Forex exchange markets
In this article, Nakul PANJABI (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2021-2024) explains how the foreign exchange markets work.
Forex Market
Forex trading can be simply defined as exchange of a unit of one currency for a certain unit of another currency. It is the act of buying one currency while simultaneously selling another.
Foreign exchange markets (or Forex) are markets where currencies of different countries are traded. Forex market is a decentralised market in which all trades take place online in an over the counter (OTC) format. By trading volume, the forex market is the largest financial market in the world with a daily turnover of 6.6 trillion dollars in 2019. At present, it is worth 2,409 quadrillion dollars. Major currencies traded are USD, EUR, GBP, JPY, and CHF.
Players
The main players in the market are Central Banks, Commercial banks, Brokers, Traders, Exporters and Importers, Immigrants, Investors and Tourists.
Central banks
Central banks are the most important players in the Forex Markets. They have the monopoly in the supply of currencies and therefore, tremendous influence on the prices. Central Banks’ policies tend to protect aggressive fluctuations in the Forex Markets against the domestic currency.
Commercial banks
The second most important players of the Forex market are the Commercial Banks. By quoting, on a daily basis, the foreign exchange rates for buying and selling they “Make the Market”. They also function as Clearing Houses for the Market.
Brokers
Another important group is that of Brokers. Brokers do not participate in the market but acts as a link between Sellers and Buyers for a commission.
Types of Transactions in Forex Markets
Some of the transactions possible in the Forex Markets are as follows:
Spot transaction
As spot transaction uses the spot rate and the goods (currencies) are exchanges over a two-day period.
Forward transaction
A forward transaction is a future transaction where the currencies are exchanged after 90 days of the deal a fixed exchange rate on a defined date. The exchange rate used is called the Forward rate.
Future transaction
Futures are standardized Forward contracts. They are traded on Exchanges and are settled daily. The parties enter a contract with the exchange rather than with each other.
Swap transaction
The Swap transactions involve a simultaneous Borrowing and Lending of two different currencies between two investors. One investor borrows the currency and lends another currency to the second investor. The obligation to repay the currencies is used as collateral, and the amount is repaid at forward rate.
Option transaction
The Forex Option gives an investor the right, but not the obligation to exchange currencies at an agreed rate and on a pre-defined date.
Peculiarities of Forex Markets
Trading of Forex is not much different from trading of any other asset such as stocks or bonds. However, it might not be as intuitive as trading of stocks or bonds because of its peculiarities. Some peculiarities of the Forex market are as follows:
Going long and short simultaneously
Since the goods traded in the market are currencies themselves, a trade in the Forex market can be considered both long and short position. Buying dollars for euros can be profitable in cases of both dollar appreciation and euro depreciation.
High liquidity and 24-hour market
As mentioned above, the Forex market has the largest daily trading volume. This large volume of trading implies the highly liquid feature of Forex Assets. Moreover, Forex market is open 24 hours 5 days a week for retail traders. This is due to the fact that Forex is exchanged electronically over the world and anyone with an internet connection can exchange currencies in any Forex market of the world. In fact for Central banks and related organisations can trade over the weekends as well. This can cause a change in the price of currencies when the market opens to retail traders again after a gap of 2 days. This risk is known as Gapping risk.
High leverage and high volatility
Extremely high leverage is a common feature of Forex trades. Using high leverage can result in multiple fold returns in favourable conditions. However, because of high trading volume, Forex is very volatile and can go in either upward or downward spiral in a very short time. Since every position in the Forex market is a short and long position, the exposure from one currency to another is very high.
Hedging
Hedging is one of the main reasons for a lot of companies and corporates to enter into a Forex Market. Forex hedging is a strategy to reduce or eliminate risk arising from negative movement in the Exchange rate of a particular currency. If a French wine seller is about to receive 1 million USD for his wine sales then he can enter into a Forex futures contract to receive 900,000 EUR for that 1 million USD. If, at the date of payment, the rate of 1 million USD is 800,000 EUR the French wine seller will still get 900,000 EUR because he hedged his forex risk. However, in doing so, he also gave up any gain on any positive movement in the EUR-USD exchange rate.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ Jayati WALIA Currency overlay
▶ Louis DETALLE What are the different financial products traded in financial markets?
▶ Akshit GUPTA Futures Contract
▶ Akshit GUPTA Forward Contracts
▶ Akshit GUPTA Currency swaps
▶ Luis RAMIREZ Understanding Options and Options Trading Strategies
Useful resources
Academic resources
Solnik B. (1996) International Investments Addison-Wesley.
Business resources
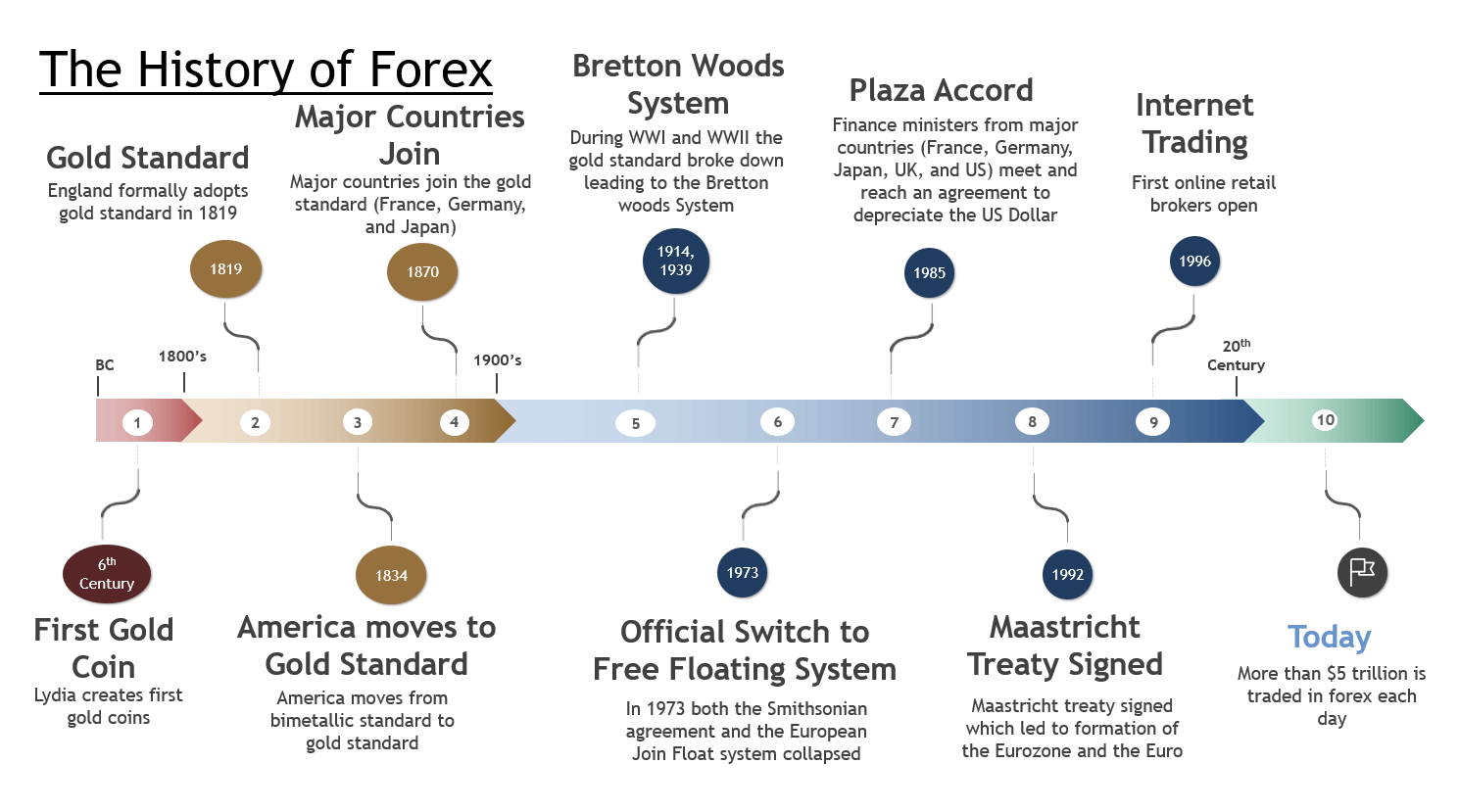
DailyFX / IG The History of Forex
DailyFX / IG Benefits of forex trading
DailyFX / IG Foreign Exchange Market: Nature, Structure, Types of Transactions
About the author
The article was written in December 2022 by Nakul PANJABI (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2021-2024).