Purchasing Managers’ Index
In this article, Bijal GANDHI (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2019-2022) elaborates on the concept of Purchasing Managers’ Index
This read will help you understand the formulation of PMI and it’s importance for each of the stakeholders.
Introduction
The Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) is a statistical estimation used to determine the economic directions in which the manufacturing and service sectors are moving forward. The PMI consists of a diffusion index that locates whether the market conditions for a particular sector are expanding, remaining the same, or contracting. The main goal of this index is to provide information about the present and future business conditions to decision-makers, analysts, investors, and the government.
The Purchasing Managers’ Index is an economic indicator formulated via surveys conducted for businesses in a particular sector.
PMI is formulated by three main institutions:
- Institute for Supply Management (ISM): This institute originated the manufacturing and non-manufacturing metrics produced for the United States.
- Singapore Institute of Purchasing and Materials Management (SIPMM): This institute formulates the Singapore PMI.
- IHS Markit Group: This institute formulates metrics based on ISM’s metrics for more than 30 countries worldwide.
Calculation of PMI
The Purchasing Managers’ Index is formulated by several different surveys of purchasing managers at businesses in a different sector but mainly revolving around manufacturing and service sectors. All the surveys are amalgamated into a single numerical result depending on several possible answers to each question.
The calculation mentioned below is the methodology of the PMI being calculated and released by the Institute for Supply Management (ISM). The PMI is formulated from a monthly survey sent to senior executives at more than 400 companies in 19 primary industries (which are selected and weighted via their contribution to the U.S. GDP). The PMI is formulated around five main survey areas: (1) new orders, (2) inventory levels, (3) production, (4) deliveries, and (5) employment. All the survey areas are equally weighed while computing the PMI. This always consists of questions about business conditions regarding the sector and if any possible changes are occurring, whether be expanding, stagnant, or contracting.
The Purchasing Managers’ Index is an index indicating whether the economic conditions are better or worse for the companies surveyed by comparing it to the previous PMI. The methodology used to calculate the PMI assigns weight to each common element. The common element is multiplied by the following for a certain situation: multiplied by 1 for improvement, multiplied by 0.5 for stagnation, and multiplied by 0 for deterioration.
The PMI is calculated as:
PMI = (P1 x 1) + (P2 x 0.5) + (P3 x 0) where,
P1 = % of answers indicating an expansion
P2 = % of answers indicating no change
P3 = % of answers indicating a contraction
The PMI is a number ranging between 0 and 100. The formulated PMI is then compared to the previous month and if the PMI is greater than 50 represents an improvement/expansion while a PMI which is less than 50 represents a contraction/deterioration. A PMI equal to 50 represents no change/stagnation. It is also important to note that the greater the difference from the midpoint of 50, the greater is the expansion/contraction.
Importance of PMI
The PMI is turning out to be one of the most tracked indicators of business activity across the globe. It provides a good picture of how an economy is functioning particularly in the manufacturing sector. It is a good representative of the boom-and-bust cycles in the economy and hence it is closely administered by investors, businesses, traders, and financial professionals including economists. Furthermore, the PMI acts as a leading indicator of economic activity. It is important to various entities as explained below.
For Manufacturers
The PMI and its relevant data formulated every month by the ISM are crucial decision-making tools for managers in various roles ranging from different sectors. For example, if a smartphone manufacturer makes their production decisions based on the expected new orders from customers in the future months. These new orders drive the management’s purchasing decisions about multiple components and raw materials. Therefore, the PMI helps manufacturers in predicting the possibility for an expansion or unexpected contraction in their sector and them to make decisions for an anticipated future.
For Suppliers
The PMI also facilitates suppliers in making their decisions. A supplier from the manufacturing sector would follow the PMI to predict the market to estimate the amount of future demand for its products. PMI’s ability to inform about supply and demand, in turn, helps the supplier adjust the prices that they can charge. For example, if the manufacturer’s new orders are growing, it might result in increased customer prices and as a result, accept a price increase from its suppliers as well. On the contrary, if the new orders are declining, the manufacturers might reduce their prices and as a result demand lower prices for the parts that they procure from suppliers.
For Investors
Investors can also utilize the data from the PMI to their advantage because the PMI acts as an indicator of economic conditions. The direction in which the PMI tends to follow is usually preceded by changes in the trends of major economic activities and outputs such as the GDP, Industrial Production, and Employability. Therefore, paying attention to the value of PMI and its movement can result in profitable foresight for the investors.
For Government
The Purchasing Managers’ Index is an important indicator for economic growth. It is used by international investors who try to formulate an opinion on the economic growth and hence consider PMI as a leading indicator for the GDP’s growth or deterioration. Central banks also utilize the results of PMI to formulate monetary policies.
Why should one be concerned about PMI?
PMI is a good indicator to provide a direction in which the economy is moving forward. If you are a potential employee, it will help you determine the increase or decrease in employability in an economy. If you are an investor, PMI helps you determine changes in the macro fundamentals of the economy and their impact on the equity market. If you are a business owner, it could help formulate and guide in making more informed and certain decisions related to the sourcing of raw materials, inventory levels, etc.
The following graph from tradingview.com depicts the PMI from 2017 to 2021. The PMI ranges between the value 0 and 100 with values below 50 showing contraction and values above 50 showing expansion in the economy. As of April 2021, the PMI was 60.70 as depicted in the chart below.
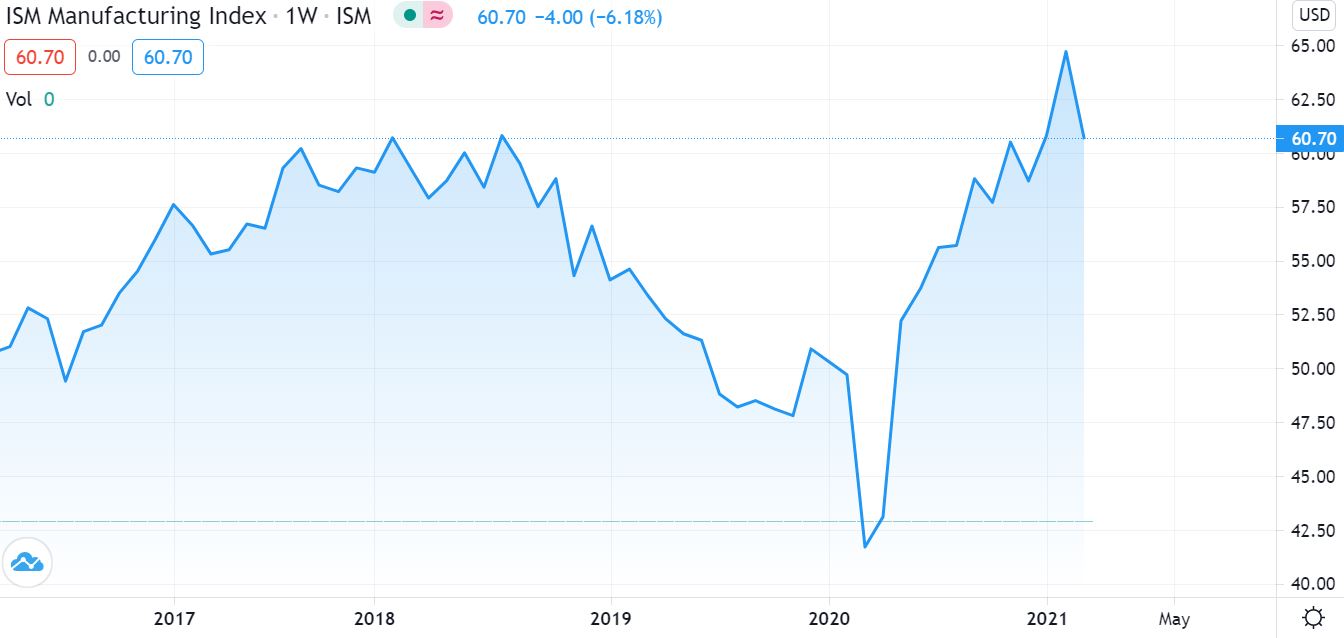
Source: www.tradingview.com
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ Bijal GANDHI Economic Indicators
▶ Bijal GANDHI Leading and Lagging Indicators
▶ Bijal GANDHI GDP
▶ Bijal GANDHI Interest Rates
▶ Bijal GANDHI Inflation Rate
Useful resources
Institute for supply management
About the author
Article written in May 2021 by Bijal GANDHI (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2019-2022).

