Wirecard: At the heart of the biggest German financial scandal of the 21st century
In this article, Louis DETALLE (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2020-2023) explains what happened with Wirecard, the German company that caused a major scandal in the German financial place.
Quick review of the Wirecard company
The Wirecard case takes its name from a German start-up specializing in online payment solutions. Listed on the Frankfurt stock exchange in 2018, this company has experienced a meteoric growth with more than 300,000 corporate customers at its peak in June 2020.

However, as early as 2015, doubts were raised about the effectiveness of the Wirecard model and suspicions of irregularities arose. It was not until June 2020 that the management admitted that €1.9 billion of its consolidated balance sheet did not exist.
Several actors bore the brunt of the scandal
The consequences of this announcement were terrible for several actors:
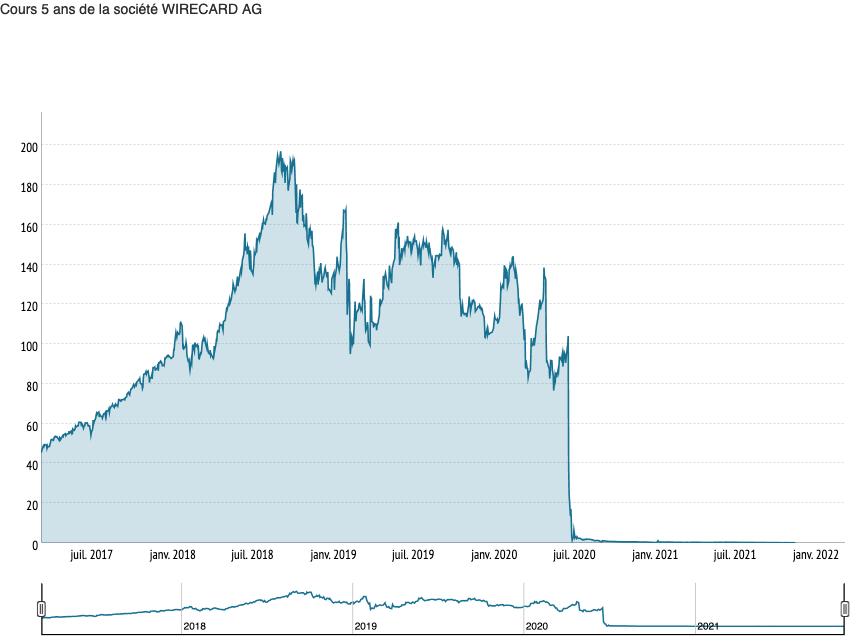
Firstly, for the company, whose share price lost 90% of its value in a few days (see chart below). Rating agencies such as Moody’s are removing Wirecard’s rating due to the falsification of the information on which the rating was based. At management level, the former CEO of Wirecard, Markus Braun, resigned and was arrested by the German justice system. He ended up in prison along with two other executives of the German company. Jan Marsalek, another Wirecard executive, has been wanted since June 2020 by Interpol to be brought before the Munich court.
Evolution of Wirecard’s stock’s value.
For EY, Wirecard’s auditor, this case is reverberating through the financial ecosystem. Indeed, the auditor EY is also in great difficulty since the teams of the big firm of the Big 4 have been certifying the accounts of the company for several years and missed important frauds. The Financial Times, for example, accused the firm of failing to check for accounting irregularities in the balance sheet, which should have been done. There are numerous legal actions against the auditor for malpractice, such as the complaint by the German law firm Schirp & Partner. The German authorities have also launched a preliminary investigation against EY, whose head of the German branch has announced his resignation following the scandal.
Finally, the Federal Financial Supervisory Authority, the regulatory and supervisory body for the financial sector in Germany, is also affected by the affair. The German Minister of Finance therefore announced a plan to reform the BaFin, which also saw its director step down.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Wirecard affair is considered to be one of the most important scandals of the 21st century as it has called into question the structures and statutes of a company, a Big 4 firm as well as German regulatory bodies.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ Louis DETALLE The 3 biggest corporate frauds of the 21st century
▶ Louis DETALLE Quick review on the most famous trading frauds ever…
▶ Louis DETALLE Quick review of the most famous investments frauds ever…
Useful resources
La Tribune (21/04/2021) Scandale Wirecard : Merkel et son ministre des Finances contraints de se justifier (in French).
About the author
The article was written in March 2022 by Louis DETALLE (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2020-2023).


 Logo of Parlamat
Logo of Parlamat