Float
In this article, Nithisha CHALLA (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2021-2023) explains float and its use in the construction financial indexes.
What is Float?
The term “float” (sometimes mentioned as “free float”) refers to the quantity of shares that are readily tradable in financial markets. The float is defined as
Float = Total outstanding shares – Closely held shares – Restricted shares
Outstanding shares are the total number of shares issued by the company.
Closely held shares are the shares of a company that are owned by a small number of shareholders and are not traded on a public stock exchange. These shareholders may include company founders, family members, or a small group of private investors.
Restricted shares are the shares that are not transferable until certain conditions are met and are typically held by corporate management, such as executives and directors. Restricted shares are a type of equity compensation that some employees receive.
The float is usually expressed as a percentage of the total number of shares issued by the company.
Float and IPO
When a company conducts an initial public offering (IPO) or a seasoned offering (SEO) to finance its operational activities and investments, it releases a certain number of shares onto the market that are available for purchase by anyone interested in acquiring a piece of the company. The number of shares issued by the company increases the float. Before the IPO, the float is equal to zero. After the IPO, the float increases but may be relatively small as the founder or top managers of the company may want or have to keep some of their shares.
Why is the float important?
The float is crucial for the calculation of market capitalization-weighted stock market indices. The weight of a company’s stock in the index and, consequently, its impact on the performance of the index as a whole, can change depending on whether shares are included in or excluded from the float. Because of this, a lot of indices base their values solely on the shares in the float, known as the float-adjusted market capitalization method.
Stock market liquidity increases as the float increases. As the number of shares that can be purchased and sold increases, it makes it simpler for an investor to enter and exit the market.
High-float stocks and low-float stocks
In the equity market, we often distinguish high-float stocks and low-float stocks according to the percentage of shares that are available for trading in the market. High-float stocks have more supply and more shares available for trading than low-float stocks.
High float stocks have greater liquidity and are less volatile. In a situation where there is extremely heavy demand, supply and demand will become imbalanced, which will lead to extreme price moves.
Example
The percentage of float shares in relation to all outstanding shares is known as the float percentage. Let us consider the case of Amazon. As of September 2021, Amazon had approximately 505 million shares outstanding. Of these shares, approximately 425 million were considered “float shares”. Float shares are the shares available for trading by the public and exclude shares held by insiders, institutional investors, and other long-term investors.
Therefore, Amazon’s float share percentage would be calculated as follows:
(425 million float shares / 505 million outstanding shares) x 100% = 84.16%
This indicates that the public had access to about 84.16% of Amazon’s outstanding shares for trading. Insiders, institutions, and other long-term investors held the remaining 15.84% of the stock.
Indexes using the float
Equity indices that track the performance of a particular group of companies, such as small-cap or mid-cap companies, are frequently created using float-based indexes. The market capitalization of each company, which is determined by multiplying the total number of outstanding shares by the current share market price, is considered in the calculation of these indices.
The Russell 2000 index, which tracks the performance of 2,000 small-cap companies in the US, and the MSCI World Small Cap index, which tracks the performance of small-cap companies in developed markets worldwide, are two of the many examples of indexes that make use of the float.
We present below the formula for a market-capitalization-weighted index and a float-adjusted market-capitalization-weighted index.
Market-capitalization-weighted index
A market capitalization-weighted index is calculated by multiplying the price of each asset in the index by its number of outstanding shares and summing the resulting values. The weighting of each asset in the index is determined by its market capitalization, so that the largest and most influential companies have the greatest impact on the overall performance of the index.
The formula for a market-capitalization-weighted index is given by
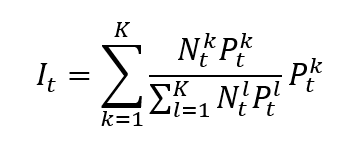
Where I is the index value, k a given asset, K the number of assets in the index, Pk the market price of asset k, Nk the number of issued shares for asset k, and t the time of calculation of the index.
In a market capitalization-weighted index, the weight of asset k is given by formula can be rewritten as
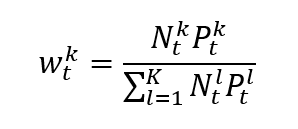
Which clearly shows that the weight of each asset in the index is its market capitalization of the asset divided by the sum of the market capitalizations of all assets.
Note that the divisor, whose calculation is based on the number of shares, is typically adjusted for events such as stock splits and dividends. The divisor is used to ensure that the value of the index remains consistent over time despite changes in the number of outstanding shares.
Float-adjusted market-capitalization-weighted index
In a float-adjusted market-capitalization-weighted index, the market-capitalization weight of each asset is adjusted for its market float. It is also called a free float. Instead of taking into account shares held by insiders, governments, or other entities that might not be available for trading, the weight is adjusted based on the percentage of shares that are actually traded on the open market.
This differs from the market capitalization weighted index as it accounts for the shares outstanding of a company. A float-adjusted market capitalization-weighted index only takes into account shares that are freely available for trading, whereas a market capitalization-weighted index takes into account all outstanding shares, providing a more accurate picture of the performance of the market.
The formula for a float-adjusted market-capitalization-weighted index is given by
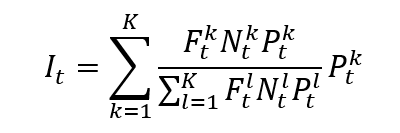
Where I is the index value, k a given asset, K the number of assets in the index, Pk the market price of asset k, Nk the number of issued shares for asset k, Fk the float factor of asset k, and t the time of calculation of the index.
In a float-adjusted market-capitalization-weighted index, the weight of asset k is given by formula can be rewritten as
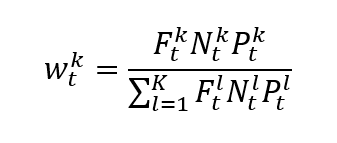
Why should I be interested in this post?
As a key idea in finance and investment, float should be covered by management students. Float has important effects on both managers and investors. Analyzing a company’s financial statements can also benefit from having a solid understanding of floats. When making a choice, a management student who is researching a company’s stock as a potential investment should keep this in mind.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ All posts about Financial techniques
▶ Nithisha CHALLA Financial indexes
▶ Nithisha CHALLA Calculation of financial indexes
▶ Nithisha CHALLA The DJIA index
Useful resources
Bankrate What is a stock float
Business Insider Floating stock: Why it’s important for investors to know a company’s float
The Economic Times Float and IPO
Russel How are indexes weighted?
About the author
The article was written in April 2023 by Nithisha CHALLA (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2021-2023).

