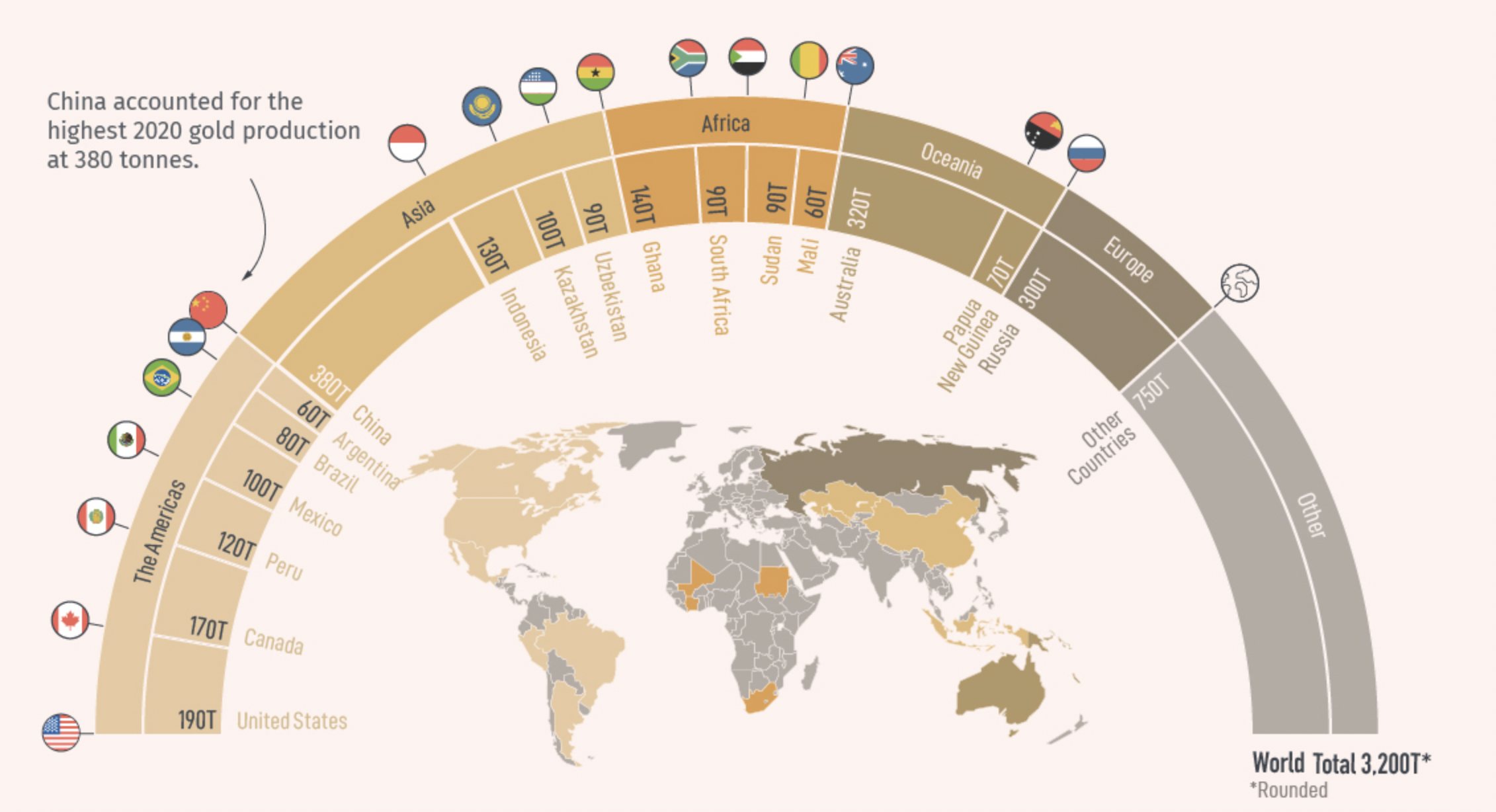
Gold mines and their story
In this article, Nithisha CHALLA (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management (MiM), 2021-2024) presents financial and economic characteristics of significant gold mines, including case studies of the most popular, scandalous, and largest gold mines.
Introduction
The history of gold mining can be traced back to prehistoric times, with the world’s oldest known underground mine being over 40,000 years old. Their history has a lot to offer to understand today’s financial and economic influence countries could have by gold. Undoubtedly being one of the biggest industries in the market, “Gold mining” has its fair share of politics involved in it. In this article, we start with discussing modern gold mining techniques and delve a little more into the economic powerhouses (most popular mines), the titans (largest gold mines in the world), and the notable news in the history of gold mines.
Modern Gold Mining Techniques
Long before any gold can be extracted, significant exploration and development need to take place, both to determine, as accurately as possible, the size of the mineral deposit, as well as how to extract and process the ore efficiently, safely, and responsibly. It can typically take between 10 and 20 years after a deposit is discovered before a gold mine is ready to produce material that can be refined into bullion.
As mentioned above there are several methods to mine minerals from the ground often depending on the environmental, and economical situations of the mine.
- Open-Pit Mining: This method involves excavating large areas to access ore bodies near the surface. It’s common in large-scale mining operations but has significant environmental impacts.
- Underground Mining: Used when ore bodies are deep beneath the surface. It’s more expensive and labor-intensive but less disruptive to the surface environment.
- Cyanidation Process: A common method for extracting gold from ore, it involves dissolving gold in a cyanide solution. While efficient, it poses environmental risks due to potential cyanide spills.
- Artisanal and Small-Scale Mining (ASM): In many developing countries, ASM provides livelihoods for millions. However, it’s often associated with poor working conditions and environmental degradation.
Famous Gold Mines
These are gold mines that have gained significant recognition and influence due to their historical importance, production levels, or economic impact. Popularity in this context is not solely about size but also about the mine’s role in shaping the gold industry, its impact on regional or global economies, and its notoriety in the public or financial sphere.
- South Africa – The Witwatersrand Basin: This region has produced more than half of the world’s gold. The discovery in 1886 led to the establishment of Johannesburg and was central to South Africa’s economy.
- United States – The California Gold Rush: The 1848 discovery at Sutter’s Mill sparked the California Gold Rush, leading to significant migration and economic development in the western U.S.
- Australia – The Super Pit: Located in Kalgoorlie, the Super Pit is one of the largest open-pit gold mines in the world and a significant contributor to Australia’s gold production.
- Peru – Yanacocha Mine: As one of the largest gold mines in the world, Yanacocha has been both an economic boon and a source of environmental controversy.
The Witwatersrand Basin (South Africa)
The Witwatersrand Basin has been the world’s most productive goldfield since its discovery in 1886. It has produced over 40% of all the gold ever mined. The Basin’s gold wealth transformed South Africa’s economy, turning Johannesburg into a major financial hub and leading to the establishment of companies like Anglo American and Gold Fields.
The gold from the Witwatersrand fueled the economic development of South Africa, contributing significantly to GDP, foreign exchange reserves, and employment. The mining companies involved became some of the largest in the world, with Anglo American, in particular, playing a crucial role in global finance.
Witwatersrand Basin mine
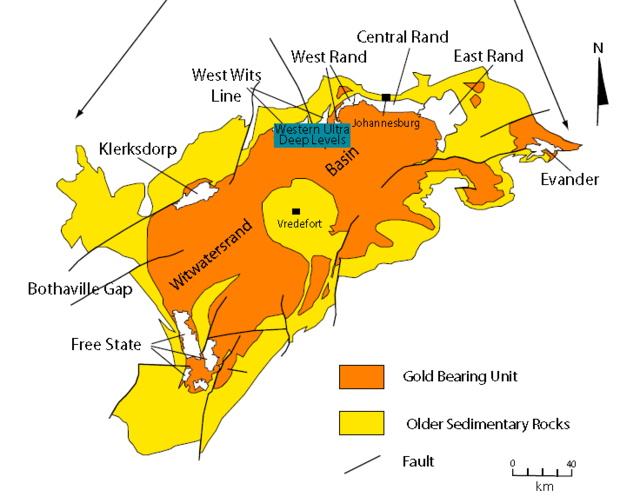
Source: Wikipedia
Case study: The diamond tycoons – The so-called Randlords, a group of mining magnates like Cecil Rhodes and Barney Barnato, amassed enormous fortunes from the Witwatersrand mines. Their influence extended beyond mining into global finance, politics, and the diamond industry, showcasing the far-reaching economic impact of gold mining in this region. Of necessity, a large workforce had to be recruited. “The South African gold mining industry in 1980 alone employed 472 000 workers, 44 000 of whom were white and 428 000 black,” notes Prof Mark Pieth, president of the Basel Institute on Governance.
The Carlin Trend (Nevada, USA)
Discovered in 1965, the Carlin Trend is one of the richest gold mining districts in the world. It accounts for over 5% of total world production, with more than 84 million ounces of gold extracted. The area is home to some of the largest gold mines in the U.S., operated by companies like Barrick Gold and Newmont Corporation.
The Carlin Trend has made Nevada one of the leading gold-producing regions globally, contributing significantly to the U.S. economy. The state benefits from mining royalties, taxes, and job creation. Barrick and Newmont’s operations have provided stable revenue streams, even during periods of economic volatility, underscoring gold’s role as a financial anchor.
A case study dated on 5th February 2021, states that in 2005, the company operated 13 open pits, four underground mines and 14 active processing facilities in Nevada. Most, including Leeville (where development ore production started in Q3 2005, totaling 16,000 oz by the year-end), are located on the Carlin Trend west of Elko, exploiting the unique mineralization identified by Newmont in 1964.
The Carlin Trend layout
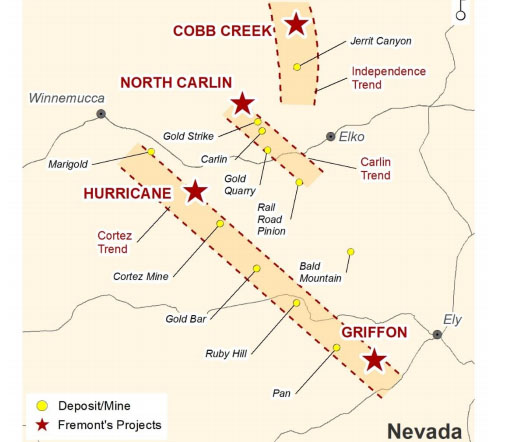
Source: Street wise reports
The Biggest Gold Mines: Titans of the Industry
These mines are defined by their sheer size, particularly in terms of gold reserves and annual production capacity. The “largest” designation typically refers to the physical quantity of gold that can be mined or the volume of gold already produced.
Grasberg Mine (Indonesia): The Grasberg Mine in Papua, Indonesia, is the largest gold mine in the world in terms of reserves. Operated by Freeport-McMoRan, it has produced over 30 million ounces of gold since operations began in 1972. The mine is also rich in copper, making it a key asset in the global mining industry.
Muruntau Mine (Uzbekistan): The Muruntau Mine in Uzbekistan is one of the largest open-pit gold mines in the world, with estimated reserves of over 170 million ounces. The mine has been in operation since the 1960s and continues to be a cornerstone of Uzbekistan’s economy. The state-owned Navoi Mining & Metallurgy Combinat (NMMC) operates the mine, and its profits play a vital role in funding national development projects.
South deep mine (South Africa): South Deep, owned by Gold Fields, is one of the world’s largest gold mines by reserves. Located in the Witwatersrand Basin, it contains an estimated 81.4 million ounces of gold. The mine’s depth and complex geology make it one of the most challenging to operate, but its vast reserves promise long-term production. The mine’s profitability is highly sensitive to gold prices, and the company has implemented various cost-cutting measures to improve financial performance. The mine also plays a key role in South Africa’s economy, providing jobs and contributing to GDP.
Economic and financial challenges in gold mining:
Operating costs and profit margins:
The profitability of gold mines is closely tied to operating costs, which include labor, energy, and equipment expenses. Mines with high All-In Sustaining Costs (AISC) are more vulnerable to fluctuations in gold prices, while those with lower costs can generate profits even during downturns.
For example, the AISC at South Deep in South Africa has historically been high, affecting profitability, while mines like Newmont’s Boddington in Australia have lower AISC, contributing to stronger financial performance.
Gold Price Volatility and Market Risks:
Gold price volatility poses significant risks for mining companies. Sharp declines in gold prices can lead to reduced revenues, making it difficult to finance operations and capital projects. Companies often use hedging strategies to manage these risks, but this can also limit potential upside during price rallies.
For example, the sudden drop in gold prices in 2013 had a profound impact on the mining industry. Many companies, including those with high-cost operations, were forced to cut costs, delay projects, or close unprofitable mines.
Capital Expenditure and Return on Investment (ROI):
Developing a gold mine requires substantial capital investment, often running into billions of dollars. These costs include exploration, feasibility studies, environmental permitting, infrastructure development, and equipment procurement. The capital intensity of gold mining makes ROI a critical financial metric.
For example, Barrick Gold’s Pueblo Viejo mine in the Dominican Republic, one of the largest and most capital-intensive gold projects in the world, required an initial investment of over $4 billion. Despite the high upfront costs, the project has become one of Barrick’s most profitable operations, with low AISC and high-grade ore contributing to strong ROI.
Environmental and Social Governance (ESG) Costs:
The modern gold mining industry faces growing pressure to adhere to stringent environmental and social governance (ESG) standards. These requirements, which include responsible mining practices, community engagement, and environmental protection, often result in higher operating costs but are essential for maintaining social license to operate and reducing financial risks.
For example, Newmont’s Yanacocha mine in Peru, one of the largest gold mines in Latin America, has faced significant ESG challenges, including protests from local communities over environmental concerns. These challenges have led to delays, increased costs, and negative publicity, illustrating the financial risks of not adequately addressing ESG issues.
Political and Regulatory Risks:
Political and regulatory environments can have a significant impact on the costs and viability of gold mining projects. Changes in government policies, tax regimes, or mining regulations can lead to increased costs or operational delays. Companies operating in politically unstable regions face heightened risks, including the potential for expropriation, legal disputes, or disruptions due to civil unrest.
For example, Acacia Mining, a subsidiary of Barrick Gold, faced severe challenges in Tanzania when the government imposed a ban on the export of unprocessed gold and accused the company of tax evasion. The dispute led to a significant drop in Acacia’s share price, legal battles, and ultimately, Barrick’s decision to buy out minority shareholders and take full control of the company to resolve the situation.
Conclusion
This article expands a detailed view of the economic and financial characteristics of global gold resources. It explores the challenges and trends shaping the future of gold mining, emphasizing case studies on popular and large gold mines.
Why should I be interested in this post?
Many emerging economies have significant gold resources, and understanding the economic impact of gold mining and trade in these regions is essential for students interested in global markets, economic development, and resource management. Management students should be aware of these challenges to promote sustainable and responsible business practices in industries reliant on natural resources.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ Nithisha CHALLA History of Gold
▶ Nithisha CHALLA Gold resources in the world
Useful resources
Wikipedia Gold
Mining technology Nevada Gold Mines, US
Geology of Investors Elephants in the Nevada Desert: Carlin-type Gold Deposits
Corruption Watch South Africa’s history of gold mining – corruption, abuse, and secrecy
Only gold A Brief History of Gold
About the author
The article was written in September 2024 by Nithisha CHALLA (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management (MiM), 2021-2024).