Short selling
This article written by Akshit GUPTA (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2019-2022) presents the trading strategy of Short Selling.
Introduction
Short selling refers to the act of selling a stock without actually owning it. By definition, an investor makes a short sell when he/she borrows a stock, then sells it and buys it later to return it to the lender.
The primary reason why investors choose to short sell is because they anticipate a drop in the price. The rationale behind the act is to make money when the investor actually sells the stock at a higher price and then buys the stock at a lower price when the market price of that asset falls.
This can be illustrated through an example:
If an investor shorts 10 shares of Apple currently priced at $100, then the investor will borrow 10 shares of Apple from his/her broker. Let’s say after 2 days, the stock price falls to $80, the investor will buy it back and make a profit of 10*(100-80) = $200.
In this case, the price of the stock decreased and hence, the investor could make money. Now in a contrasting scenario, the price of the stock can increase, in which case the investor will lose money.
In the above example, imagine that the investor goes short for 10 shares of Apple at $100 each and the price after 2 days increases to $150. In this case, the loss for the investor is 10*(150-100)= $500.
Since the price of the stock can keep increasing or decreasing in theory, short selling position can lead to huge losses or profits. Hence short selling comes with high risk and is usually used by hedge fund managers and institutional investors for speculation with high-risk appetite. Hedge funds are in fact the most active users of short selling positions to mitigate losses in a security or portfolio they already own.
Who short sells the most in the stock market?
Short selling can be practiced by any trader participating in the financial markets but due to the high risk involved and requirement of strong market understanding it is generally practiced by:
- Hedgers: An investor who already is long in the market using options or futures contracts, will naturally short the underlying security. This is referred to as Delta Hedge.
- Speculators: Speculative investors are involved in short selling to take advantage of market movements. They in fact account for a significant share of short activity.
- Day Traders: These short term traders with a lot of risk exposure keep a close eye on the market movements and take short position from time to time for a very short term to hedge against their current positions.
- Hedge funds: Active entities who manage funds for high net worth individuals, enterprises, or other market participants short sell on various stocks by betting on sectors, industries or companies where they expect a fall in value of the asset prices.
Mechanism of Short Selling
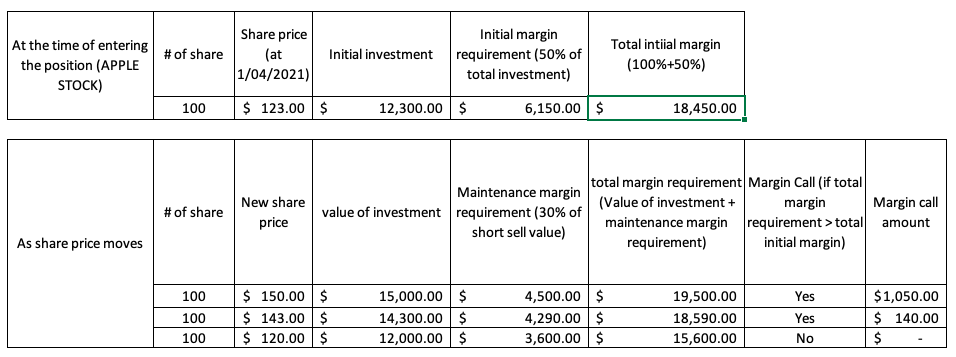
Since the short sell involves borrowing stock, an initial margin is required by the broker at the time the trade is initiated. For instance, this initial margin is set to 50% of the value of the short sale. This money is essentially the collateral on the short sale to protect the lender in the future against the default of the borrower.
Followed by this, a maintenance margin is required at any point of time after the trade is initiated. The maintenance is taken as 30% of the total value of the position. The short seller has to ensure that any time the position falls below this maintenance margin requirements, he/she will get a margin call and has to increase funds into the margin account.
Here is an example of a typical case of short selling and its margin mechanism:
Related posts
▶ Akshit GUPTA Trader – Job description
▶ Akshit GUPTA Analysis of the Big Short movie
▶ Akshit GUPTA Analysis of the Margin call movie
▶ Akshit GUPTA Analysis of the Trading places movie
Useful resources
BusinessInsider article: What is short selling?
About the author
Article written by Akshit GUPTA (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2019-2022).