Trading strategies based on market profiles and volume profiles

In this third article on a series on market profiles, Michel Henry VERHASSELT (ESSEC Business School – Master in Finance, 2023-2025) explains trading strategies based on market profiles and volume profiles.
Introduction
We have defined and seen illustrations of all the key concepts related to both market profiles and volume profiles. Let us now look at their practical applications and trading strategies that may be applied.
These techniques apply to both market profiles and volume profiles.
Mean reversion
A mean reversion strategy is a trading approach based on the idea that prices tend to revert to their historical average or mean over time. Traders employing this strategy look for opportunities to enter trades when prices deviate significantly from their historical average, anticipating a return to the mean.
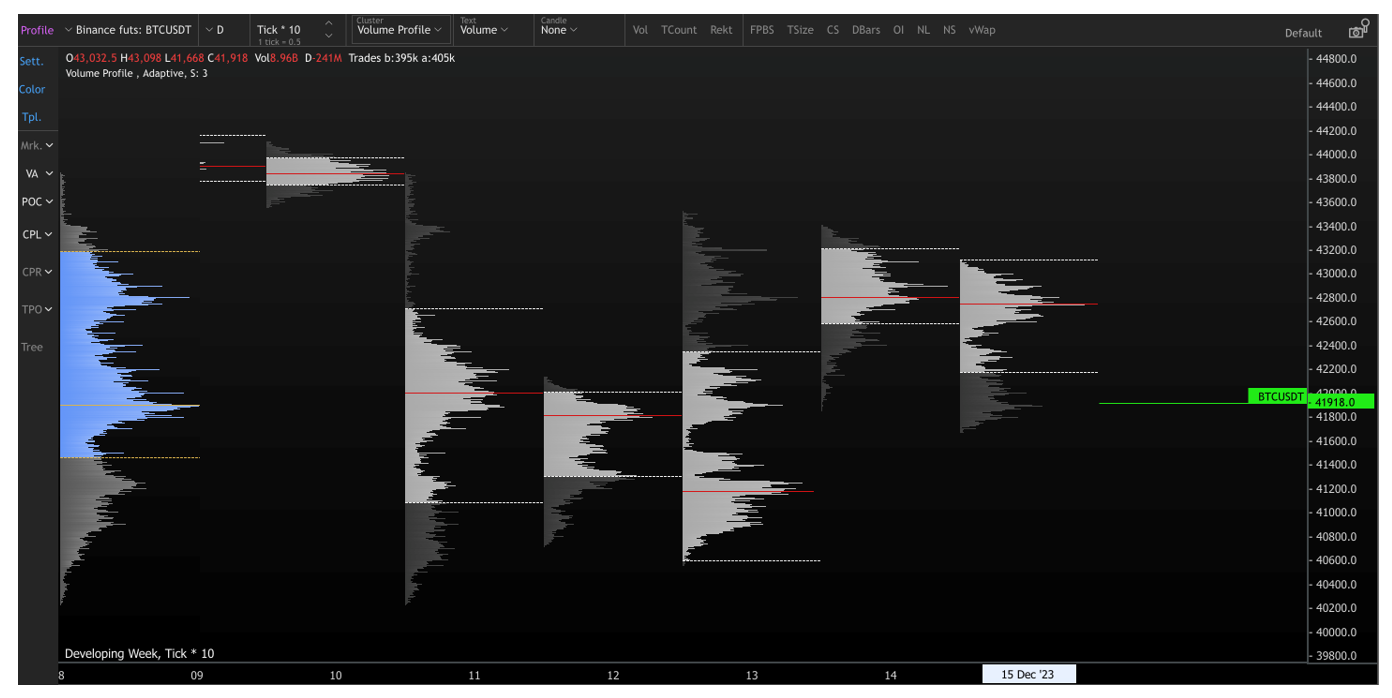
Market profiles naturally fit this kind of strategy, as their whole point is to show where participants have deemed the price to be fair. For example, a trader could consider that when the price is trading below a high-volume area, that area will act as a magnet to pull the price up. The prices in that region were indeed considered fairer, and the current low price would be an anomaly to be corrected by market participants. Therefore, the trader would buy at the current price and sell around the POC or at least within the value area.
Resistance and support
Conversely, a different interpretation within the same framework involves viewing these highly-traded areas as potential resistance or support zones. Support is a crucial level preventing an asset from further decline, often due to an upsurge in buying interest. In contrast, resistance is a pivotal level inhibiting an asset from rising higher, typically caused by intensified selling activity.
For a trader emphasizing resistance and support concepts, consider a rising price nearing a heavily traded zone encountering resistance, similar to reaching a ceiling. The outcome may lead to either a breakout to new highs or a reversal downward. In this context, the value area is not seen as a magnetic force drawing prices toward fair value; instead, it functions as a testing ground. The result hinges on whether the attempt to breach resistance is rejected, leading to a lower price, or successful, resulting in an upward move past this pivotal point. This dynamic interaction adds layers of complexity to mean reversion and support/resistance strategies within the realm of market profiles.
Entries and exits
More generally, traders employ various tools to make well-informed decisions about when to enter or exit market positions. One such powerful tool is the market profile. Even if a trader’s primary strategy relies on other triggers to look at a trade, say for example macro events, they can still leverage market profiles. These profiles help determine optimal entry or exit points, considering factors like obtaining liquidity with minimal market impact and identifying levels for stop losses and target profits based on perceived resistance and support.
Breakouts
As mentioned above, breakout trading is a strategy employed in financial markets where traders capitalize on significant price movements beyond established levels of support or resistance. In a breakout, the price surpasses a predefined range or pattern, triggering potential buying or selling signals. Traders often interpret breakouts as indicators of strong momentum, with the expectation that the price will continue moving in the breakout direction. The aim of breakout trading is to enter positions early in a new trend and ride the momentum for profitable gains.
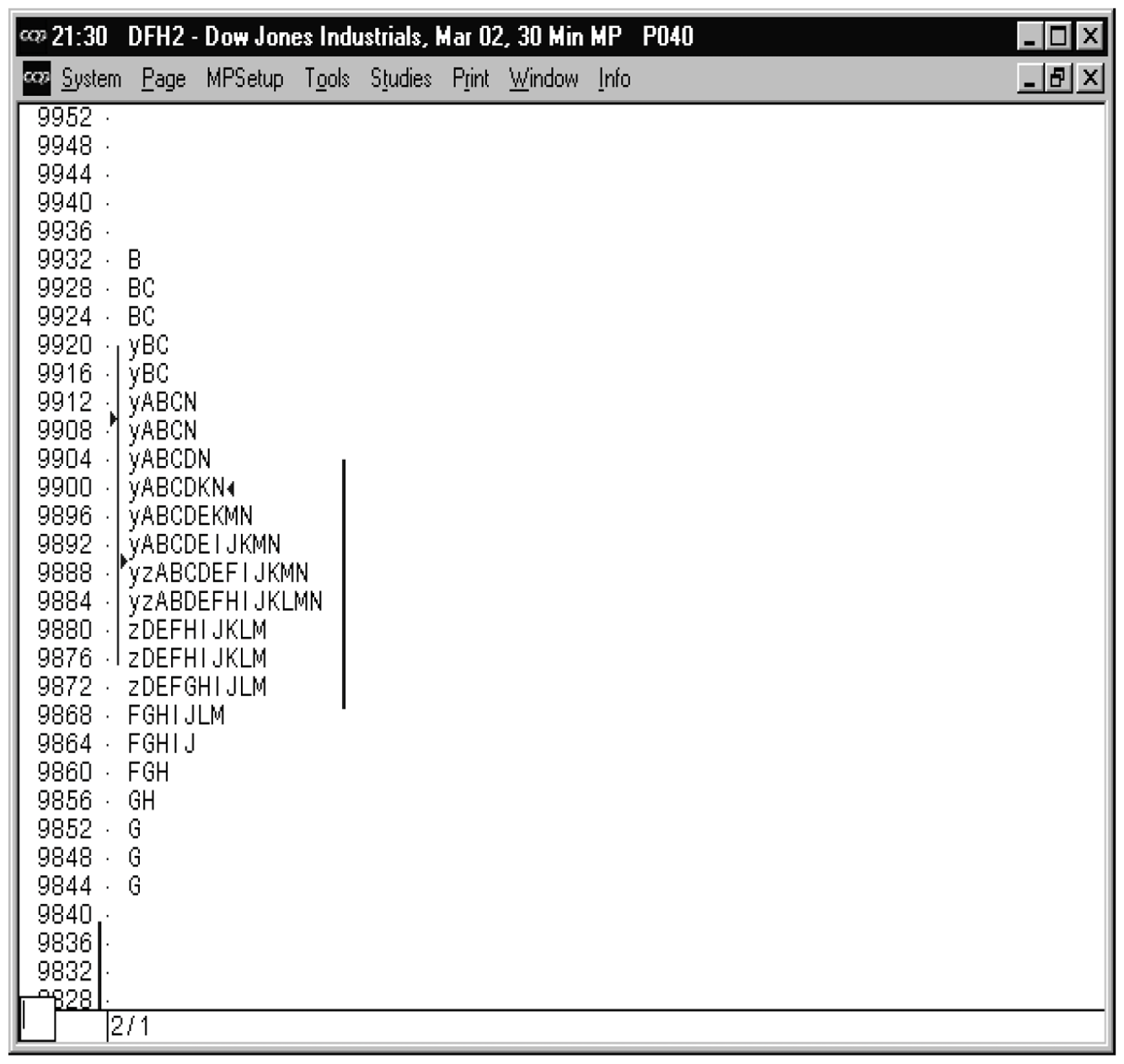
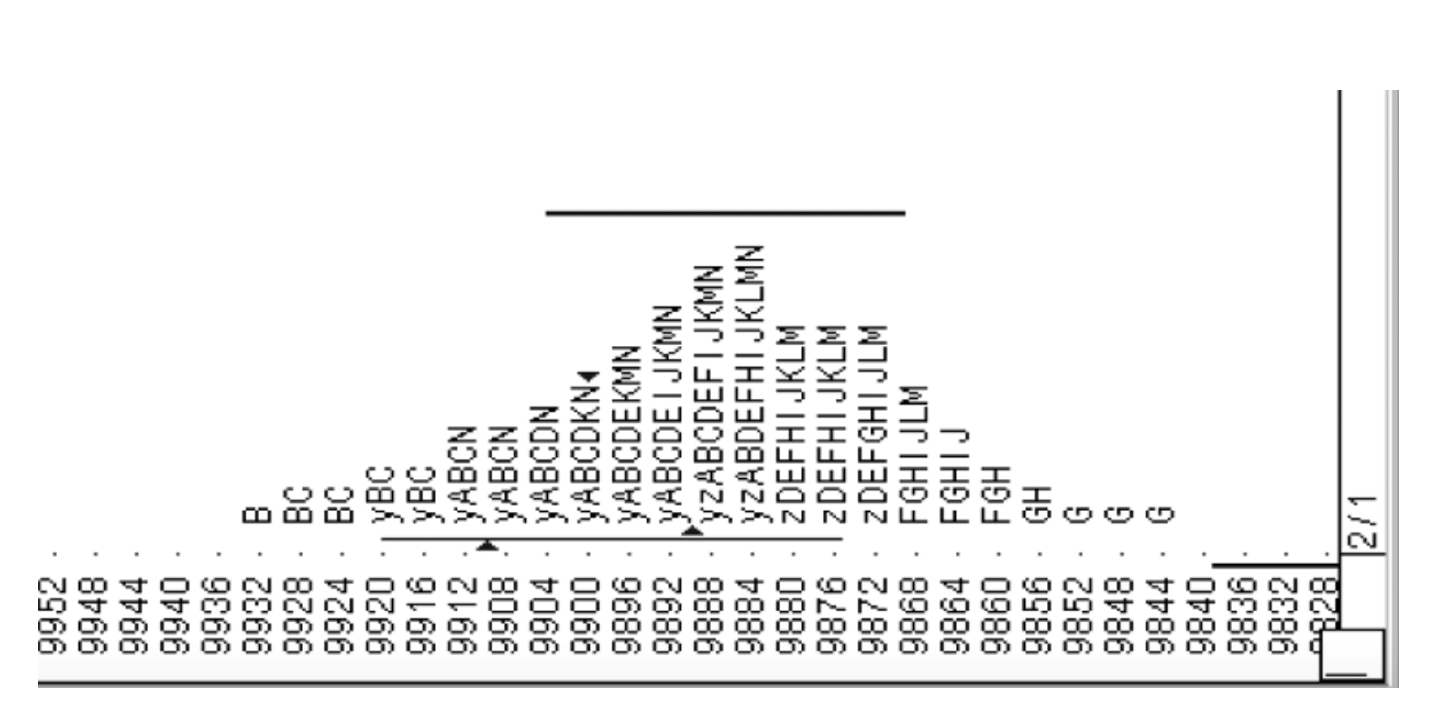
Market profile can help identify breakout opportunities. For example, when a market exhibits confined trading within a narrow range and the profile reveals an accumulation of TPOs (Time Price Opportunities) near the boundaries of this range, a breakout surpassing these levels could indicate a potential trading opportunity.
False breakout strategy
The false breakout trading strategy relies on discerning instances where the price briefly moves beyond a trading range but subsequently retraces, indicating potential weaknesses in the current trend. In a false bullish breakout, signaling buyers’ weakness, traders might opt for short positions. Conversely, in retraced bearish breakouts, suggesting sellers’ uncertainty, opportunities for long positions may emerge. The effectiveness of this strategy lies in recognizing imbalances in supply and demand, a task facilitated by market profiles.
Market profiles offer a nuanced visual representation of price movements over time, highlighting areas of significant trading activity and the distribution of volume at different price levels. This information aids traders in identifying potential entry and exit points more precisely. By integrating market profiles into the false breakout strategy, traders gain insights into the dynamics of supply and demand within specific price ranges. This, in turn, enhances their ability to navigate market sentiment shifts and make informed decisions, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the false breakout trading strategy.
Single prints
The Market Profile Single Print strategy is a dynamic approach leveraging the unique concept of single prints within the Market Profile chart to identify potential breakout opportunities.
The strategy’s foundation lies in identifying single prints—instances where a price level remains untouched throughout the trading session, creating a gap in the Market Profile chart. Price can often revisit these areas to test these inefficiencies. These single prints therefore act as crucial markers, indicating potential areas of support or resistance. The significance of this lies in the ability to pinpoint breakout levels: a break above a single print suggests a bullish breakout, while a break below indicates a bearish breakout.
Crucially, market profiles assist in managing risk effectively by providing a visual representation of potential areas of support or resistance. Continual monitoring of the trade is emphasized, with adjustments made based on evolving market conditions. Trailing stop-loss orders are recommended to protect profits as the trade progresses favorably.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ Michel VERHASSELT Market profiles
▶ Michel VERHASSELT Difference between market profiles and volume profiles
▶ Theo SCHWERTLE Can technical analysis actually help to make better trading decisions?
▶ Theo SCHWERTLE The Psychology of Trading
▶ Clara PINTO Strategy and Tactics: From military to trading
Useful resources
Steidlmayer P.J. and S.B. Hawkins (2003) Steidlmayer on Markets: Trading with Market Profile, John Wiley & Sons, Second Edition;
Steidlmayer P.J. and K. Koy (1986) Markets and Market Logic: Trading and Investing with a Sound Understanding and Approach, Porcupine Press.
About the author
The article was written in December 2023 by Michel Henry VERHASSELT (ESSEC Business School – Master in Finance, 2023-2025).