Initial and maintenance margins in futures contracts
This article written by Akshit GUPTA (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2019-2022) explains the mechanisms of initial and maintenance margin used in futures contracts.
Introduction
In financial markets, margin requirements are present in leveraged positions in derivative products. They refer to a percentage of assets that an investor must pay for with his or her own cash or assets (collateral) as a means of protection against the risk exposure to its potential default for the other counterpart.
Margin requirements serve as a guarantee that the investor providing the margins will fulfil its trade obligations. Many exchanges across the world provide leverage facilities to investors for trading in different derivative assets. For example, an investor can use leverage facilities for trading in futures contracts across different asset classes like equities, bonds, currencies, interest rates, etc.
Margin requirements can be categorized as initial and maintenance margin requirements.
Initial margin
Initial margin (or IM) refers to the initial deposit required when an investor opens a position in a derivative product and amounts to a percentage of the nominal contract value. The amount for initial margin requirement is calculated in accordance with approved margin models that are based on the market’s regulatory rules. The determination of the initial margin requirement is essentially based on the volatility of the underlying asset of the derivative product being covered. The more volatile the underlying asset, the higher the initial margin requirement.
You can download below the file to learn about the different Euronext Clearing margin requirements used in derivatives trading.
Maintenance margin
When an investor holds an underlying asset on margin, she is required to maintain a minimum margin amount of that asset position in her portfolio to keep her position open and this is known as the maintenance margin. Maintenance margin requirements aim to protect against excess losses and ensures the broker has enough capital to cover any losses the investor may incur. Maintenance margin is generally calculated on a daily mark-to-market basis between the period starting from the trading date to the contract expiration date.
In case the investor is unable to fulfil the maintenance margin requirements, she receives a margin call initiated from the broker to deposit further amount in order to keep her position open. If she fails to provide adequate maintenance margins, the broker has the power to close her positions.
Mechanism of initial and maintenance margins
Now, we will see how initial and maintenance margins work in the financial markets using S&P 500 mini futures contract. Since the investor has bought the futures contract, he/she is required by its broker to post an initial margin at the time the trade is initiated. For instance, this initial margin is set to 40% of the nominal value of the contract. This money is essentially the collateral on the purchase to protect the seller of the contract in the future against the default of the buyer (the investor).
Followed by this, a maintenance margin is required at any point of time after the trade is initiated. The maintenance margin call is triggered when the value of the initial margin falls below the 30% threshold (i.e. 70% of the initial margin). The buyer has to ensure that any time the position falls below this maintenance margin requirements, he will get a margin call and has to increase funds into the margin account.
Example with initial margin
Here is an example of a typical case of buying a futures contract and its margin mechanism:
The characteristics of the contract and market data include:

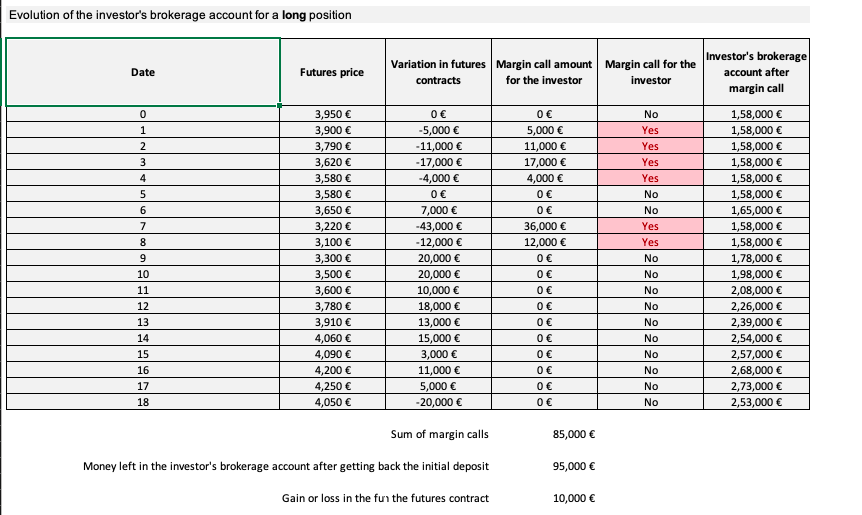
The final value of the investor’s brokerage account is equal to $253,000. At the end of the contract, the investor can get back its initial margin of $158,000 leaving $95,000 on its account. The gain is equal to $10,000 which is the amount left on the account ($95,000) minus the sum of the margin calls ($85,000).
Here is an example of a typical case of selling a futures contract and its margin mechanism using the same characteristics and market data:
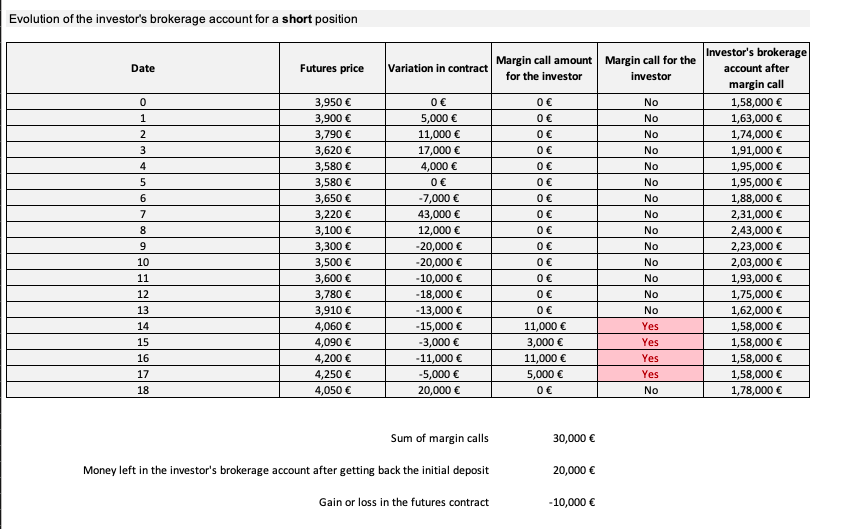
The final value of the investor’s brokerage account is equal to $178,000. At the end of the contract, the investor can get back its initial margin of $158,000 leaving $20,000 on its account. The loss is equal to $10,000 which is the amount left on the account ($20,000) minus the sum of the margin calls ($30,000).
You can download below the Excel file for the computation of the Intial and Maintenance Margins for the futures contracts.
Related posts in the SimTrade blog
▶ Akshit GUPTA Initial and Maintenance margin in stocks
▶ Akshit GUPTA Analysis of the Big Short movie
▶ Akshit GUPTA Analysis of the Margin call movie
▶ Akshit GUPTA Analysis of the Trading places movie
Useful resources
Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA)
Prof. Longin’s website Margin Call mechanism for a futures contract (in French).
About the author
Article written in August 2022 by Akshit GUPTA (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2019-2022).


