In this article, Youssef LOURAOUI (Bayes Business School, MSc. Energy, Trade & Finance, 2021-2022) presents the dedicated short bias strategy. The strategy holds a net short position, which implies more shorts (selling) than long (buying) positions. The objective of the dedicated bias strategy is to profit from shorting overvalued equities.
This article is structured as follow: we introduce the dedicated short bias strategy. Then, we present a practical case study to grasp the overall methodology of this strategy. We also present a performance analysis of this strategy and compare it a benchmark representing all hedge fund strategies (Credit Suisse Hedge Fund index) and a benchmark for the global equity market (MSCI All World Index).
Introduction
According to Credit Suisse (a financial institution publishing hedge fund indexes), a dedicated short bias strategy can be defined as follows: “Dedicated Short Bias funds take more short positions than long positions and earn returns by maintaining net short exposure in long and short equities. Detailed individual company research typically forms the core alpha generation driver of dedicated short bias managers, and a focus on companies with weak cash flow generation is common. To affect the short sale, the manager borrows the stock from a counter-party and sells it in the market. Short positions are sometimes implemented by selling forward. Risk management consists of offsetting long positions and stop-loss strategies”.
This strategy makes money by short selling overvalued equities. The strategy can potentially generate returns in falling markets but would underperform in rising equity market. The interesting characteristic of this strategy is that it can potentially offer to investors the added diversification by being non correlated with equity market returns.
Example of the dedicated short bias strategy
Jim Chanos (Kynikos Associates) short selling trade: Enron
In 2000, Enron dominated the raw material and energy industries. Kenneth Lay and Jeffrey Skilling were the two leaders of the group that disguised the company’s financial accounts for years. Enron’s directors, for instance, hid interminable debts in subsidiaries in order to create the appearance of a healthy parent company whose obligations were extremely limited because they were buried in the subsidiary accounts. Enron filed for bankruptcy on December 2, 2001, sparking a big scandal, pulling down the pension funds intended for the retirement of its employees, who were all laid off simultaneously. Arthur Andersen, Enron’s auditor, failed to detect the scandal, and the scandal ultimately led to the dissolution of one of the five largest accounting and audit firms in the world (restructuring the sector from the Big 5 to the Big 4). Figure 1 represents the share price of Enron across time.
Figure 1. Performance Enron across time.
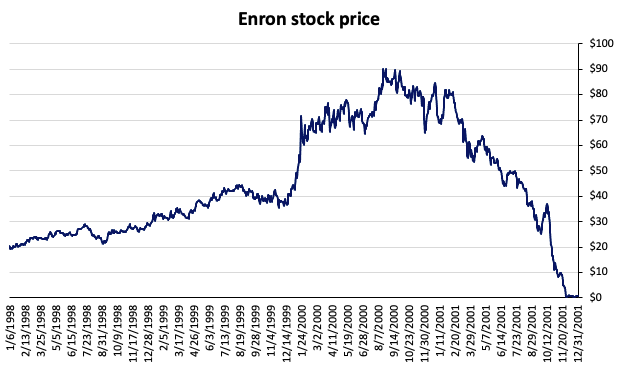
Source: Computation by the author
Fortune magazine awarded Enron Corporation “America’s Most Innovative Company” annually from 1996 to 2000. Enron Corporation was a supposedly extremely profitable energy and commodities company. At the beginning of 2001, Enron had around 20,000 employees and a market valuation of $60 billion, approximately 70 times its earnings.
Short seller James Chanos gained notoriety for identifying Enron’s problems early on. This trade was dubbed “the market call of the decade, if not the past fifty years” (Pederssen, 2015).
Risk of the dedicated short bias strategy
The most significant risk that can make this strategy loose money is a short squeeze. A short seller can borrow shares through a margin account if he/she believes a stock is overvalued and its price is expected to decline. The short seller will then sell the stock and deposit the money into his/her margin account as collateral. The seller will eventually have to repurchase the shares. If the price of the stock has decreased, the short seller gains money owing to the difference between the price of the stock sold on margin and the price of the stock paid later at the reduced price. Nonetheless, if the price rises, the buyback price may rise the initial sale price, and the short seller will be forced to sell the security quickly to avoid incurring even higher losses.
We illustrate below the risk of a dedicated short bias strategy with Gamestop.
Gamestop short squeeze
GameStop is best known as a video game retailer, with over 3,000 stores still in operation in the United States. However, as technology in the video game business advances, physical shops faced substantial problems. Microsoft and Sony have both adopted digital game downloads directly from their own web shops for their Xbox and Playstation systems. While GameStop continues to offer video games, the company has made steps to diversify into new markets. Toys and collectibles, gadgets, apparel, and even new and refurbished mobile phones are included.
However, given the increased short pressure by different hedge funds believing that the era of physical copies was dead, they started positioning in Gamestop stock and traded short in order to profit from the decrease in value. In this scenario, roughly 140% of GameStop’s shares were sold short in January 2021. In this case, investors have two choices: keep the short position or cover it (to buy back the borrowed securities in order to close out the open short position at a profit or loss). When the stock price rises, covering a short position means purchasing the shares at a loss since the stock price is now higher than what was sold. And when 140% of a stock’s float is sold short, a large number of positions are (have to be) closed. As a result, short sellers were constantly buying shares to cover their bets. When there is that much purchasing pressure, the stock mechanically continued to rise. From the levels reached in early 2020 to the levels reached in mid-2021, the stock price climbed by a factor of a nearly a hundred times (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Performance of Gamestop stock price.
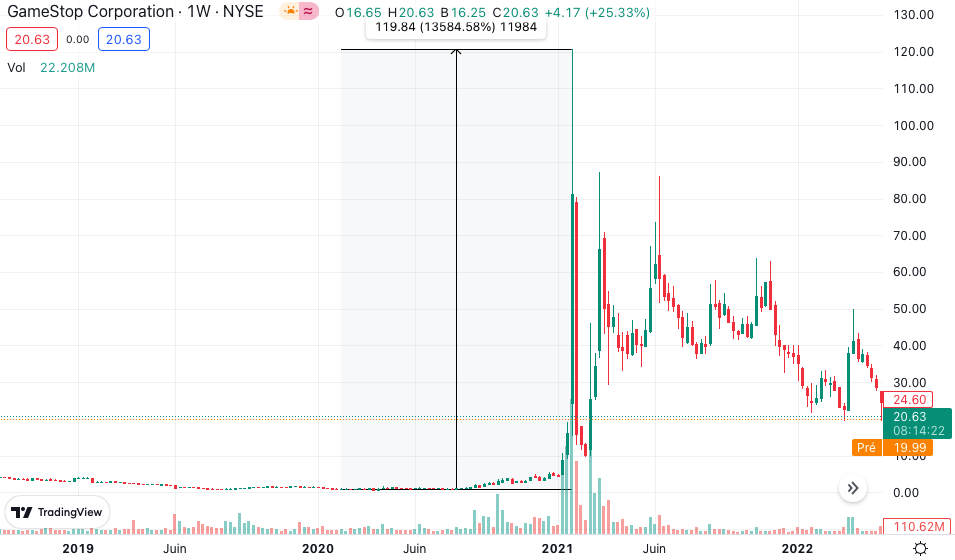
Source: (Data: Tradingview)
In the Gamestop story, the short sellers lost huge amount of money. Especially, the hedge fund Melvin Capital lost billions of dollars after being on the wrong side of the GameStop short squeeze.
Why should I be interested in this post?
Understanding the profits and risks of such a strategy might assist investors in incorporating this hedge fund strategy into their portfolio allocation.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
Hedge funds
▶ Youssef LOURAOUI Introduction to Hedge Funds
▶ Youssef LOURAOUI Global macro strategy
▶ Youssef LOURAOUI Long/short equity strategy
Financial techniques
▶ Akshit GUPTA Short selling
▶ Youssef LOURAOUI Portfolio
Useful resources
Academic research
Pedersen, L. H., 2015. Efficiently Inefficient: How Smart Money Invests and Market Prices Are Determined. Princeton University Press.
Business Analysis
Credit Suisse Hedge fund strategy
Credit Suisse Hedge fund performance
Wikipedia Gamestop short squeeze
TradingView, 2023 Gamestop stock price historical chart
About the author
The article was written in January 2023 by Youssef LOURAOUI (Bayes Business School, MSc. Energy, Trade & Finance, 2021-2022).


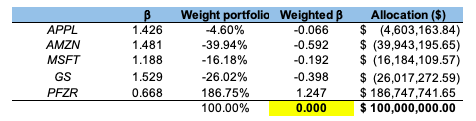 Source: computation by the author (Data: Bloomberg)
Source: computation by the author (Data: Bloomberg)
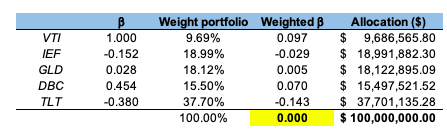 Source: computation by the author. (Data: Reuters Eikon)
Source: computation by the author. (Data: Reuters Eikon)