The CAC 40 index
In this article, Nithisha CHALLA (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2021-2023) presents the CAC 40 index and details its characteristics.
The CAC 40 index
The CAC 40 index is one of the main indices of the Paris Bourse. It was launched on December 31, 1987. CAC is the abbreviation for Cotation Assistée en Continu which translates to “Continuous Assisted Quotation”. CAC 40 is a benchmark stock market index that tracks the performance of the 40 largest and most actively traded companies on the Euronext Paris exchange.
The companies in the CAC 40 index represent a variety of industries, including financial services, energy, consumer goods, and technology. Some of the largest and most well-known companies in the index include Total, L’Oréal, and Sanofi. Due to its extremely diverse portfolio, it enables investors to view a variety of French industries.
The CAC 40 index uses a free-float market-capitalization weighting methodology, which means that only the shares that are available for trading are used to determine the index’s weighting.
Given that France is the second-largest economy in the European Union (EU), and the CAC 40 index plays an important role in the French economy, it is a good benchmark for investors. The companies included in the index account for a significant portion of the country’s GDP and provide employment for a large number of people.
While the CAC 40 is a French stock market index, many of the companies included in the index have a global reach and operate in multiple countries. As a result, the index can serve as a gauge for the wider European and global economies in addition to the French economy.
How is the CAC 40 index represented in trading platforms and financial websites? The ticker symbol used in the financial industry for the CAC 40 index is “PX1”.
Table 1 gives the Top 10 stocks in the CAC 40 index in terms of market capitalization as of January 31, 2023.
Table 1. Top 10 stocks in the CAC 40 index.
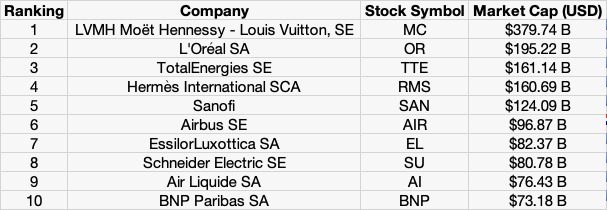
Source: computation by the author (data: YahooFinance! financial website).
Table 2 gives the sector representation of the CAC 40 index in terms of number of stocks and market capitalization as of January 31, 2023.
Table 2. Sector representation in the CAC 40 index.
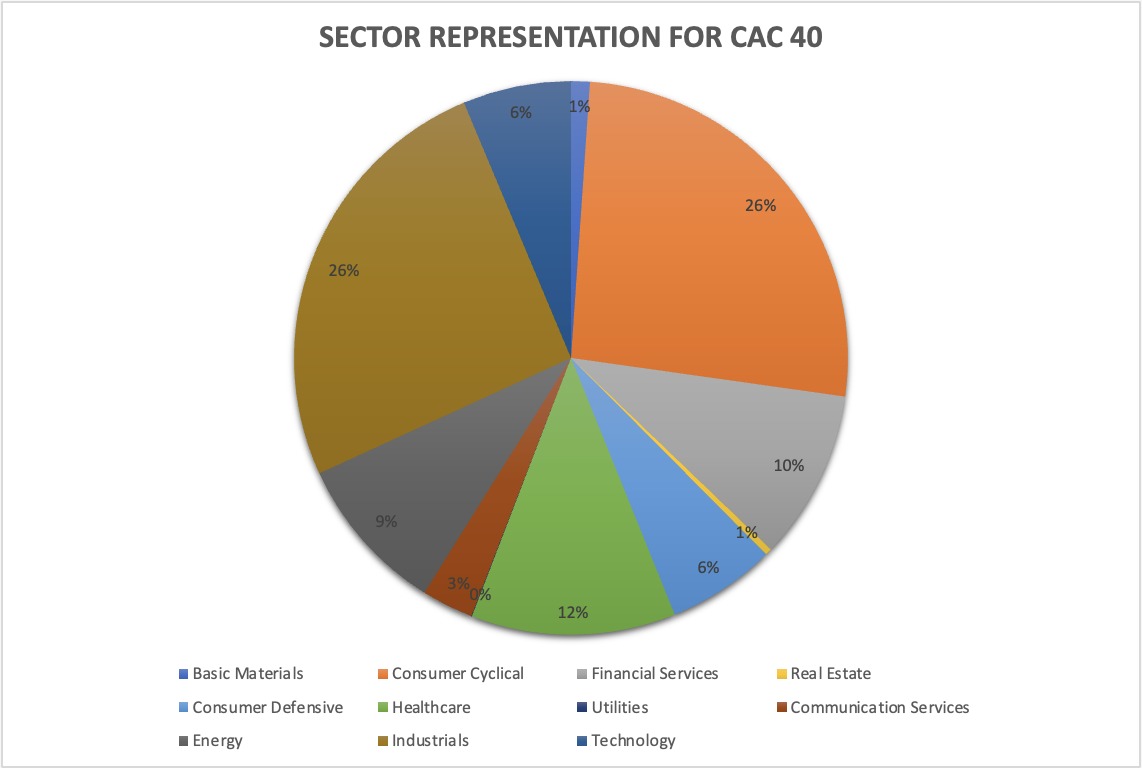
Source: computation by the author (data: YahooFinance! financial website).
Calculation of the CAC 40 index value
The value of the CAC 40 index is determined using a market-capitalization-weighted formula that is float-adjusted, which means that only the shares that are available for trading in the secondary market are used to determine the index weighting. This helps to ensure that the index is representative of the companies that are actively traded in the market.
The formula to compute the CAC 40 index is given by
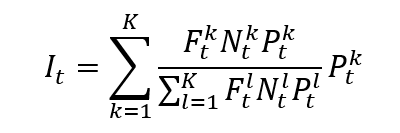
where I is the index value, k a given asset, K the number of assets in the index, Pk the market price of asset k, Nk the number of issued shares for asset k, Fk the float factor of asset k, and t the time of calculation of the index.
In a float-adjusted market-capitalization-weighted index, the weight of asset k is given by formula can be rewritten as
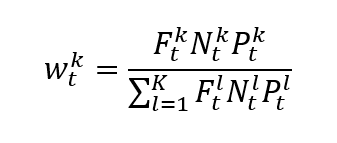
The index is reviewed quarterly to ensure that it remains representative of the French stock market and to add or remove companies based on their size, liquidity, and sector classification.
Use of the CAC 40 index in asset management
The CAC 40 index is a useful tool for asset managers to manage risk because it is quite diverse and represents the French economy across a variety of industries. While the CAC 40 index is primarily composed of French companies, many of these companies also have significant international exposure. The CAC 40 index is one of Europe’s most liquid stock market indices, with a high level of trading volume and relatively low bid-ask spreads. This can be particularly important for investors who are looking to trade in and out of positions quickly, or for those who are managing large portfolios and need to execute trades efficiently. Some index funds and ETFs based on the CAC 40 index have particular ESG standards for the businesses they invest in. This may be appealing to investors who want to match their investments with their values.
Benchmark for equity funds
Equity funds are types of investment funds that invest primarily in stocks or shares of companies that are publicly traded. These funds give investors exposure to equity markets and offer the potential growth for capital appreciation in the long term. Given that it gives a good enough picture of the French market, there are multiple financial products around the index. Using these products can help investors diversify their holdings and control risk. The CAC 40 index can also be used to create multi-asset portfolios, acting as a representative of the portfolio’s equity component. By including the CAC 40 index in a multi-asset portfolio, investors can potentially achieve diversification and reduce risk through exposure to a broad range of companies in the French economy.
Financial products around the CAC 40 index
Financial products around the CAC 40 index offer investors a range of options to gain exposure to the French equity market, including products with sustainability and ESG considerations.
- Investment funds traded like stocks are called exchange-traded funds, or ETFs. The Lyxor ETF CAC 40 is the largest ETF that tracks the CAC 40 index, and other ETFs that do so include the Amundi ETF CAC 40, the BNP Paribas Easy CAC 40, and the Xtrackers CAC 40
- Some mutual funds and investment trusts that make CAC 40 index investments have an environmental, social, and governance (ESG) or sustainability focus. For instance, the CAC 40 index and European businesses with strong ESG performance are among the investments made by the Mirova Europe Sustainable Equity Fund
- The main stock exchange in France, Euronext Paris, offers futures and options on the CAC 40 index. Institutional investors and traders use these highly liquid financial contracts
- Structured products linked to the CAC 40 index can have various features, such as capital protection, leverage, and participation rate
Historical data for the CAC 40 index
How to get the data?
The CAC 40 index is the most common index used in finance, and historical data for the CAC 40 index can be easily downloaded from the internet.
For example, you can download data for the CAC 40 index from March 1, 1990 on Yahoo! Finance (the Yahoo! code for CAC 40 index is ^FCHI).
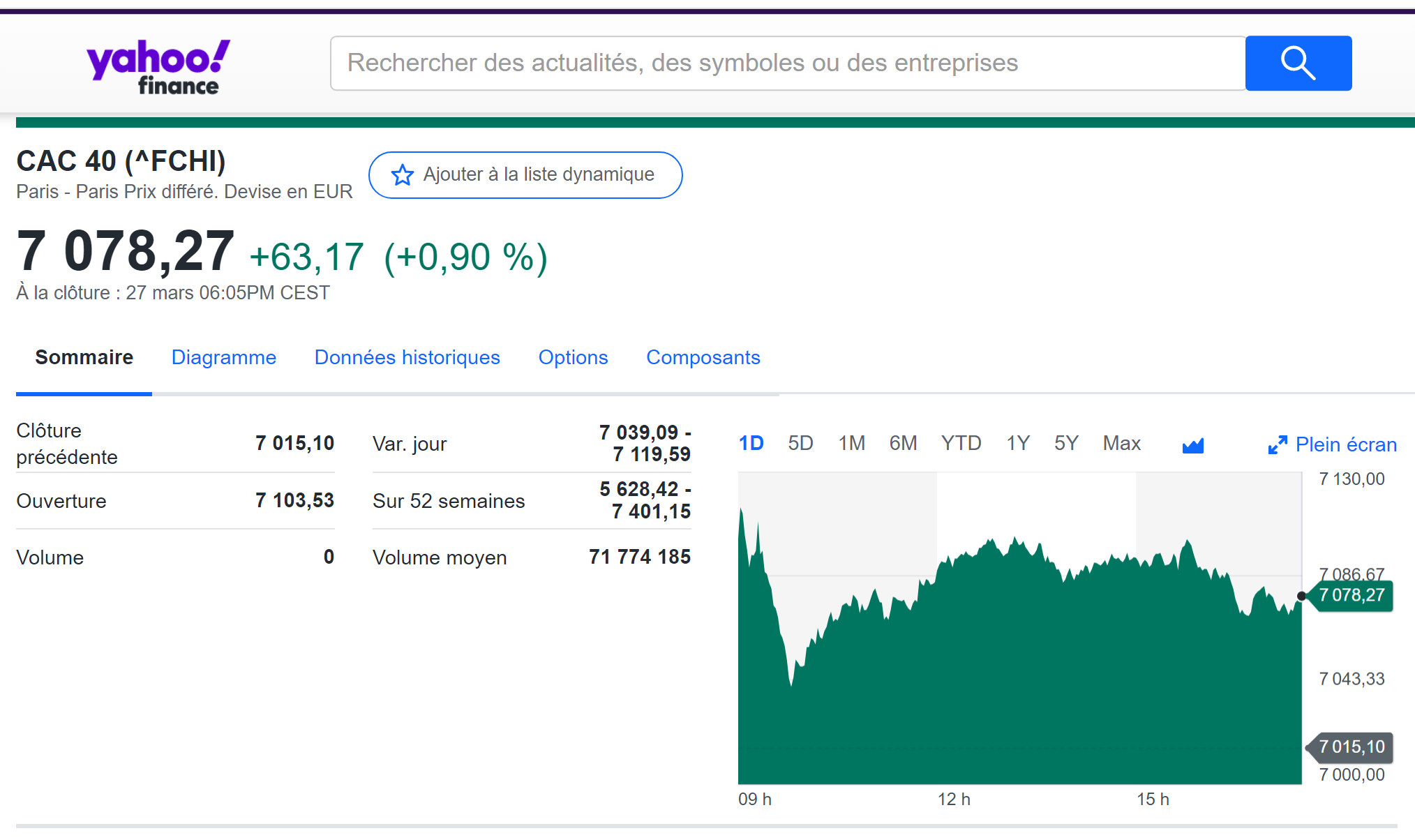
Source: Yahoo! Finance.
You can also download the same data from a Bloomberg terminal.
R program
The R program below written by Shengyu ZHENG allows you to download the data from Yahoo! Finance website and to compute summary statistics and risk measures about the CAC 40 index.
Data file
The R program that you can download above allows you to download the data for the CAC 40 index from the Yahoo! Finance website. The database starts on March 1, 1990. It also computes the returns (logarithmic returns) from closing prices.
Table 3 below represents the top of the data file for the CAC 40 index downloaded from the Yahoo! Finance website with the R program.
Table 3. Top of the data file for the CAC 40 index.
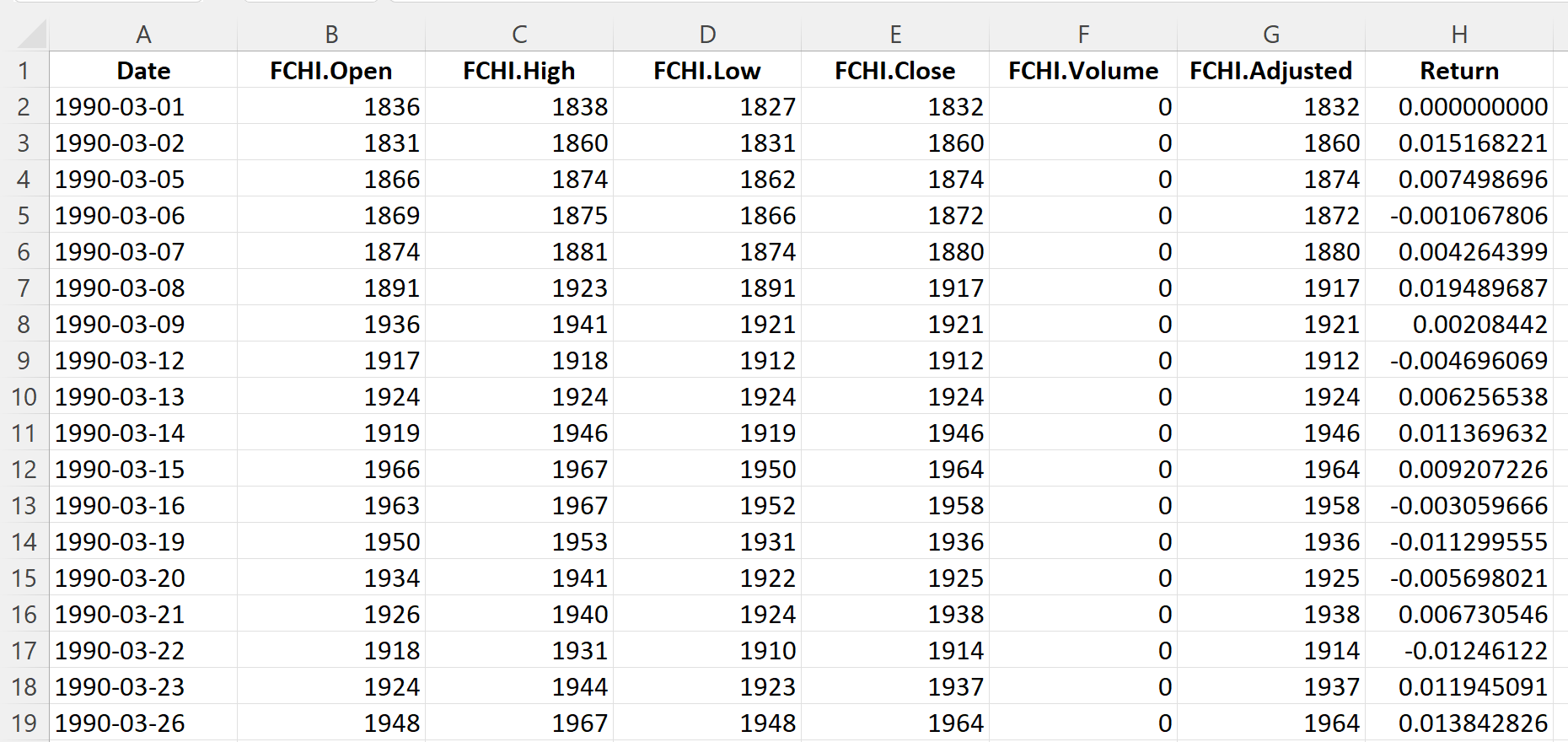
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
Evolution of the CAC 40 index
Figure 1 below gives the evolution of the CAC 40 index from March 1, 1990 to December 30, 2022 on a daily basis.
Figure 1. Evolution of the CAC 40 index.
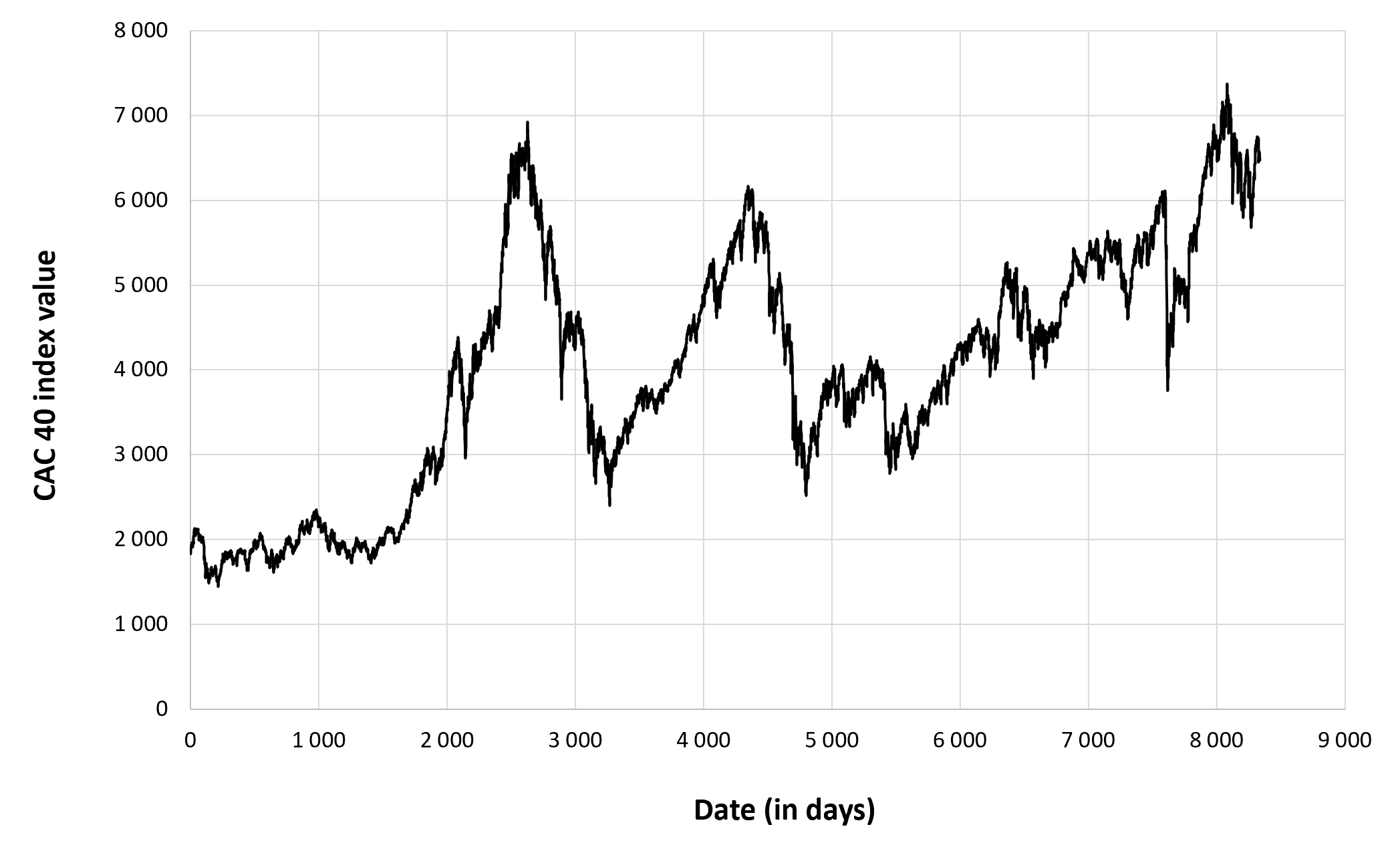
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
Figure 2 below gives the evolution of the CAC 40 index returns from March 1, 1990 to December 30, 2022 on a daily basis.
Figure 2. Evolution of the CAC 40 index returns.
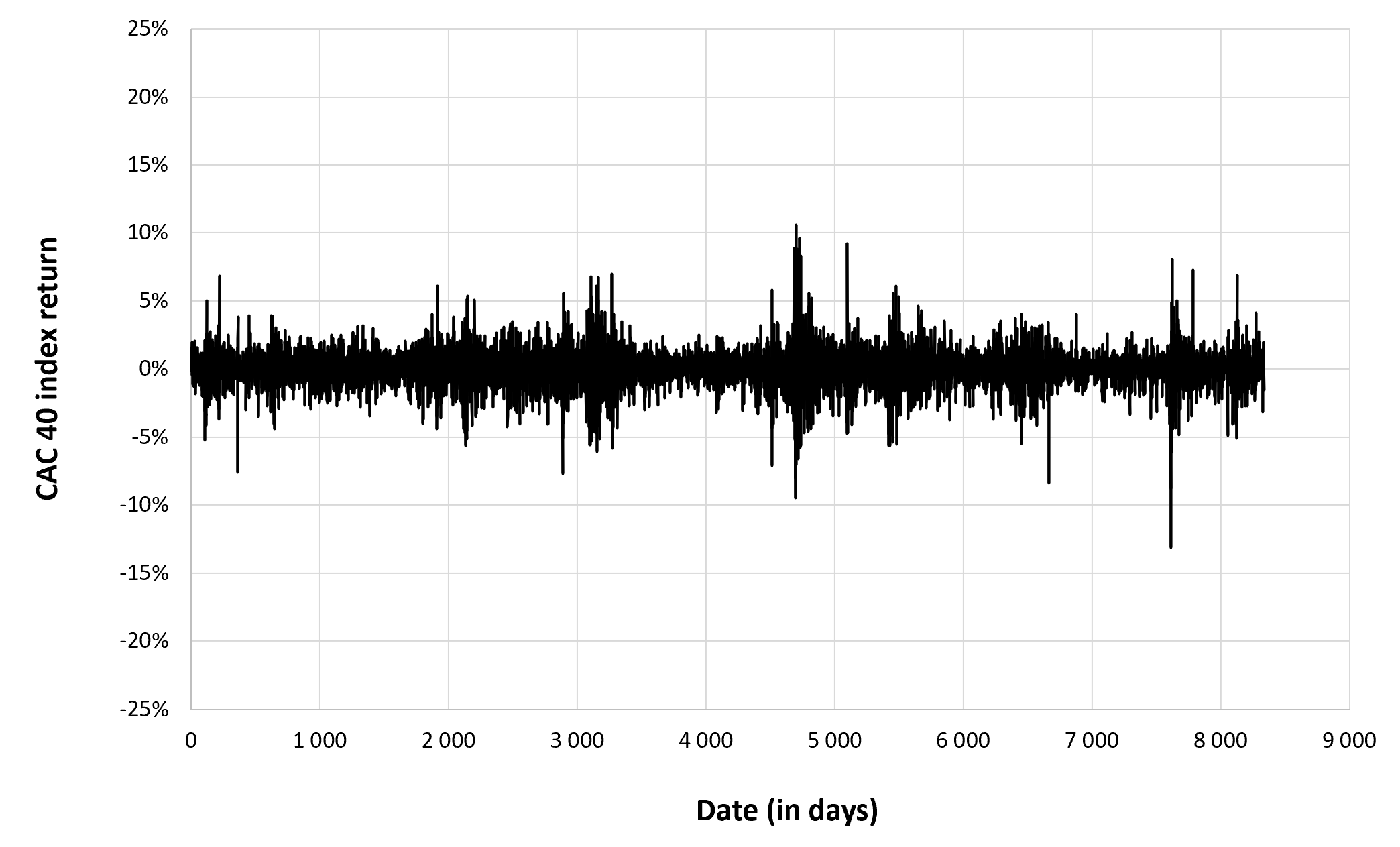
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
Summary statistics for the CAC 40 index
The R program that you can download above also allows you to compute summary statistics about the returns of the CAC 40 index.
Table 4 below presents the following summary statistics estimated for the CAC 40 index:
- The mean
- The standard deviation (the squared root of the variance)
- The skewness
- The kurtosis.
The mean, the standard deviation / variance, the skewness, and the kurtosis refer to the first, second, third and fourth moments of statistical distribution of returns respectively.
Table 4. Summary statistics for the CAC 40 index.
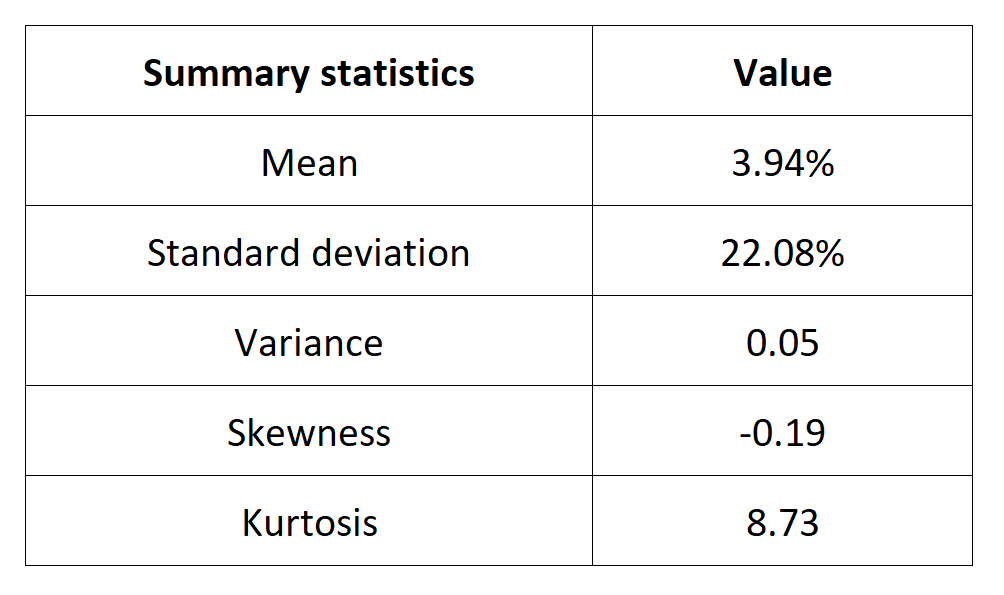
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
Statistical distribution of the CAC 40 index returns
Historical distribution
Figure 3 represents the historical distribution of the CAC 40 index daily returns for the period from March 1, 1990 to December 30, 2022.
Figure 3. Historical distribution of the CAC 40 index returns.
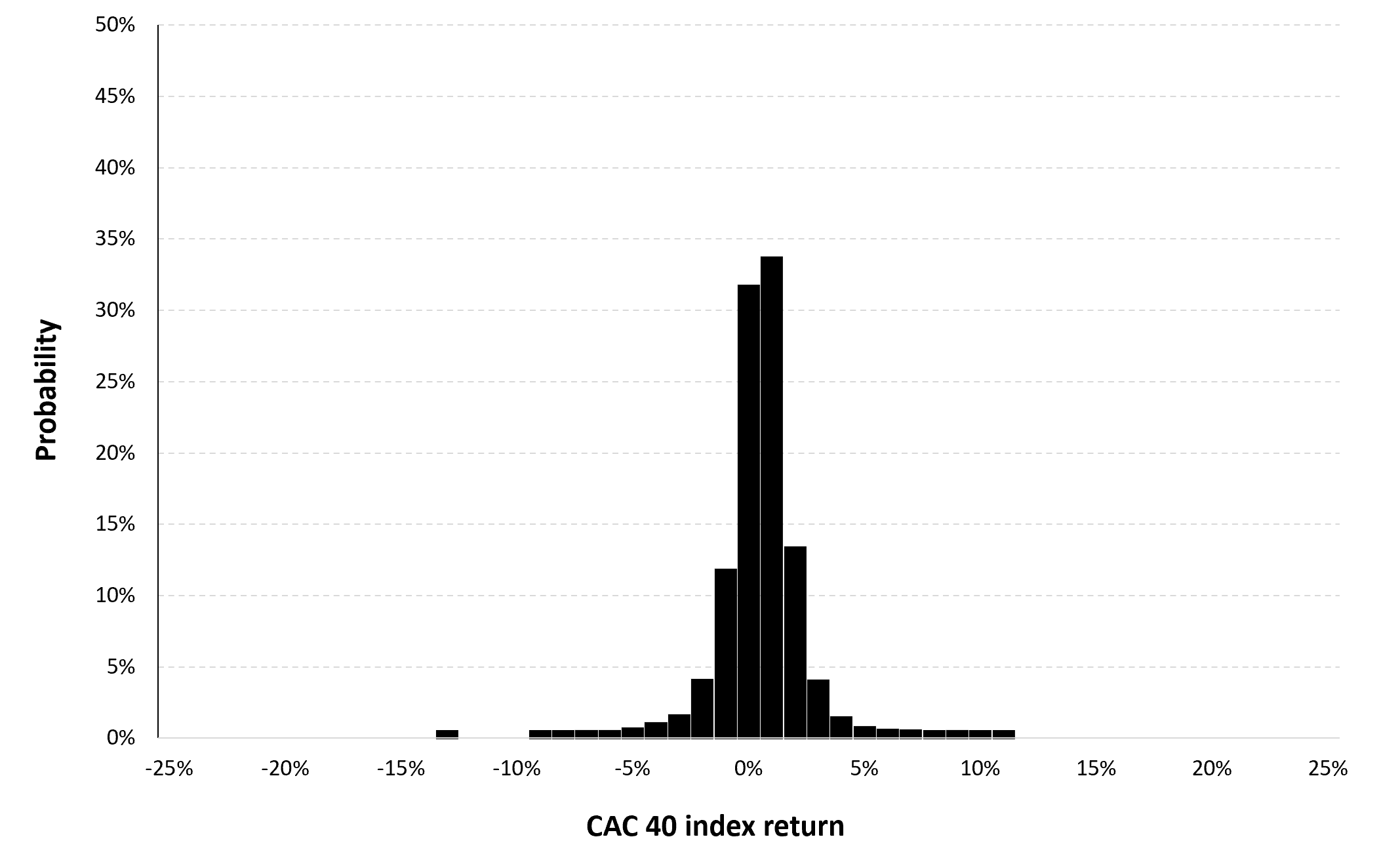
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
Gaussian distribution
The Gaussian distribution (also called the normal distribution) is a parametric distribution with two parameters: the mean and the standard deviation of returns. We estimated these two parameters over the period from March 1, 1990 to December 30, 2022. The mean of daily returns is equal to 0.02% and the standard deviation of daily returns is equal to 1.37% (or equivalently 3.94% for the annual mean and 28.02% for the annual standard deviation as shown in Table 3 above).
Figure 4 below represents the Gaussian distribution of the CAC 40 index daily returns with parameters estimated over the period from March 1, 1990 to December 30, 2022.
Figure 4. Gaussian distribution of the CAC 40 index returns.
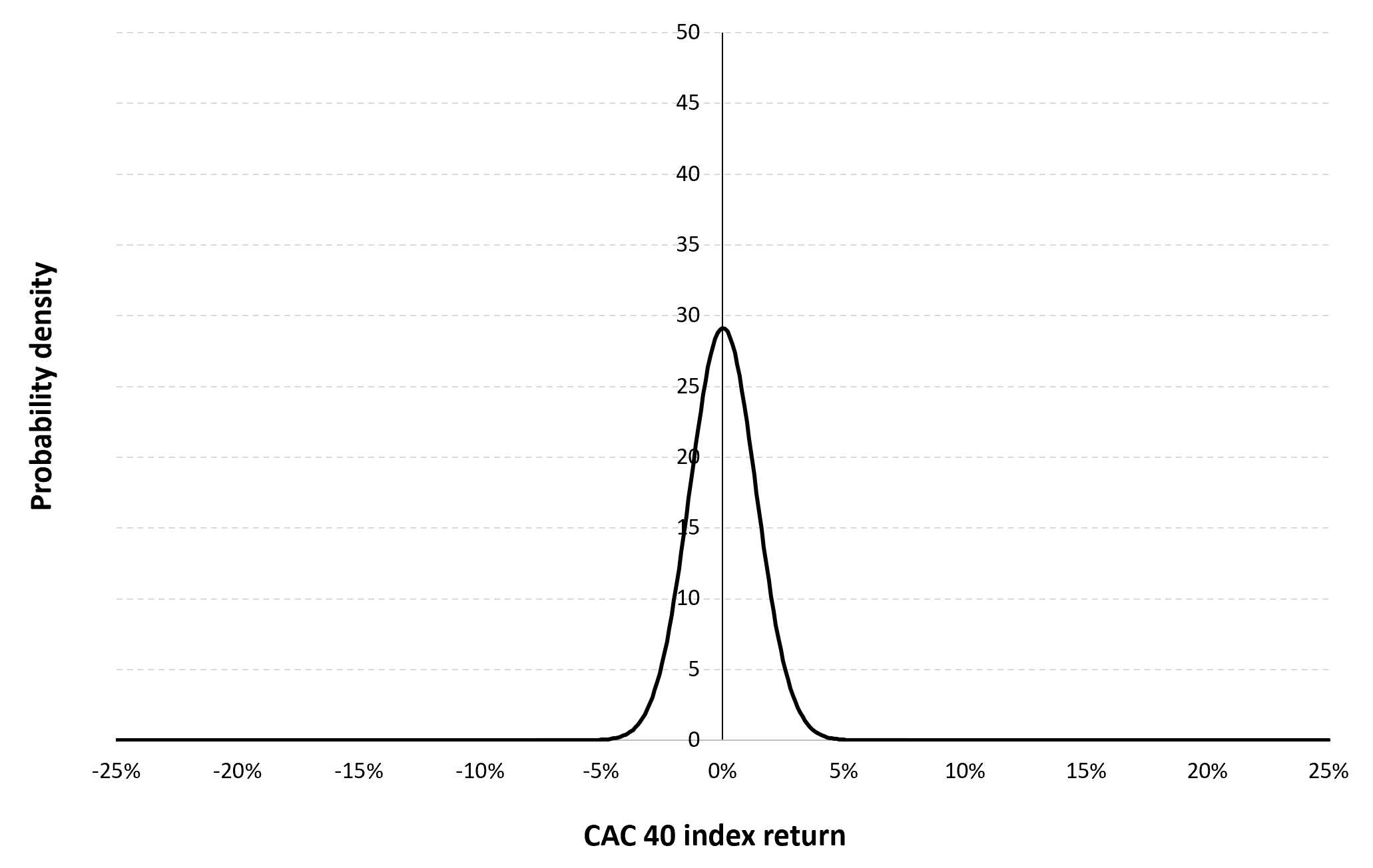
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
Risk measures of the CAC 40 index returns
The R program that you can download above also allows you to compute risk measures about the returns of the CAC 40 index.
Table 5 below presents the following risk measures estimated for the CAC 40 index:
- The long-term volatility (the unconditional standard deviation estimated over the entire period)
- The short-term volatility (the standard deviation estimated over the last three months)
- The Value at Risk (VaR) for the left tail (the 5% quantile of the historical distribution)
- The Value at Risk (VaR) for the right tail (the 95% quantile of the historical distribution)
- The Expected Shortfall (ES) for the left tail (the average loss over the 5% quantile of the historical distribution)
- The Expected Shortfall (ES) for the right tail (the average loss over the 95% quantile of the historical distribution)
- The Stress Value (SV) for the left tail (the 1% quantile of the tail distribution estimated with a Generalized Pareto distribution)
- The Stress Value (SV) for the right tail (the 99% quantile of the tail distribution estimated with a Generalized Pareto distribution)
Table 5. Risk measures for the CAC 40 index.
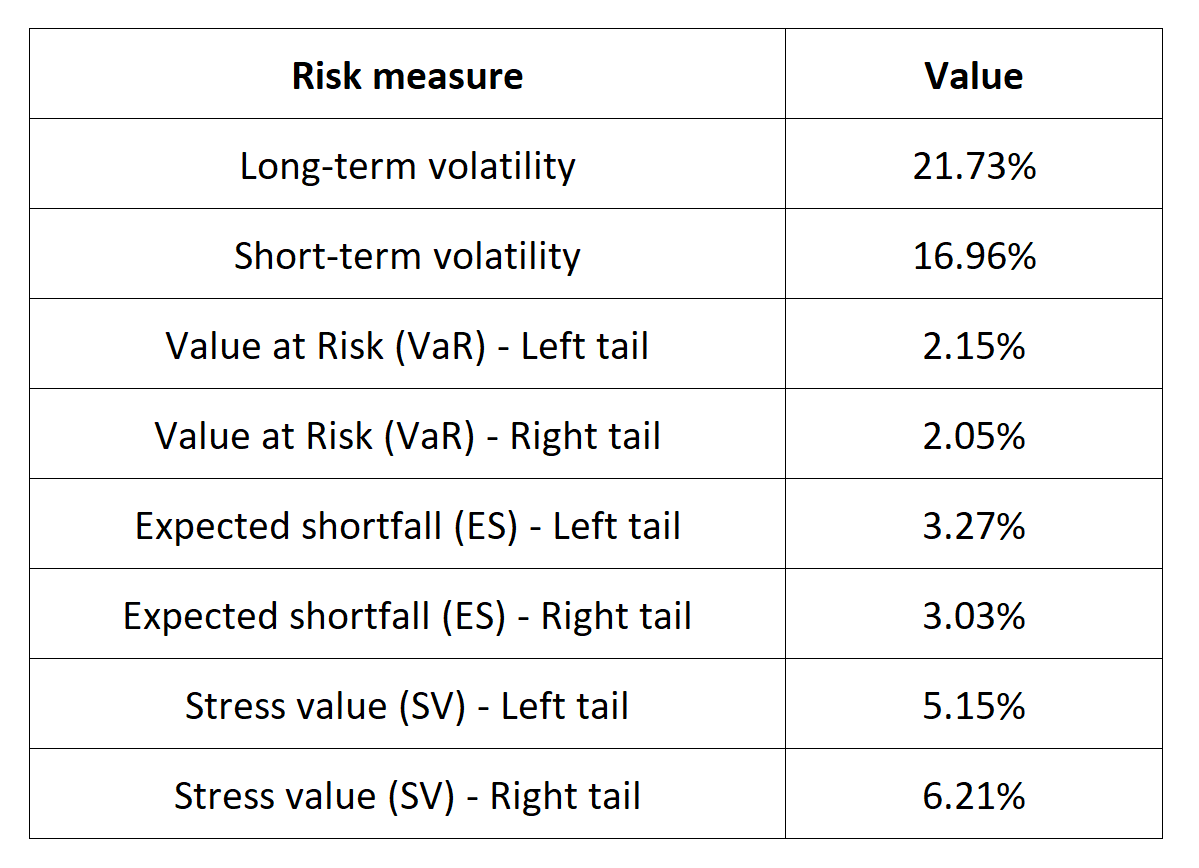
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
The volatility is a global measure of risk as it considers all the returns. The Value at Risk (VaR), Expected Shortfall (ES) and Stress Value (SV) are local measures of risk as they focus on the tails of the distribution. The study of the left tail is relevant for an investor holding a long position in the CAC 40 index while the study of the right tail is relevant for an investor holding a short position in the CAC 40 index.
Why should I be interested in this post?
For a number of reasons, management students (as future managers and individual investors) should learn about the CAC 40 index. The performance of large-cap listed French companies is tracked by this stock market index, which is first and foremost well-known and respected. Gaining a deeper understanding of the French large-cap stock market and the businesses that fuel its expansion requires knowledge of the CAC 40 index.
Individual investors can assess the performance of their own investments and those of their organization by comprehending the CAC 40 index and its components. Last but not least, a lot of businesses base their mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) on the CAC 40 index which can considered as interesting assets to diversify a portfolio.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
About financial indexes
▶ Nithisha CHALLA Financial indexes
▶ Nithisha CHALLA Calculation of financial indexes
▶ Nithisha CHALLA The business of financial indexes
▶ Nithisha CHALLA Float
Other financial indexes
▶ Nithisha CHALLA The S&P 500 index
▶ Nithisha CHALLA The FTSE 100 index
▶ Nithisha CHALLA The CSI 300 index
▶ Nithisha CHALLA The Nikkei 225 index
▶ Nithisha CHALLA The DAX 30 index
About portfolio management
▶ Youssef LOURAOUI Portfolio
▶ Jayati WALIA Returns
About statistics
▶ Shengyu ZHENG Moments de la distribution
▶ Shengyu ZHENG Mesures de risques
Useful resources
Academic research about risk
Longin F. (2000) From VaR to stress testing: the extreme value approach Journal of Banking and Finance, N°24, pp 1097-1130.
Longin F. (2016) Extreme events in finance: a handbook of extreme value theory and its applications Wiley Editions.
Other
Wikipedia CAC 40
FXCM Everything you need to know about the CAC 40 index
EFMAE The introduction of CAC40 Master unit
Data
Yahoo Finance CAC 40 index
About the author
The article was written in April 2023 by Nithisha CHALLA (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2021-2023).