Reverse Convertibles
In this article, Shengyu ZHENG (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2020-2023) explains reverse convertibles, which are a structured product with a fixed-rate coupon and downside risk.
Introduction
The financial market has been ever evolving, witnessing the birth and flourish of novel financial instruments to cater to the diverse needs of market participants. On top of plain vanilla derivative products, there are exotic ones (e.g., barrier options, the simplest and most traded exotic derivative product). Even more complex, there are structured products, which are essentially the combination of vanilla or exotic equity instruments and fixed income instruments.
Amongst the structured products, reverse convertible products are one of the most popular choices for investors. Reverse convertible products are non-principal protected products linked to the performance of an underlying asset, usually an individual stock or an index, or a basket of them. Clients can enter into a position of a reverse convertible with the over-the-counter (OTC) trading desks in major investment banks.
In exchange for an above-market coupon payment, the holder of the product gives up the potential upside exposure to the underlying asset. The exposure to the downside risks still remains. Reserve convertibles are therefore appreciated by the investors who are anticipating a stagnation or a slightly upward market trend.
Construction of a reverse convertible
This product could be decomposed in two parts:
- On the one hand, the buyer of the structure receives coupons on the principal invested and this could be considered as a “coupon bond”;
- On the other hand, the investor is still exposed to the downside risks of the underlying asset and foregoes the upside gains, and this could be achieved by a short position of a put option (either a vanilla put option or a down-and-in barrier put option).
Positions of the parties of the transaction
A reverse convertible involves two parties in the transaction: a market maker (investment bank) and an investor (client). Table 1 below describes the positions of the two parties at different time of the life cycle of the product.
Table 1. Positions of the parties of a reverse convertible transaction
| t | Market Maker (Investment Bank) | Investor (Client) |
|---|---|---|
| Beginning |
|
|
| Interim |
|
|
| End |
|
|
Based on the type of the put option incorporated in the product (either plain vanilla put option or down-and-in barrier put option), reserve convertibles could be categorized as plain or barrier reverse convertibles. Given the difference in terms of the composition of the structured product, the payoff and pricing mechanisms diverge as well.
Here is an example of a plain reverse convertible with following product characteristics and market information.
Product characteristics:
- Investment amount: USD 1,000,000.00
- Underlying asset: S&P 500 index (Bloomberg Code: SPX Index)
- Investment period: from August 12, 2022 to November 12, 2022 (3 months)
- Coupon rate: 2.50% (quarterly)
- Strike level : 100.00% of the initial level
Market data:
- Current risk-free rate: 2.00% (annualized)
- Volatility of the S&P 500 index: 13.00% (annualized)
Payoff of a plain reverse convertible
As is presented above, a reverse convertible is essentially a combination of a short position of a put option and a long position of a coupon bond. In case of the plain reverse convertible product with the aforementioned characteristics, we have the blow payoff structure:
- in case of a rise of the S&P 500 index during the investment period, the return for the reverse convertible remains at 2.50% (the coupon rate);
- in case of a drop of the S&P 500 index during the investment period, the return would be equal to 2.50% minus the percentage drop of the underlying asset and it could be negative if the percentage drop is greater than 2.5%.
Figure 1. The payoff of a plain reverse convertible on the S&P 500 index
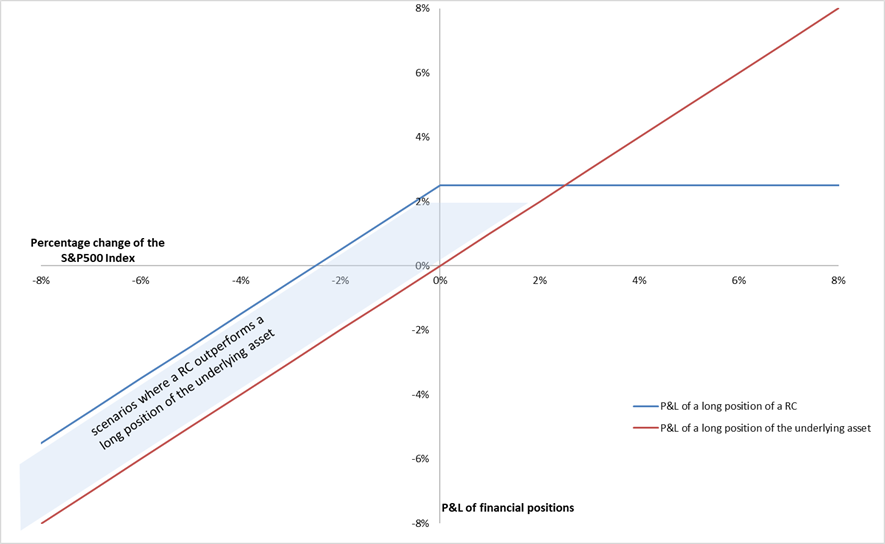
Source: Computation by author.
Pricing of a plain reverse convertible
Since a reverse convertible is essentially a structured product composed of a put option and a coupon bond, the pricing of this product could also be decomposed into these two parts. In terms of the pricing a vanilla option, the Black–Scholes–Merton model could do the trick (see Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing model) and in terms of pricing a barrier option, two methods, analytical formula method and Monte-Carlo simulation method, could be of help (see Pricing barrier options with analytical formulas; Pricing barrier options with simulations and sensitivity analysis with Greeks).
With the given parameters, we can calculate, as follows, the margin for the bank with respect to this product. The calculated margin could be considered as the theoretical price of this product.
Table 2. Margin for the bank for the plain reverse convertible
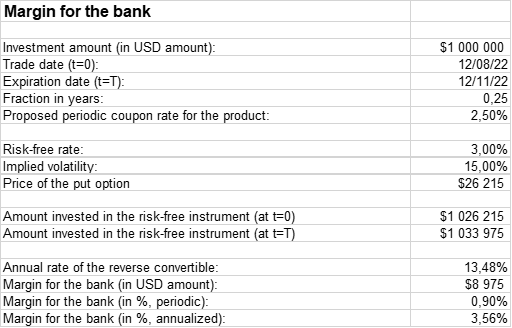
Source: Computation by author.
Download the Excel file to analyze reverse convertibles
You can find below an Excel file to analyze reverse convertibles.

Why should I be interested in this post
As one of the most traded structured products, reverse convertibles have been an important instrument used to secure return amid mildly negative market prospect. It is, therefore, helpful to understand the product elements, such as the construction and the payoff of the product and the targeted clients. This could act as a steppingstone to financial product engineering and risk management.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ Jayati WALIA Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing model
▶ Akshit GUPTA The Black Scholes Merton Model
▶ Shengyu ZHENG Barrier options
▶ Shengyu ZHENG Pricing barrier options with analytical formulas
▶ Shengyu ZHENG Pricing barrier options with simulations and sensitivity analysis with Greeks
Resources
Academic references
Broadie, M., Glasserman P., Kou S. (1997) A Continuity Correction for Discrete Barrier Option. Mathematical Finance, 7:325-349.
De Bellefroid, M. (2017) Chapter 13 (Barrier) Reverse Convertibles. The Derivatives Academy. Accessible at https://bookdown.org/maxime_debellefroid/MyBook/barrier-reverse-convertibles.html
Haug, E. (1997) The Complete Guide to Option Pricing. London/New York: McGraw-Hill.
Hull, J. (2006) Options, Futures, and Other Derivatives. Upper Saddle River, N.J: Pearson/Prentice Hall.
Merton, R. (1973). Theory of Rational Option Pricing. The Bell Journal of Economics and Management Science, 4:141-183.
Paixao, T. (2012) A Guide to Structured Products – Reverse Convertible on S&P500
Reiner, E. S. (1991) Breaking down the barriers. Risk Magazine, 4(8), 28–35.
Rich, D.R. (1994) The Mathematical Foundations of Barrier Option-Pricing Theory. Advances in Futures and Options Research: A Research Annual, 7, 267-311.
Business references
Six Structured Products. (2022). Reverse Convertibles et barrier reverse Convertibles
About the author
The article was written in August 2022 by Shengyu ZHENG (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2020-2023).

