In this article, Zineb ARAQI (ESSEC Business School, Global Bachelor in Business Administration (GBBA), 2021-2025) shares her experience as an apprentice at Capgemini Invent within the Data & AI practice for Financial Services, where she contributed to major digital transformation programs across global banking institutions.
About the company
Capgemini Invent is the digital innovation, design and transformation brand of the Capgemini Group. Created in 2018, it combines strategy, technology, data, and creative design to help organizations reinvent their business models. Capgemini Invent operates in more than 30 countries and brings together over 10,000 consultants, data scientists, designers, and industry experts.
Capgemini Invent works at the intersection of strategy and execution, supporting clients through their end-to-end transformation journeys. Its expertise spans digital transformation, artificial intelligence, cloud modernization, sustainability strategy, customer experience, and data-driven operating models.
Within the wider Capgemini Group (over 340,000 employees worldwide), Invent plays a critical role in bridging management consulting with advanced technological execution. This unique positioning allows consultants to work on strategic topics while staying close to the technical realities of implementation, particularly in fast-evolving domains like AI, data governance, and digital banking.
Logo of Capgemini.

Source: Capgemini Invent
About the department: Data & AI for Financial Services
I completed my apprenticeship within the Data & AI Financial Services practice, the division supporting major French and international banks in their data strategy and AI-driven transformation. This department works closely with Chief Data Officers (CDOs), Chief Analytics Officers, and executive committees to design, deploy, and govern enterprise-wide data architectures and AI solutions.
During my apprenticeship, I worked on strategic missions covering Europe, Middle East, and Africa, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Our team addressed high-impact topics such as data governance, regulatory compliance and Environmental, Social, and Governance reporting, customer intelligence, risk modelling, AI use-case acceleration, cloud migration, and the operationalization of large-scale data platforms. The practice serves flagship clients across retail banking, corporate & investment banking, insurance, and payments.
My apprenticeship experience at Capgemini Invent
My Missions
Throughout my apprenticeship, I contributed to large digital transformation programs for top French banks. My work spanned across all regions, EMEA, the Americas, and Asia reflecting the global scale of modern banking operations and the cross-regional governance challenges faced by CDOs.
My missions included:
- Supporting Chief Data Officers in defining and implementing enterprise-wide data governance frameworks (metadata, lineage, quality, operating models).
- Designing AI use-case portfolios, including prioritization matrices, feasibility assessments, and Return on Investment evaluations for retail and corporate banking.
- Analyzing cross-regional data issues across APAC, the Americas, and EMEA to harmonize data standards and reporting structures.
- Contributing to ESG & sustainable finance reporting, helping banks adapt to emerging CSRD (the EU’s new mandatory sustainability reporting directive), TNFD (the global framework for nature-related risk disclosures) and ESRS (the detailed European sustainability reporting standards) requirements using improved data pipelines.
- Supporting cloud transformation initiatives by assessing data migration readiness and defining new operating models for data platforms.
- Supporting cloud transformation initiatives by assessing data migration readiness and defining new operating models for data platforms.
- Building dashboards and analytics tools using SQL, PowerBI, and Python to transform raw data into clear insights that support risk, compliance, and business teams in their decision-making.
These projects exposed me to the complexity of financial data ecosystems, the challenges of legacy infrastructures, and the role of AI in reshaping operational models at scale.
Required skills and knowledge
Working at the intersection of consulting, data governance, and financial services required a combination of analytical, technical, and communication skills. On the technical side, I relied on knowledge of banking business lines (retail, Corporate & Investment Banking, payments), data modelling fundamentals, SQL, cloud concepts, and AI/ML logic. Understanding regulatory frameworks and risk data aggregation standards was essential, especially when advising CDOs on compliance or data lineage workflows.
Soft skills were equally important: client communication, structured problem-solving, stakeholder management, and the ability to translate complex data topics into actionable recommendations. Working across multiple regions strengthened my adaptability and cross-cultural communication, as I collaborated with teams in Europe, the U.S., and Asia.
What I learned
This apprenticeship taught me how central data has become to the competitiveness and resilience of financial institutions. I learned how banks leverage data to enhance customer experience, reduce risk, improve compliance, and accelerate digital transformation. I also gained firsthand exposure to how global banks structure their operating models, from governance to platforms to analytics, and how AI can be responsibly integrated into decision-making processes.
Most importantly, working with CDO organizations helped me understand the strategic importance of data leadership and the challenges of transforming legacy institutions into data-driven organizations. This experience reinforced my interest in financial technology, analytics, and sustainable finance.
Business concepts related to my internship
I present below three financial, economic, and management concepts related to my apprenticeship. These concepts illustrate how data strategy, regulatory expectations, and AI-driven transformation shape the operating models of large financial institutions and how my work experience aligned with these challenges.
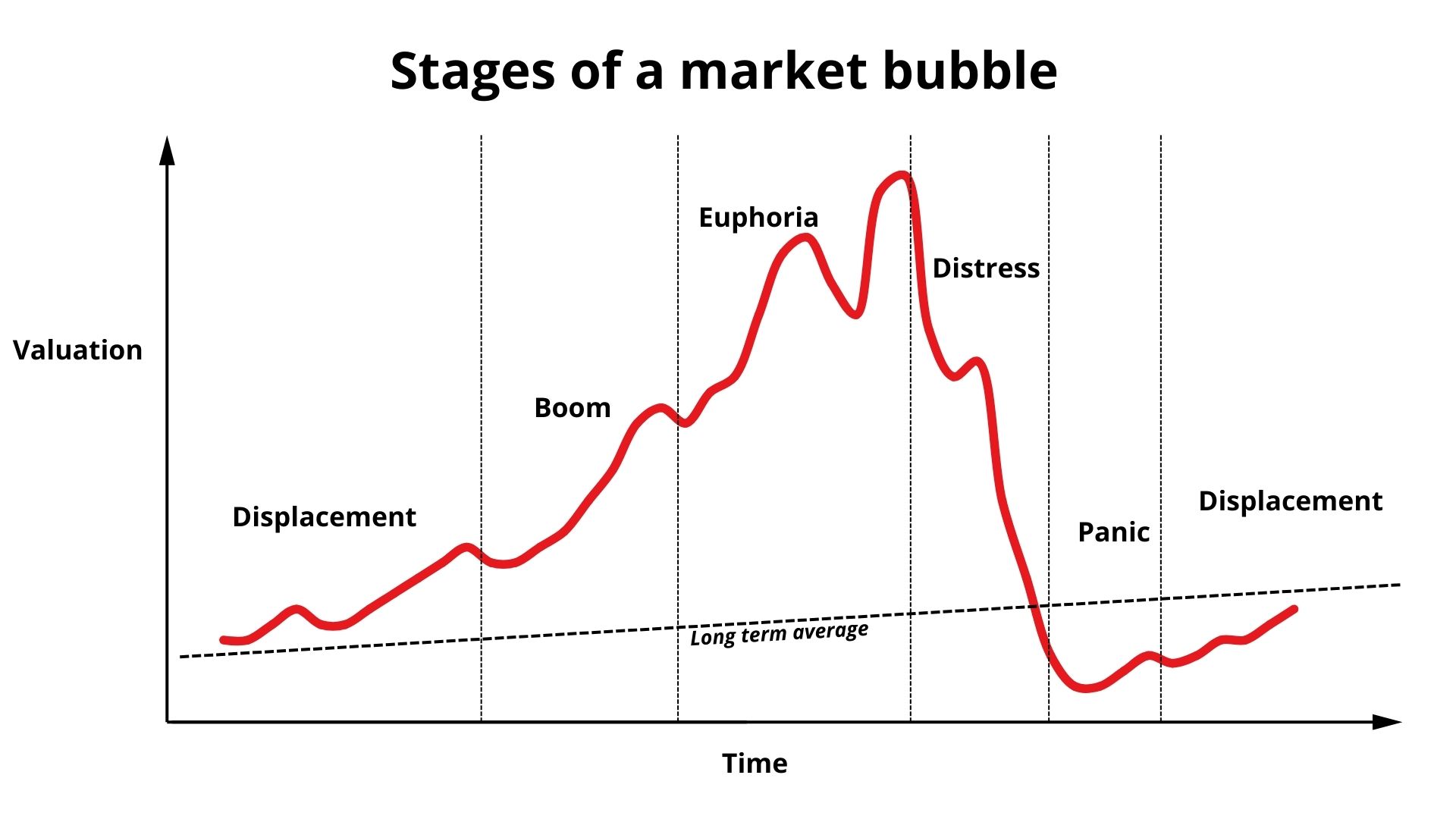
Data Governance and Regulatory Compliance (BCBS 239, CSRD, ESRS)
During my missions, the concept of data governance was central. Financial institutions operate under strict regulatory expectations such as BCBS 239 (risk data aggregation), CSRD (corporate sustainability reporting), and ESRS (European sustainability standards). These frameworks require banks to demonstrate full control of their data including lineage, quality, documentation, accessibility in order to produce reliable regulatory reports. My role consisted in helping banking groups structure governance models, build data quality controls, and harmonize data definitions across regions. This concept is at the heart of banking transformation, as regulatory pressure and data modernization are now inseparable.
AI Use-Case Prioritization and ROI Evaluation
A second concept I applied throughout my apprenticeship is the prioritization of AI use-cases based on business value, feasibility, and risk. Banks often have dozens of potential AI initiatives, but only a fraction deliver measurable Return on Investment (ROI). My work involved constructing prioritization matrices, evaluating data readiness, estimating financial impact, and supporting executive committees in building realistic AI roadmaps. This required balancing quantitative evaluation (cost savings, efficiency gains) with qualitative factors (regulatory risk, bias mitigation, ethical constraints). This concept is fundamental to ensuring that AI programs are scalable, responsible, and aligned with strategic objectives.
Operating Model Transformation for Data Platforms and Cloud Migration
The third concept closely linked to my missions is the transformation of operating models for data platforms migrating to the cloud. Banks are progressively replacing legacy infrastructure with modern cloud-based architectures to improve scalability, reduce costs, and accelerate analytics capabilities. My work consisted in assessing migration readiness, defining roles and responsibilities, and designing new governance processes adapted to cloud environments. This concept is essential because technology alone cannot transform an organization, it must be accompanied by clear processes, change management, and redesigned workflows.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ All posts about Professional experiences
▶ Nicolas SCHULZ-SEMBTEN My experience as a Working Student in Infrastructure Investment Inhouse Consulting at Munich Re
▶ Julien MAUROY My internship experience at BearingPoint – Finance & Risk Analyst
▶ Rohit SALUNKE My professional experience as Business & Data Analyst at Tikehau Capital
About the author
This article was written in December 2025 by Zineb ARAQI (ESSEC Business School, Global Bachelor in Business Administration (GBBA), 2021–2025).
▶ Read all articles by Zineb ARAQI.