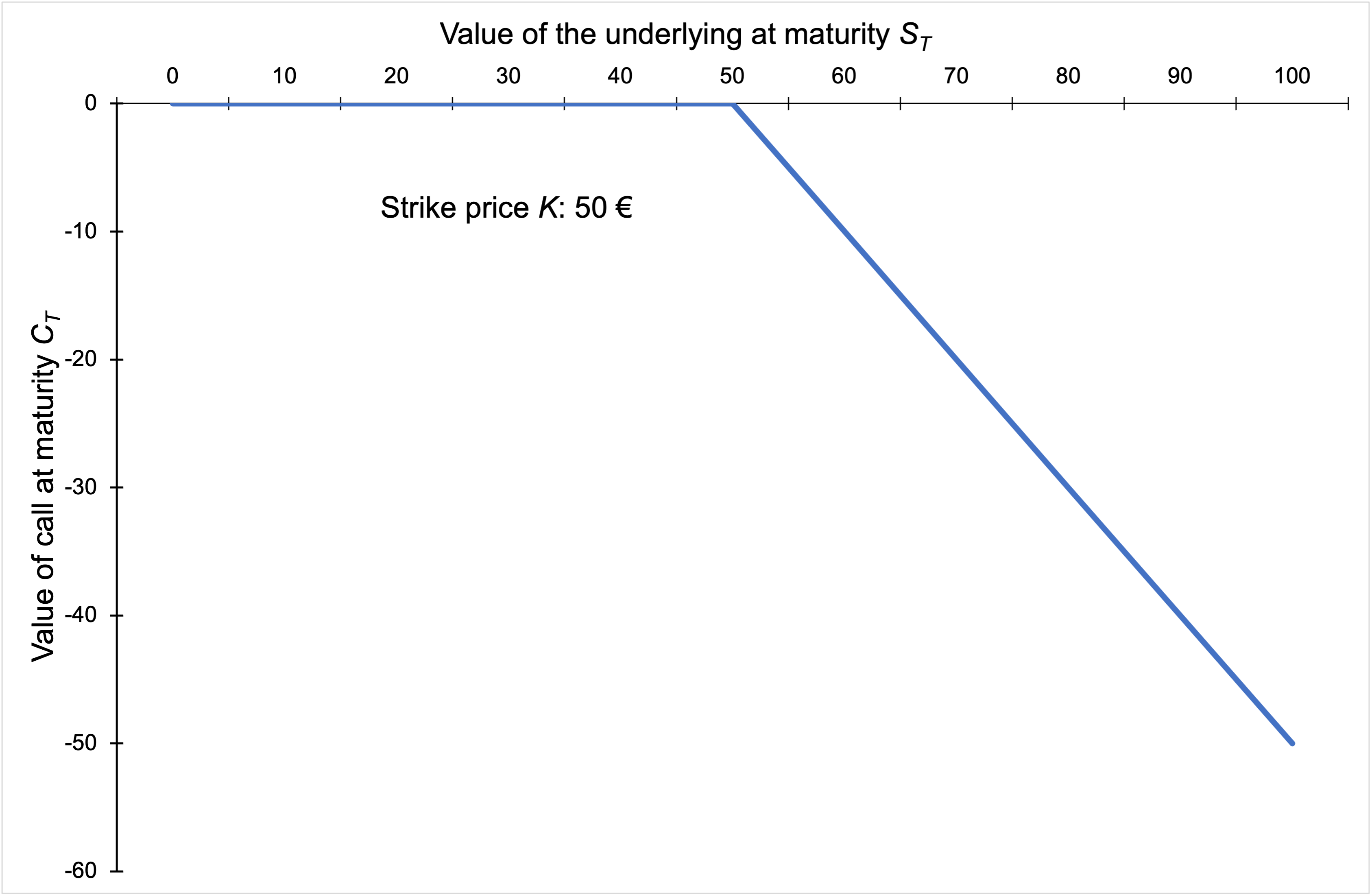
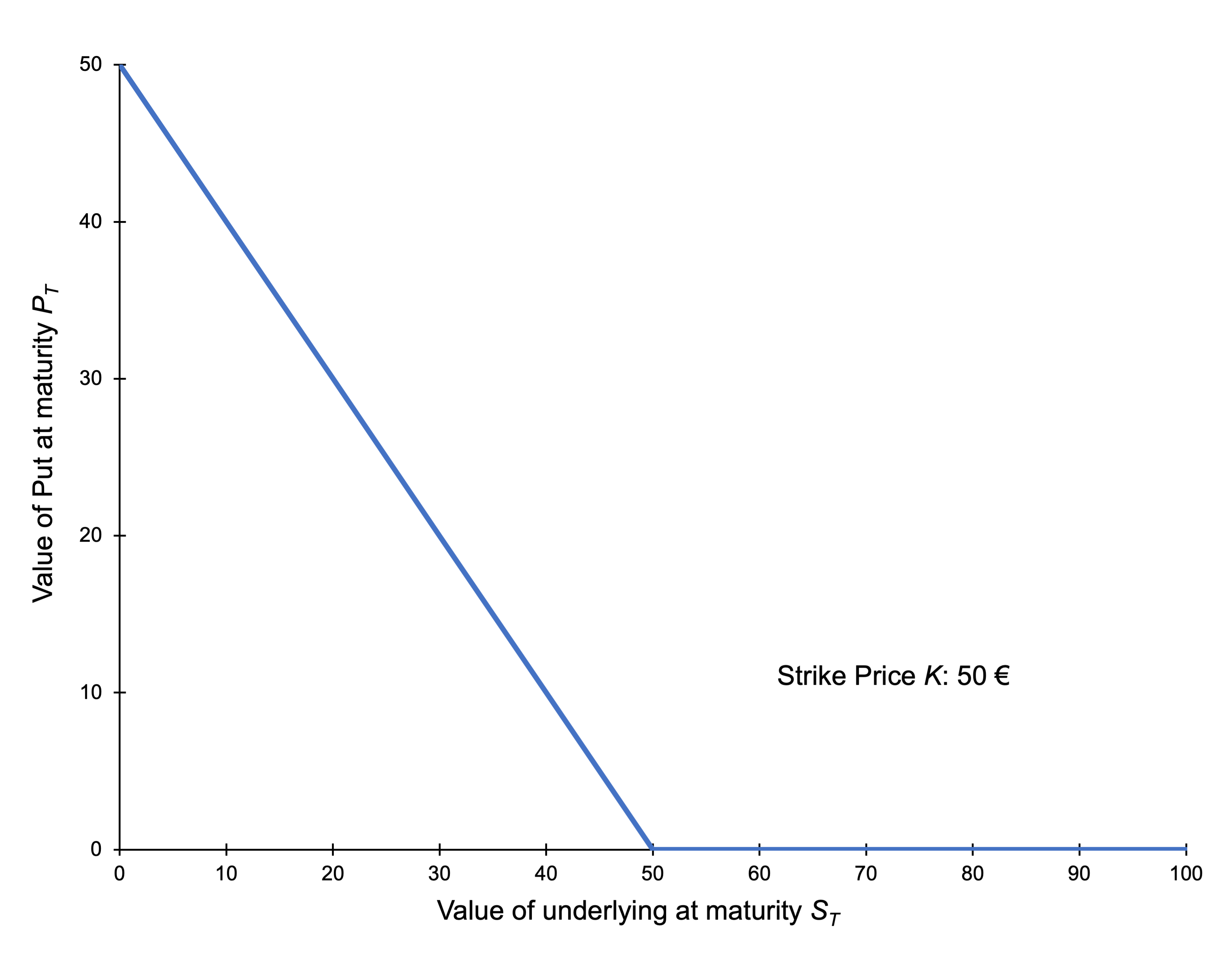
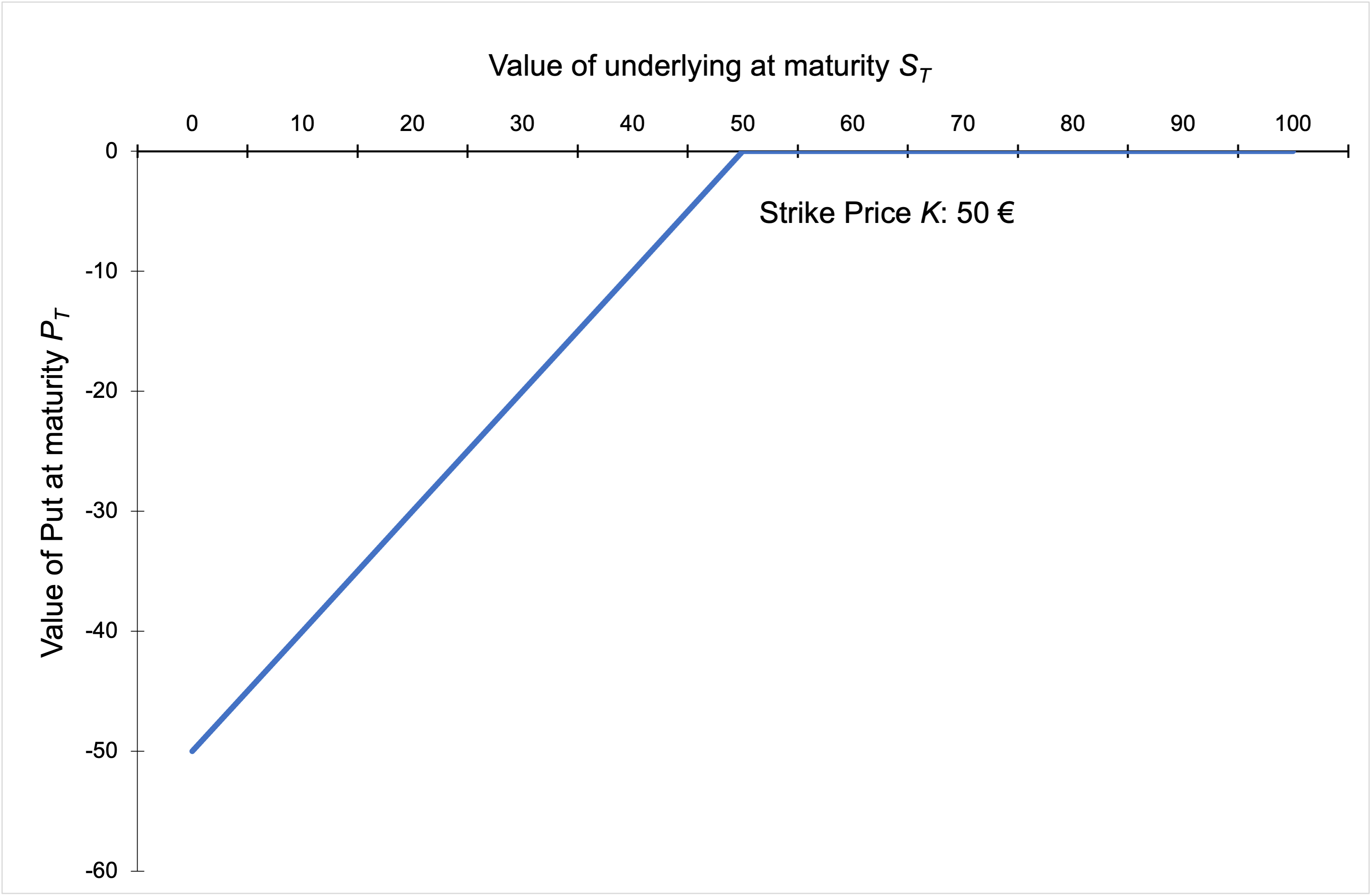
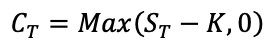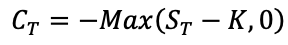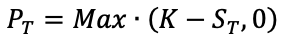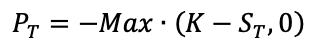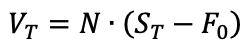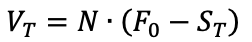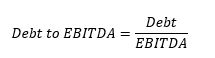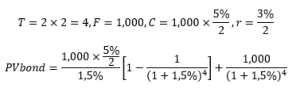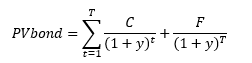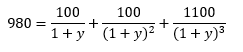How does the stock price of a firm change according to the shift of its capital structure?
In this article, Raphaël ROERO DE CORTANZE (ESSEC Business School, Master in Management, 2018-2022) analyses the effects of the shifts of capital structure on the stock price.
Capital structure and asymmetric information
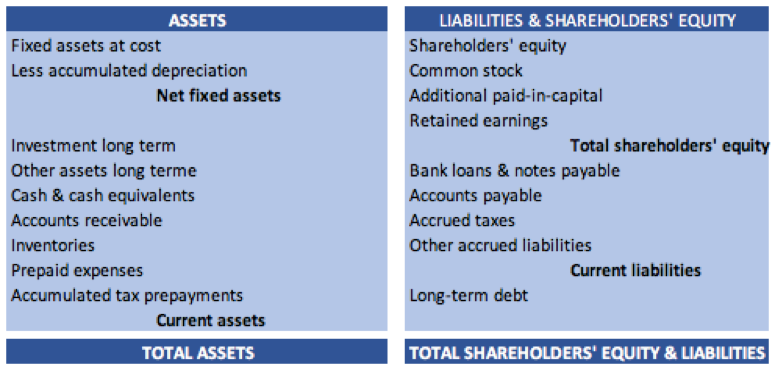
The capital structure of a firm can be defined as the mix of the company’s debt and equity. Debt can be long-term or short-term. Equity can be common or preferred equity. The capital structure discloses the different sources of funding a firm uses in order to finance its operations and growth. It is usually measured through the gearing ratio: Debt / (Debt + Equity).
The overall capital structure of a firm varies across the firm’s life and development through equity or debt issuances. Equity and debt issuance are seen on the balance sheet as an increase on the liabilities side.
Nonetheless, the balance sheet does not reveal the future decisions regarding the capital structure of the firm. Indeed, firms’ managers are suspected to hold information that outside investors and/or the market lack. These information discrepancies between the firm (managers) and the market (investors) are known as “asymmetric information”. Almost all economic transactions involve information asymmetries. These information failures influence the managers’ financial decision, and influence the market perception of the firm, through changes in stock price.
Announcement effects
The debt-equity choice conveys information for two reasons:
- Managers will avoid increasing the firm’s leverage if the firm could have financial difficulties in the future.
- Managers are reluctant to issue equity when the stock is thought to be undervalued.
Stock price reactions to capital structure changes are usually the following:
- Common stock issuance: negative
- Convertible debt issuance: negative
- Straight debt: negative but insignificant
- Bank debt (renewal): positive
Debt issuance
In 1958, Modigliani and Miller stated that in a world without taxes, bankruptcy costs, agency costs and asymmetric information, and in an efficient market, the value of a firm is unaffected by how it is financed. In other word, the choice of capital structure is irrelevant as it does not impact the value of the firm. As a result, debt issuance does not have any impact on the value of the firm according to their theory.
In 1963, Modigliani and Miller adapted their theory by integrating the notion of corporate taxation. In this framework, they show that the value of the levered firm is equal to the value of the unlevered firm plus the present value of the tax savings associated with the tax deductibility of the interests on the debt. In effect, debt conveys a taxable benefit called the “tax shield”.
In our non-Modigliani Miller perfect world, an increase in a firm’s debt ratio is often seen as a positive signal by the market as it shows that the firm managers believe in the firm capacity to generate taxable earnings in the future.
In order to come to this conclusion, Grinblatt and Titman (2002) have explained that firms choose their capital structure by comparing the tax benefit of debt financing and the cost of financial distress.

Let us consider two firms, A (unlevered) and B (levered). Firm A has no debt, thus no interest expense, and Firm B has a debt of 100 with a 10% interest rate. A and B have the same EBIT. Through its debt, B has a yearly tax shield of 3 (the tax rate is 30%), meaning that B pays less tax than A which has no debt and then no tax shield.
Nonetheless, the effects of issuing straight debt (a debt which cannot be converted into something else) is negative but insignificant. But renewing bank debt translates into an increase in stock prices. Overall, the announcement of a debt issuance has on average little impact on the stock price, as it shows to the market that the firms:
- Needs funding
- Expects taxable income in the future
- Will pay less tax as it will benefit from a higher tax shield
- Is financially stable enough to convince banks or investors to lend it money.
Security sales
The table below (from Grinblatt and Titman (2002) summarizes a number of event studies that examine stock price reaction to the announcements of new security issues. It shows that raising capital is considered as a negative signal. For instance, when industrial firms issue common stock, their stock prices decline, on average about 13.1%.
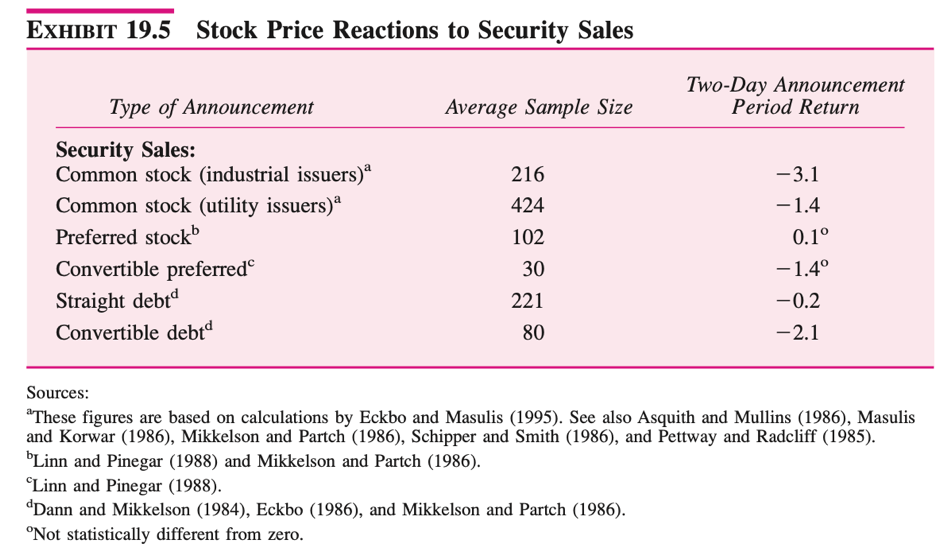
This is explained by the “adverse selection theory”, which states that firms are reluctant to issue common equity when the stock is undervalued. Thus, the market often assumes than common equity issuance and overvaluation go hand in hand. The issuing of common equity will thus have a negative effect on stock prices, as the market will think the stock is overvalued. As convertible bonds have a strong equity-like component, Grinblatt and Titman (2002) argue that the “adverse selection theory” can also explain why the market usually reacts negatively to the issuance of convertible bonds.
Pecking order theory
The market reacts favorably to leverage increase and unfavorably to leverage decrease. As a result, firms will use either internal financing (inside equity) or debt to finance their project over outside equity (equity issuance). This is called the “pecking order theory” of capital structure.
The theory of the financial pecking order states that, of the three possible forms of financing for a firm (internal cash flow, debt, equity), a firm will prefer to finance itself from internal cash flow, then debt, and finally, in the last case, by selling equity. This has a practical consequence on the way the company operates: once it has emptied its internal cash flow, it will issue debt. If it can no longer generate debt, it will issue equity.
Myers and Majluf (1984) highlight the consequences of information asymmetry between managers and investors. If the company finances itself with shares, it is because it believes that shares are overvalued and can therefore provide easy and abundant financing. If the company finances itself with debt, it is because it believes that shares are undervalued.
Nonetheless, firms can prefer to resort to equity rather than debt when they are experiencing financial difficulties. Indeed, in case of financial distress, the risk of having to suffer financial distress costs can be greater than the cost of issuing equity. Furthermore, firms can also decide to issue preferred equity in difficult times rather than common equity. In effect, preferred shareholders cannot force a firm into bankruptcy when it fails to meet its dividend obligations (while common shareholders can).
Useful resources
Grinblatt M. and S. Titman (2002) Financial Markets & Corporate Strategy, Second Edition – Chapter 19: The information conveyed by financial decisions.
Myers S.C. and N.S. Majluf (1984) Corporate financing and investment decisions when firms have information that investors do not have, Journal of Financial Economics, 13(2) 187-221.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ Shruti CHAND Balance sheet
▶ Louis DETALLE A quick review of the DCM (Debt Capital Market) analyst’s job…
▶ Louis DETALLE A quick review of the ECM (Equity Capital Market) analyst’s job…
About the author
Article written in June 2021 by Raphaël ROERO DE CORTANZE (ESSEC Business School, Master in Management, 2019-2022).