In this article, William LONGIN (EDHEC Business School, Global BBA, 2020-2024) shares his experience as a leisure tourism management assistant at Atout France USA, which is the French Tourism Development Agency in the United States of America.
Atout France
Atout France is the official French National Tourism Development Agency. It is a government agency responsible for promoting France as a tourism destination to visitors and tourism professionals (tour operators and travel agents) from around the world.
Logo of the Atout France.
Source: Atout France.
Atout France was created in 2009 through the merger of three existing organizations that focused on tourism promotion: Maison de la France, ODIT France, and France Tourism Development Agency. The name Atout France comes from “Atout” meaning asset and “France” the nation that it services. The agency’s main mission is to develop and implement strategies for promoting France as a tourism destination by working with French companies and tourism professionals from around the world. We will explore the strategies used by Atout France in more depth in this article.
Atout France objectives are set by the French government and reflect the needs of French businesses in the tourism sector. To attain the objectives set by the government, Atout France organizes and attends multiple business-to-business (B2B) events to create visibility and encourages French networking. Another key objective set by the French government is promoting the new offers for sustainable tourism called eco-tourism, still overlooked by many international travelers. For example, Atout France in the United States launched an e-learning platform covering eco-tourism in France.
I interned in the branch of Atout France located in New York, as a “leisure tourism manager assistant”. As a foreign worker in the United States, I was granted a diplomatic A2 Visa for my internship. Kind of cool! My experience in New York was really valuable in addition to the experience I had in the company as I was able to make many friends and discover the city through a new lens (a worker and not a tourist). Indeed New York is home to many international institutions such as the United Nations, many consulates, and schools such as New York University (NYU) and Columbia University. New York, also called the Melting Pot, has a developed French community and culture particularly in the areas of art, cuisine, and fashion. The numerous French restaurant venues in the city allows Atout France to showcase French cuisine when organizing events. We could almost call French restaurants the culinary consulates of France in New York!
My personal experience at Atout France
My experience at Atout France USA was very valuable as I learned about company culture, the tourism industry and about the various software used by the company.
My experience of the company culture and workplace at Atout France USA is very positive. As an intern I have been well received and helped in the beginning of my internship. However, I realized very early on that in order to be useful it was important to be proactive. I cannot emphasize enough on the word ‘proactive’ because it is central to understanding how to be a useful coworker in the trade and events department of the company. I learned that it is important to ask questions about tasks, especially that you could be unfamiliar with as an intern. For example, when building the slide show for an internal proposition I made, I went in a freestyle but learned afterwards that there was a corporate template that was essential to respect in order to keep things more organized.
The tourism industry was a completely new industry for me as I have never interned or leaned towards a career in this sector before. What attracted me the most for this internship was to learn more about the industry, have the opportunity to work in New York and serve the nation of France. Throughout my internship I learned about jobs and vocabulary that I was unfamiliar with before such as what travel writers do, what is MICE (which is an acronym for business tourism), or what is eco-tourism. My time in the industry allowed me also to learn about the importance of networking events for professionals and their ways of communicating. Overall, my experience at Atout France encouraged me to learn more about the different forms of tourism and how professionals operate.
The large number of valuable contacts (from the United States and from France) that Atout France possesses is a key asset that adds value for the local and French companies interested in developing businesses. In order to organize its contacts, Atout France uses a Customer Relation Management tool (CRM) called HubSpot. HubSpot is a cloud-based software platform that provides marketing, sales, and customer service tools for businesses. In the case of Atout France, the main purpose is to store data about its contacts. Data about area, domain of expertise and level of engagement with the company are useful for selectively picking the most adequate contacts when organizing events. For example, amongst the tour operator companies of the network, only a segment of them is already selling French packaged trips. This segment of tour operators is interesting for French companies because they already have an interest in the country and are more likely to create more deals or tailor new offers. Throughout my internship I was taught to get accustomed with the use of the software for searching information, creating spreadsheets for business analytics and creating invite lists for events.
Core missions and duties
Event planning
Part of my responsibilities as an intern at Atout France USA were to contribute to organizing events by finding venues, inviting business representatives and communicating with our clients to best build the event according to their needs. Atout France USA organizes events for its local partners and French institutions to increase their visibility on the American market and meet travel professionals that could be interested in doing business with them. Generally, the size of events ranges from dinners with 10 guests to larger events going over 100 guests. As an intern it was my duty to look for appropriate venues matching the style, theme, and logistical capability of the venue according to the needs of the client.
Market research
As part of my duties as an intern I was asked to perform market research for various missions notably to contribute to the updating of the market presentation of the United States created and regularly updated by Atout France. Atout France puts an emphasis on design and credibility of sources when gathering data. Performing such research is very enriching as it allows you to have a better understanding of the industry and analyze the industry better.
Must do tasks – Mindset
When preparing an event, there were many manual tasks that needed to be done. For example, it was imperative to set up the event space with a well-thought decor, and other necessary equipment. When preparing for the event it also involved managing vendors by making sure they delivered food, beverages, audio-visual equipment, or other services. During events interns were often asked to handle registration and troubleshooting during the event by handling any issues that arise, such as technical difficulties or unexpected changes to the schedule.
Required skills and knowledge
To perform well as an intern at Atout France in New York, there are several prerequisites that you should consider such as strong communication skills. Interns are asked to communicate with different stakeholders, including industry professionals, tourists, and colleagues. Therefore, having the ability to clearly communicate and proactively ask questions is a must. Knowledge of the French language is an excellent plus for talking to partners. It can ease communication and make it easier for both French and American partners. Familiarity with the events and tourism industry is largely valued by Atout France as it is a good indicator for adaptability. Atout France has a dynamic workplace, and as an intern, you may have to manage multiple tasks simultaneously so having good time management and a sense of organization can come in very handy.
Learned skills and knowledge
During my internship I have improved and worked on my hard skills and soft skills. Hard skills such as my knowledge of the industry, learned how to use HubSpot, perform market research in the tourism industry. Soft skills such as flexibility during events, bilingual communication and team empathy skills.
Key concepts
Cultural awareness
Cultural awareness is the ability to recognize and appreciate different cultures, values, and beliefs. It involves understanding and respecting differences between cultures and being able to navigate and communicate effectively with people from different backgrounds. Cultural awareness also involves recognizing one’s own biases and assumptions and being open to learning from and about different cultures. Cultural awareness involves developing attitudes of respect, openness, and curiosity toward other cultures, which can help to build stronger relationships and promote mutual understanding. When performing missions it is important to take into account the image that Americans have of France.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tool is a tool that organizations use to manage and analyze their interactions with customers and improve customer relationships. CRM involves collecting and analyzing customer data from various sources, including sales, marketing, and customer service, to gain insights into customer behavior, preferences, and needs. The CRM was a very useful tool for analyzing email opening rates, network contracting and marketing data.
Ecotourism
Ecotourism is a type of tourism that focuses on responsible travel to natural areas that conserve the environment and improve the welfare of local communities. Ecotourism examples are visiting and experiencing natural areas, such as national parks, wildlife reserves, and cultural sites, while minimizing the negative impact on the environment and supporting local communities. Ecotourism is also characterized by responsible travel practices, such as reducing waste, etc.
Ecotourism is of growing interest to France in its pioneering mission of the eco touristic industry and carbon neutral objectives for 2030. At the same time ecotourism can provide economic benefits to the local community by promoting conservation efforts by providing financial incentives for protecting natural resources and wildlife.
MICE
MICE is an acronym that stands for Meetings, Incentives, Conferences, and Exhibitions. It refers to a type of tourism that involves the organization and hosting of business events, such as conferences, seminars, trade shows, exhibitions, and meetings. MICE tourism is a growing industry that often involves large groups of people traveling to a specific destination for a specific purpose, such as attending a conference or meeting.
MICE tourism is of interest to Atout France as it provides significant economic benefits such as revenue for French hotels, restaurants, transportation providers, and other businesses.
Travel Agent VS Tour Operator
A travel agent is an intermediary that personally helps clients plan and book their travel arrangements. On the other hand, a tour operator specializes in organizing and selling complete travel packages, which may include transportation, accommodations, meals, and activities. Both professions are both of interest to Atout France as a majority of Americans use their services to plan their travel to Europe.
B2B and B2C
B2B and B2C are abbreviations for “Business to Business” and “Business to Consumer” respectively. Indeed, different companies rely on different business models. Relations and commerce with different customers change the way companies do business. At Atout France, the company’s services are for companies, so it operates on a B2B model when organizing events. However, Atout France also interacts with the public through marketing campaigns. Whether that interaction is a B2C is arguable because the “product” sold by Atout France is the whole nation of France and the operation is made in the nation’s interest rather than in the businesses’ interest as the income gained from such an operation is not directly earned from the consumer.
Why should you be interested in this post?
My article about my experience as an intern for Atout France in New York should be of great interest to people who are interested in the travel and tourism industry, as well as those who are considering pursuing an internship or career in this field. The article provides valuable insights into what it’s like to work for a destination marketing organization and gives a behind-the-scenes look at the operations of Atout France in New York. Readers can learn about the different departments and functions within a tourism development agency, as well as the challenges and opportunities that come with working in this field. Readers can also learn about the vocabulary, skills and qualities that are important to excel in this industry.
Word of conclusion
In conclusion, my experience as an intern at Atout France in New York was an incredibly valuable opportunity for me. I had the chance to work with a talented and dedicated team, passionate about promoting France as a premier travel destination.
During my internship, I gained valuable insights into the operations of the government in the tourism area abroad and learned about the different strategies and tactics used to promote tourism. I had the chance to work on a variety of projects, from developing marketing materials to conducting research and analysis on industry trends.
Throughout my internship, I was impressed by the level of professionalism and expertise demonstrated by the Atout France team. I also had the chance to network with industry professionals and attend industry events, which provided me with valuable connections and insights into the travel industry.
Overall, my internship at Atout France in New York was an incredible learning experience and a valuable steppingstone in my career. It has provided me with a strong foundation in destination marketing and tourism. I would highly recommend an internship with Atout France to anyone who is passionate about travel and tourism and looking to gain valuable insights and experiences in this industry.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ All posts about Professional experiences
▶ Nithisha CHALLA My experience as a Risk Advisory Analyst in Deloitte
▶ Alexandre VERLET My experience as an investment banking analyst intern at G2 Capital Advisors
Useful resources
Atout France Organization website
Atout France USA LinkedIn group
HubSpot Firm website
About the author
Article written in March 2023 by William LONGIN (EDHEC Business School, Global BBA, 2020-2024).
▶ Read all articles by William LONGIN.











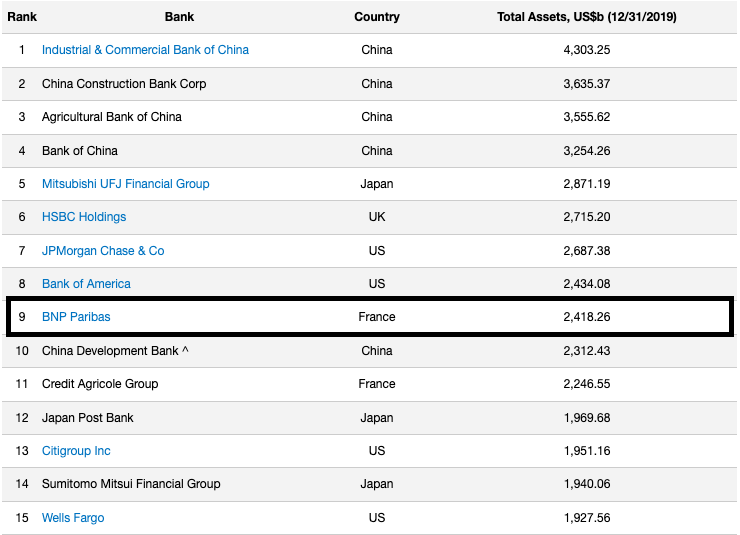

















 Source: www.advratings.com
Source: www.advratings.com Source: Amundi
Source: Amundi