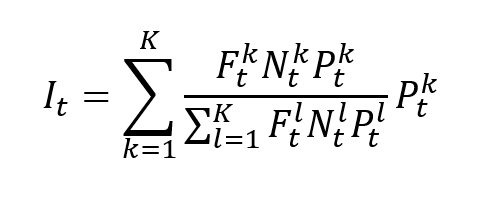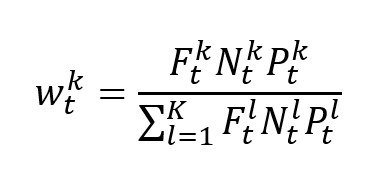Extreme returns and tail modelling of the CSI 300 index for the Chinese equity market
In this article, Shengyu ZHENG (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2020-2024) describes the statistical behavior of extreme returns of the CSI 300 index for the Chinese equity market and explains how extreme value theory can be used to model the tails of its distribution.
The CSI 300 index for the Chinese equity market
The CSI 300 Index, or China Securities Index 300, is a comprehensive stock market benchmark that tracks the performance of the top 300 A-share stocks listed on the Shanghai and Shenzhen stock exchanges. Introduced in 2005, the index is designed to represent a broad and diverse spectrum of China’s leading companies across various sectors, including finance, technology, consumer goods, and manufacturing. The CSI 300 is a crucial indicator of the overall health and direction of the Chinese stock market, reflecting the dynamic growth and evolution of China’s economy.
The CSI 300 employs a free-float market capitalization-weighted methodology. This means that the index’s composition and movements are influenced by the market value of the freely tradable shares, providing a more accurate representation of the companies’ actual impact on the market. As China continues to play a significant role in the global economy, the CSI 300 has become a key reference point for investors seeking exposure to the Chinese market and monitoring economic trends in the dynamic economy. With its emphasis on the country’s most influential and traded stocks, the CSI 300 serves as an essential tool for both domestic and international investors navigating the complexities of the Chinese financial landscape.
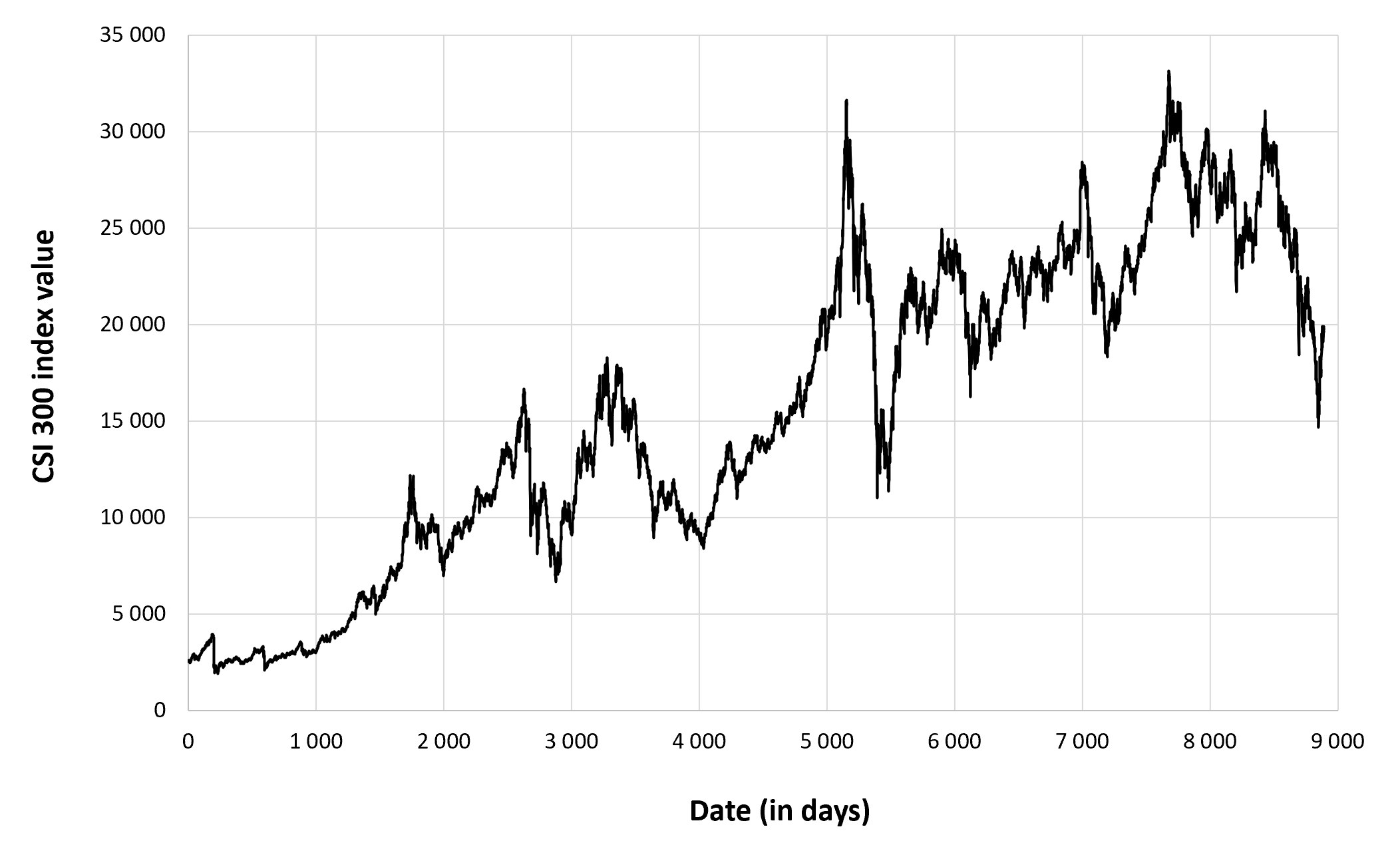
In this article, we focus on the CSI 300 index of the timeframe from March 11th, 2021, to April 1st, 2023. Here we have a line chart depicting the evolution of the index level of this period.
Figure 1 below gives the evolution of the CSI 300 index from March 11th, 2021, to April 1st, 2023 on a daily basis.
Figure 1. Evolution of the CSI 300 index.
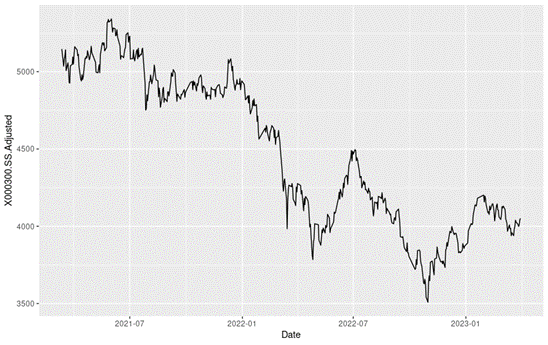
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
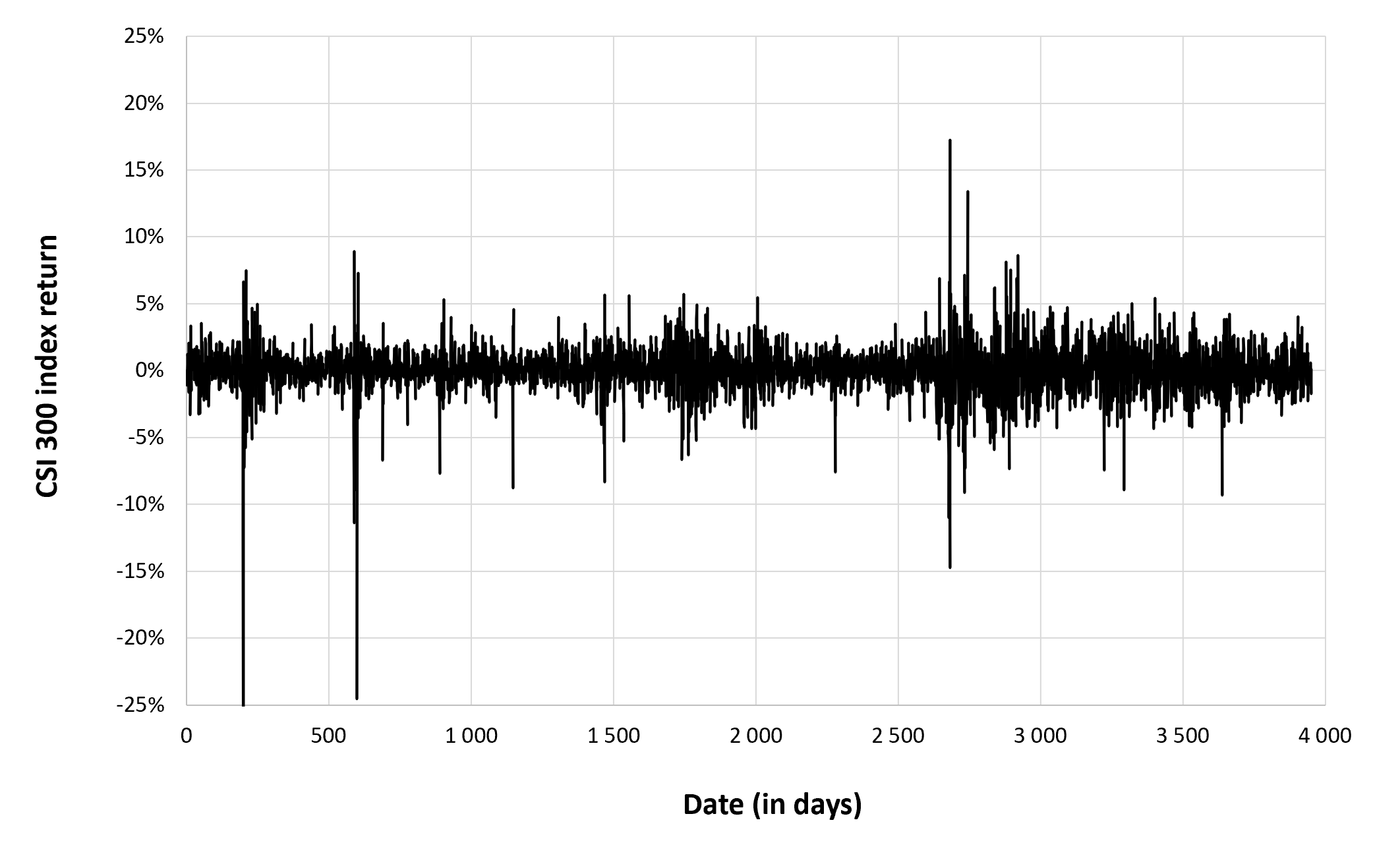
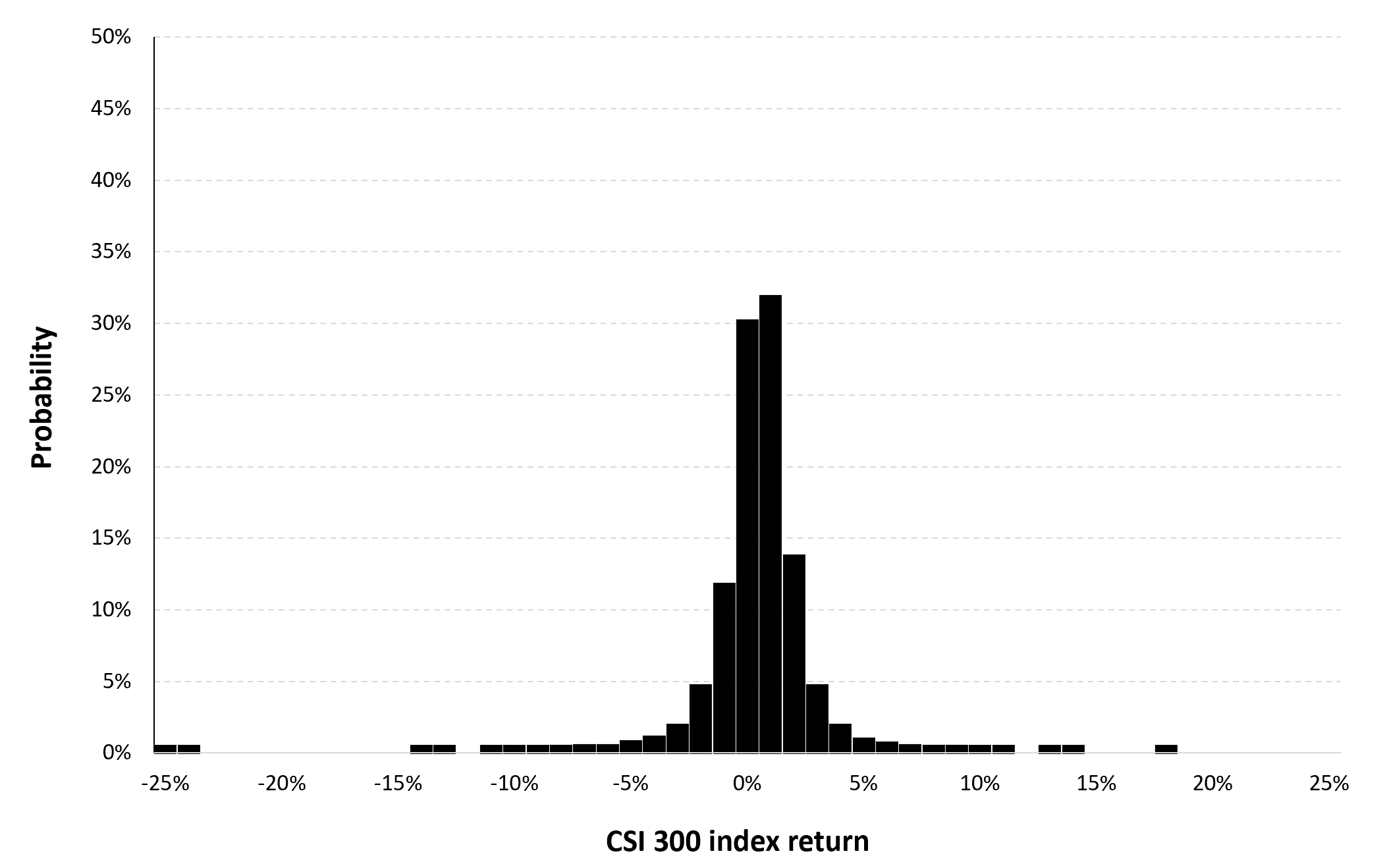
Figure 2 below gives the evolution of the logarithmic returns of CSI 300 index from March 11th, 2021, to April 1st, 2023 on a daily basis. We observe concentration of volatility reflecting large price fluctuations in both directions (up and down movements). This alternation of periods of low and high volatility is well modeled by ARCH models.
Figure 2. Evolution of the CSI 300 index logarithmic returns.
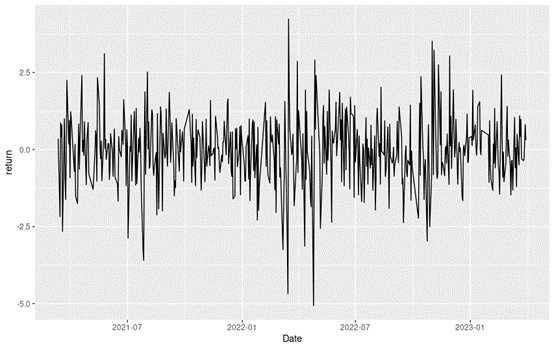
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
Summary statistics for the CSI 300 index
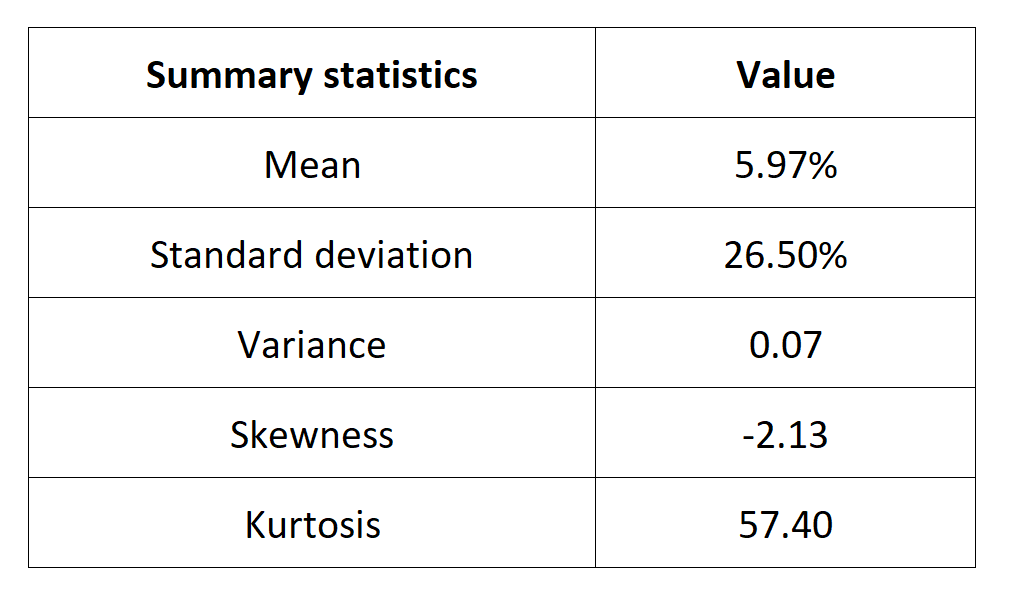
Table 1 below presents the summary statistics estimated for the CSI 300 index:
Table 1. Summary statistics for the CSI 300 index.
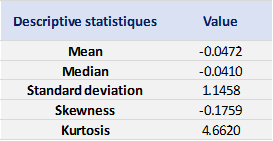
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
The mean, the standard deviation / variance, the skewness, and the kurtosis refer to the first, second, third and fourth moments of statistical distribution of returns respectively. We can conclude that during this timeframe, the CSI 300 index takes on a downward trend, with relatively important daily deviation, negative skewness and excess of kurtosis.
Tables 2 and 3 below present the top 10 negative daily returns and top 10 positive daily returns for the index over the period from March 11th, 2021, to April 1st, 2023.
Table 2. Top 10 negative daily returns for the CSI 300 index.
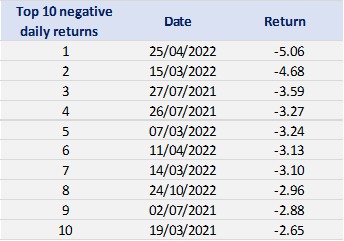
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
Table 3. Top 10 positive daily returns for the CSI 300 index.
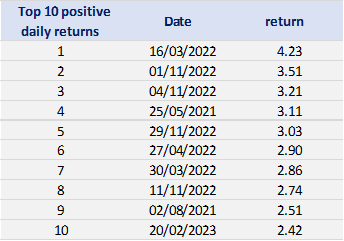
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
Modelling of the tails
Here the tail modelling is conducted based on the Peak-over-Threshold (POT) approach which corresponds to a Generalized Pareto Distribution (GPD). Let us recall the theoretical background of this approach.
The POT approach takes into account all data entries above a designated high threshold u. The threshold exceedances could be fitted into a generalized Pareto distribution:
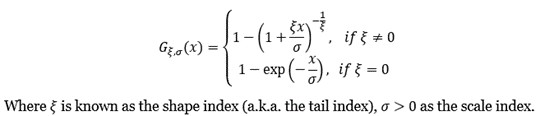
An important issue for the POT-GPD approach is the threshold selection. An optimal threshold level can be derived by calibrating the tradeoff between bias and inefficiency. There exist several approaches to address this problematic, including a Monte Carlo simulation method inspired by the work of Jansen and de Vries (1991). In this article, to fit the GPD, we use the 2.5% quantile for the modelling of the negative tail and the 97.5% quantile for that of the positive tail.
Based on the POT-GPD approach with a fixed threshold selection, we arrive at the following modelling results for the GPD for negative extreme returns (Table 4) and positive extreme returns (Table 5) for the CSI 300 index:
Table 4. Estimate of the parameters of the GPD for negative daily returns for the CSI 300 index.
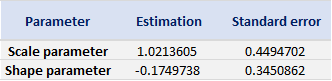
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
Table 5. Estimate of the parameters of the GPD for positive daily returns for the CSI 300 index.
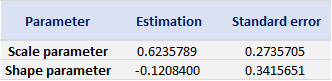
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
Figure 3 represents the historical distribution of negative return exceedances and the estimated GPD for the left tail.
Figure 3. GPD for the left tail of the CSI 300 index returns.
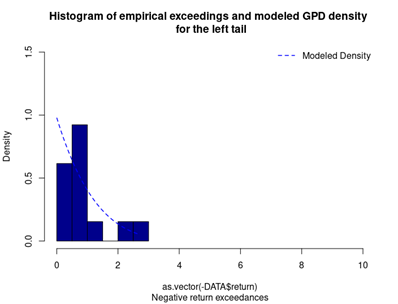
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
Figures 4 represents the historical distribution of positive return exceedances and the estimated GPD for the right tail.
Figure 4. GPD for the right tail of the CSI 300 index returns.
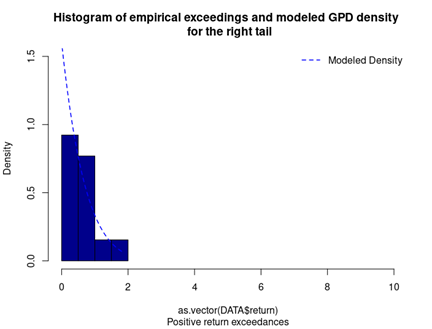
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
Applications in risk management
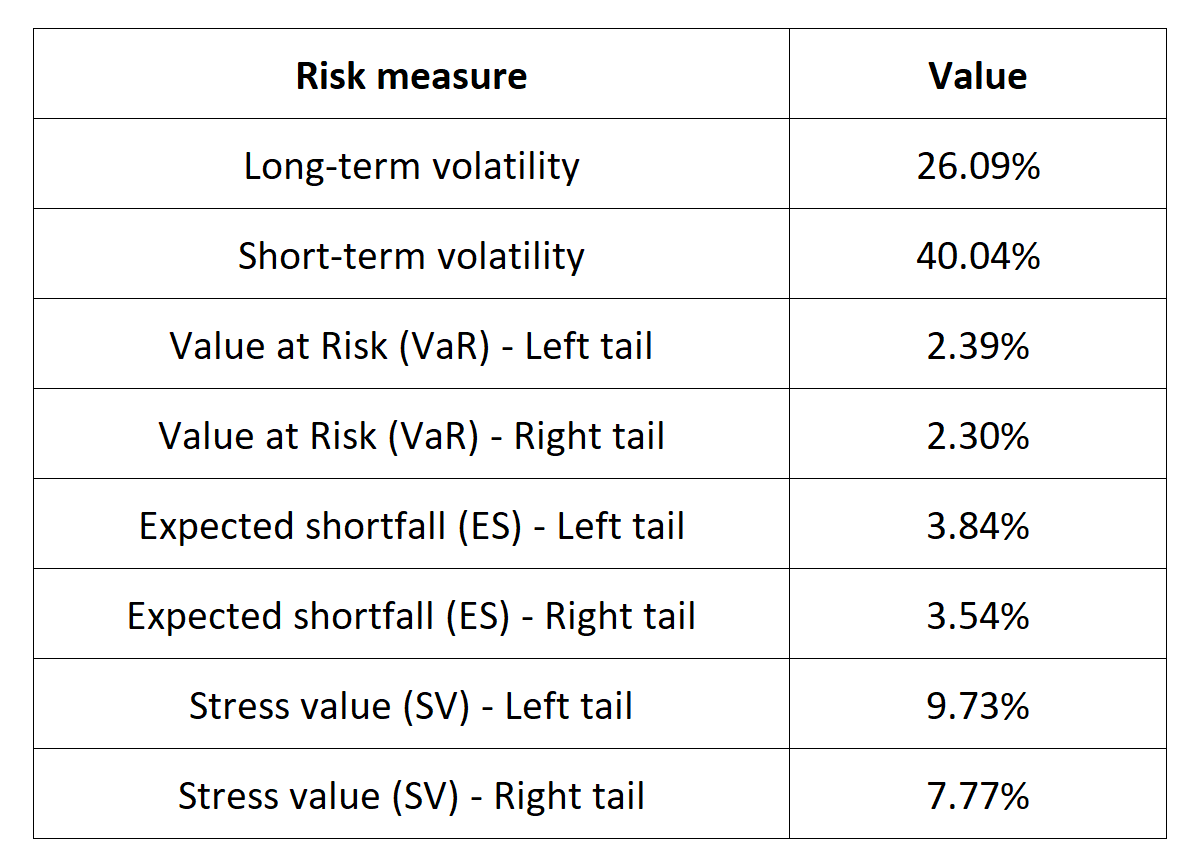
Extreme Value Theory (EVT) as a statistical approach is used to analyze the tails of a distribution, focusing on extreme events or rare occurrences. EVT can be applied to various risk management techniques, including Value at Risk (VaR), Expected Shortfall (ES), and stress testing, to provide a more comprehensive understanding of extreme risks in financial markets.
Why should I be interested in this post?
Extreme Value Theory is a useful tool to model the tails of the evolution of a financial instrument. In the ever-evolving landscape of financial markets, being able to grasp the concept of EVT presents a unique edge to students who aspire to become an investment or risk manager. It not only provides a deeper insight into the dynamics of equity markets but also equips them with a practical skill set essential for risk analysis. By exploring how EVT refines risk measures like Value at Risk (VaR) and Expected Shortfall (ES) and its role in stress testing, students gain a valuable perspective on how financial institutions navigate during extreme events. In a world where financial crises and market volatility are recurrent, this post opens the door to a powerful analytical framework that contributes to informed decisions and financial stability.
Download R file to model extreme behavior of the index
You can find below an R file (file with txt format) to study extreme returns and model the distribution tails for the CSI 300 index.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
About financial indexes
▶ Nithisha CHALLA Financial indexes
▶ Nithisha CHALLA Calculation of financial indexes
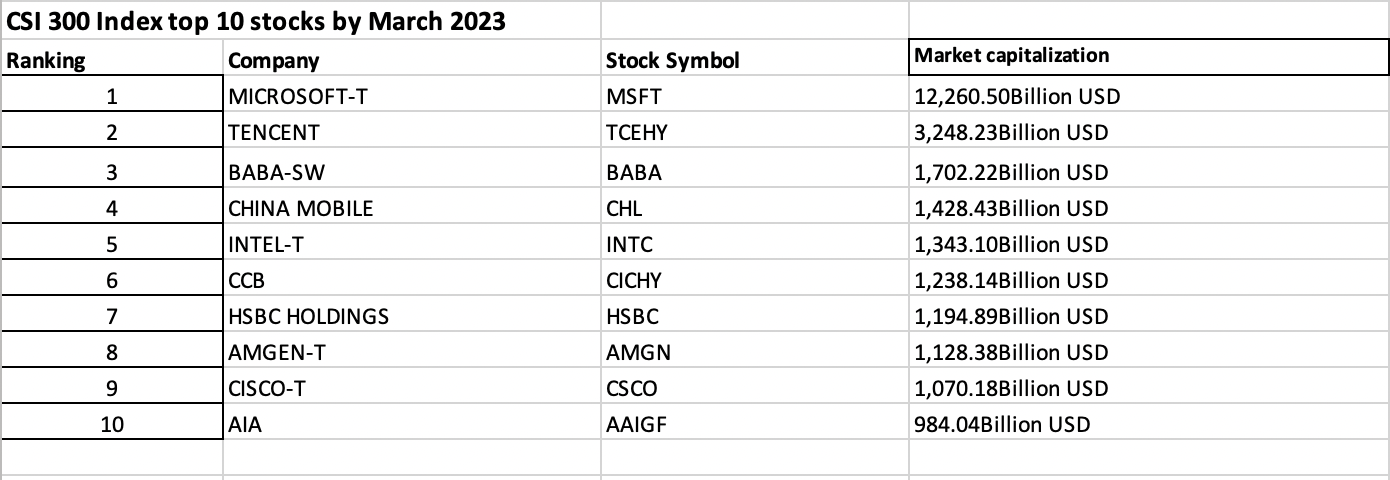
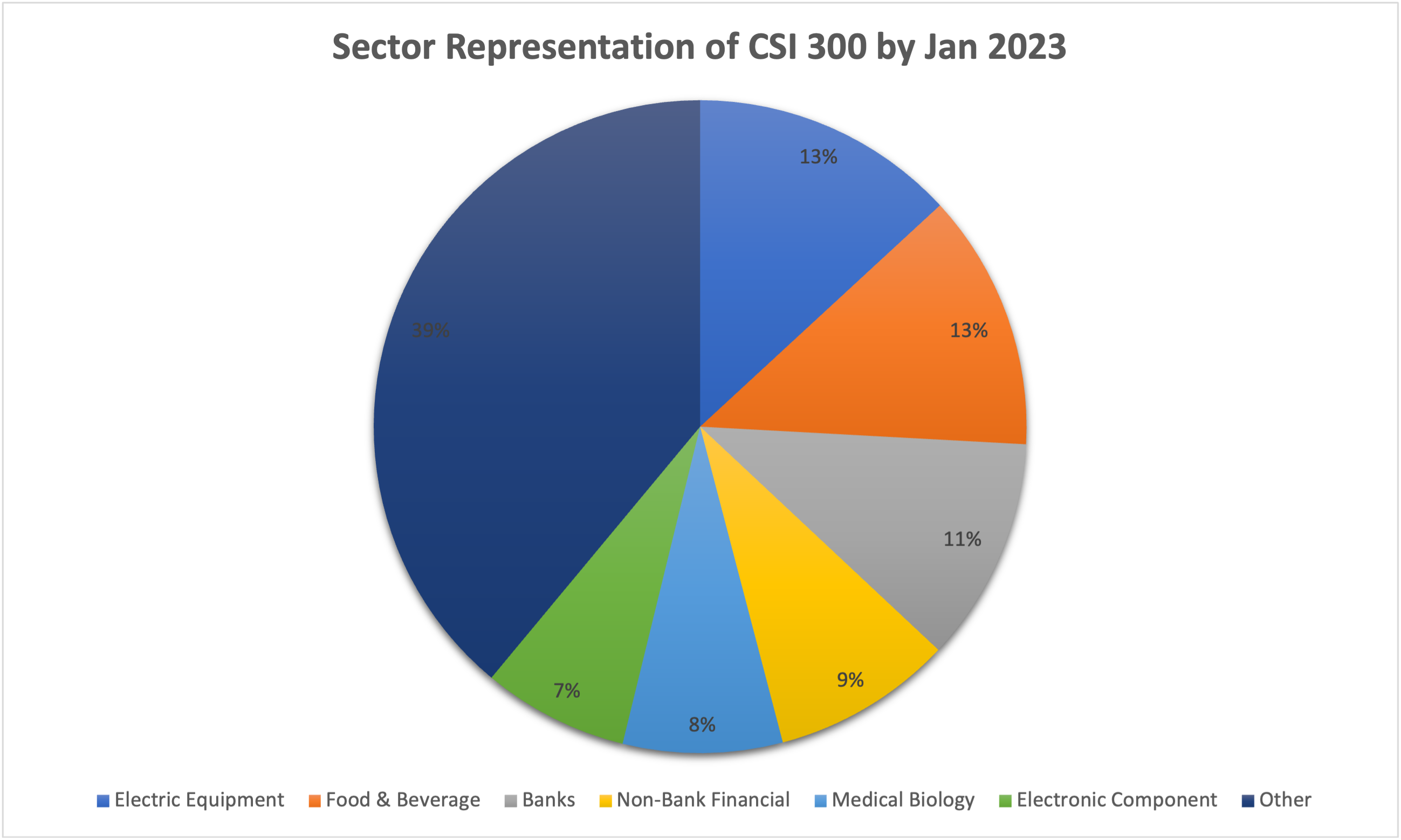
▶ Nithisha CHALLA The CSI 300 index
About portfolio management
▶ Youssef LOURAOUI Portfolio
▶ Jayati WALIA Returns
About statistics
▶ Shengyu ZHENG Moments de la distribution
▶ Shengyu ZHENG Mesures de risques
▶ Shengyu ZHENG Extreme Value Theory: the Block-Maxima approach and the Peak-Over-Threshold approach
▶ Gabriel FILJA Application de la théorie des valeurs extrêmes en finance de marchés
Useful resources
Academic resources
Embrechts P., C. Klüppelberg and T. Mikosch (1997) Modelling Extremal Events for Insurance and Finance Springer-Verlag.
Embrechts P., R. Frey, McNeil A.J. (2022) Quantitative Risk Management Princeton University Press.
Gumbel, E. J. (1958) Statistics of extremes New York: Columbia University Press.
Longin F. (2016) Extreme events in finance: a handbook of extreme value theory and its applications Wiley Editions.
Other resources
Chan S. Statistical tools for extreme value analysis
Rieder H. E. (2014) Extreme Value Theory: A primer (slides).
About the author
The article was written in November 2023 by Shengyu ZHENG (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2020-2024).