Consumer Confidence Index
In this article, Bijal Gandhi (ESSEC Business School, Master in Management, 2019-2022) elaborates on the concept of Consumer Confidence Index.
This reading will help you understand the meaning, calculation, and importance of consumer confidence index.
Introduction
The consumer confidence index (CCI) is a statistical estimation that measures the current and future economic conditions. This indicator provides estimates based on households’ expectations and view of their financial situation like employability, saving capacity, consumption, etc.
It is a barometer that mainly measures the optimistic/pessimistic nature of the consumers regarding their future financial situation. The CCI is based on the concept that when consumers are optimistic about the future, they are likely to spend more currently and stimulate the economy but if the consumers are pessimistic about the future, then they are likely to save more in the present and hence this could lead to a recession. This index tells you about the optimal levels of the households about the economy and their ability to find jobs.
Measuring Consumer Confidence Index
The Consumer Confidence Index measures the degree of optimism/pessimism of the households for the future state of the economy by measuring household current saving and spending patterns. While the Consumer Confidence Index is measured differently in every economy based on various underlining factors, we talk about how it is measured in the U.S. economy to provide an understanding of its calculation process.
In the U.S. economy, the Conference Board calculates the Consumer Confidence Index. It was first calculated in 1985 and is now used as a benchmark to assess the CCI. The value of CCI is calculated monthly based on the results of a household survey of (1) consumers’ opinions on the current conditions as well as their (2) future economic positions. The former constitutes 40% of the index, while the latter constitutes the remaining 60%.
When the confidence increases, consumers spend more money in the present time ,and as a result, indicates the sustainability of an economy. And when the confidence decreases, consumers are prone to save more in the present time, and as a result, indicates the possibility of future economic turmoil.
Each month, the Conference Board conducts a survey for 5,000 U.S. households the survey participants are asked to answer each question in any of the three forms as positive, negative, or neutral. The survey is comprised of five questions about the following:
Present Situation Index
- Current business conditions
- Current employment conditions
Expectations Index
- Business situation for the next six months
- Employment situation for the next six months
- Total family income situation for the next six months
A relative value is calculated separately for each question, it is then compared to the relative value from the 1985 survey. This comparison of the relative value is used to calculate the “index value” for each question.
Finally, the average of all five index values forms the final consumer confidence index. In the U.S. Economy, this data is calculated for the economy as a whole. In the following graph, we can see the impact of the corona virus pandemic on the consumer confidence index in April 2020.
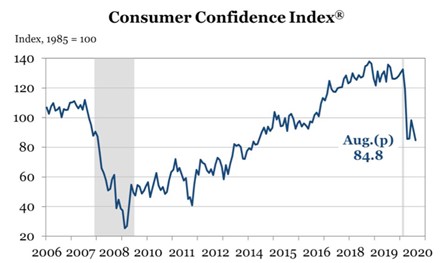
Source: The Conference Board
Interpreting Consumer Confidence Index
The consumer confidence index measures the spending/savings pattern of the consumers currently and their response to the economy’s future growth prospects.
Higher index value means that the consumers have confidence in the future of the economy and its growth and as a result will be spending more currently. On the contrary, a lower index value means that consumers have low confidence in the future of the economy and as a result will be likely to save more in the present. Therefore, the consumer confidence index does not only help to interpret the household’s opinion on the future of the economy’s growth but also helps businesses, banks, retailers, and government to factor in and adapt to the changes in the household’s future consumption/saving patterns.
For example, if the consumer confidence index shows a consistent decrease in its value, it means that the consumers are currently saving more and, in the future, as well. As a result, consumers will be less willing to spend. Based on these manufacturers’ can adapt to their production of retail goods, banks can interpret a decrease in the lending activity and credit card usage, the government can adapt its fiscal or monetary policies to stimulate the economy. On the contrary, if the consumer confidence index shows a consistent increase in its value it means that the consumers are willing to spend more currently and, in the future, because they have confidence that the economy will boost. As a result, the manufacturers can increase their supply of non-essential goods and luxury goods, banks can expect the increase of withdrawal from the consumers saving accounts, etc.
The consumer confidence index is a lagging indicator, as mentioned by many economists. This means that the indicator is not necessarily good at predicting future economic trends. On the contrary, it is more like the index follows the future economic conditions after they have occurred. For example, even after a regressive period is over, the impacts will remain. There will still be an increased unemployment rate in the economy. This simply means that the consumer confidence index is more like the aftershocks of an earthquake that already happened in the economy.
CCI therefore helps get an idea of the consumer spending/saving pattern and the degree with which it will increase/decrease. An increase in spending can increase the growth of businesses and therefore result in higher earnings in stock market prices for businesses. Hence, investors are more likely to buy stocks if the consumer confidence index rises. As a result, the stock market may move drastically during the publication date of the confidence index.
Useful resources
About the author
Article written in May 2021 by Bijal Gandhi (ESSEC Business School, Master in Management, 2019-2022).

