In this article, Tianyi WANG (ESSEC Business School, Global Bachelor in Business Administration (GBBA), 2022-2026) shares her professional experience as an Analyst Assistant at China Bond Rating in Beijing.
About the company
China Bond Rating Co., Ltd. (CBR), established in 2010 with a registered capital of RMB 50 million, has grown into one of the core credit rating institutions in China’s fixed-income market. The company employs around 280 professionals and operates under an “investors-pay” model designed to enhance its independence and objectivity. Over the years, it has built a comprehensive analytical framework covering macroeconomic research, sectoral risk evaluation, credit modelling, structured finance, and green finance.
Logo of China Bond Rating .

Source: the company.
CBR provides a wide range of services including issuer credit ratings, bond and ABS credit assessments, credit-risk-based valuation models, market pricing services, and risk monitoring tools. Its clients span local governments, state-owned enterprises, financial institutions, corporates across industries, and institutional investors in the interbank bond market. According to regulatory disclosures, the company issued over 1,180 new credit ratings in a recent year, covering more than RMB 34 trillion in bond issuance. These credit opinions are widely used for investment decisions, regulatory compliance, and bond pricing, making the firm a key contributor to transparency and information efficiency in China’s fixed-income ecosystem.
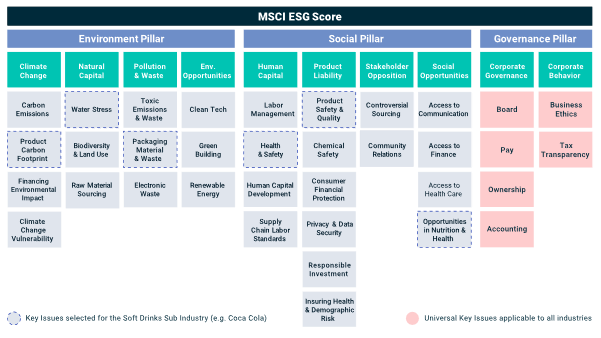
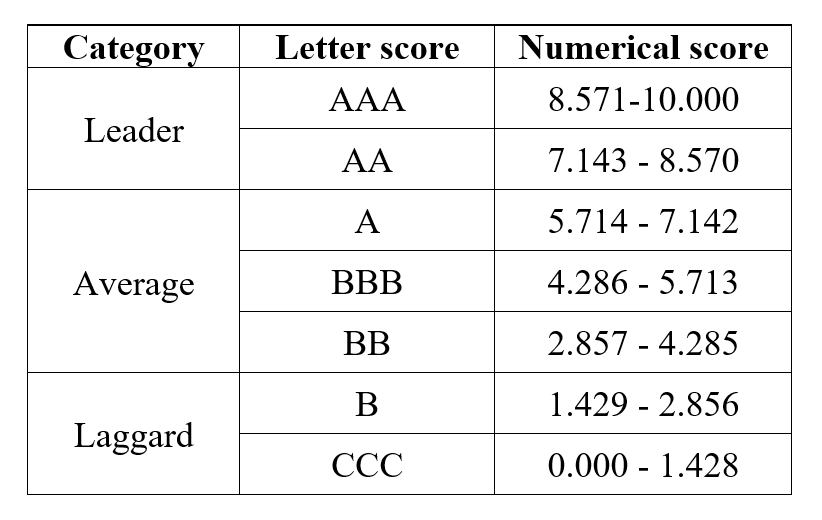
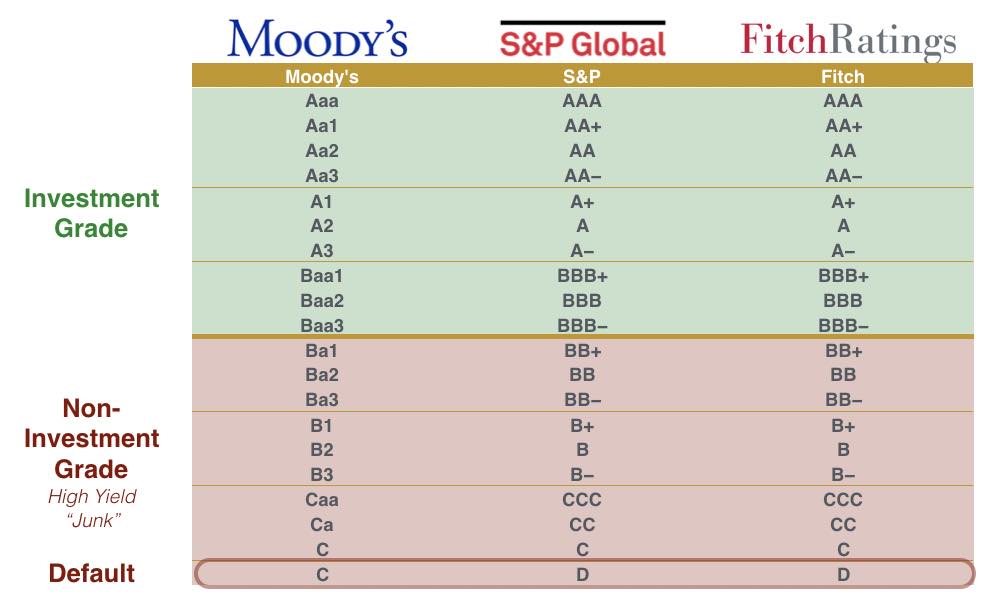
As part of its methodology, China Bond Rating uses a structured rating grid similar to international rating agencies, ranging from high-grade ratings (AAA, AA, A) to speculative-grade categories (BBB, BB, B, etc.). Credit ratings help investors assess default risk, determine appropriate yield spreads, and monitor changes in an issuer’s financial strength over time.
Grid of China Bond Rating.
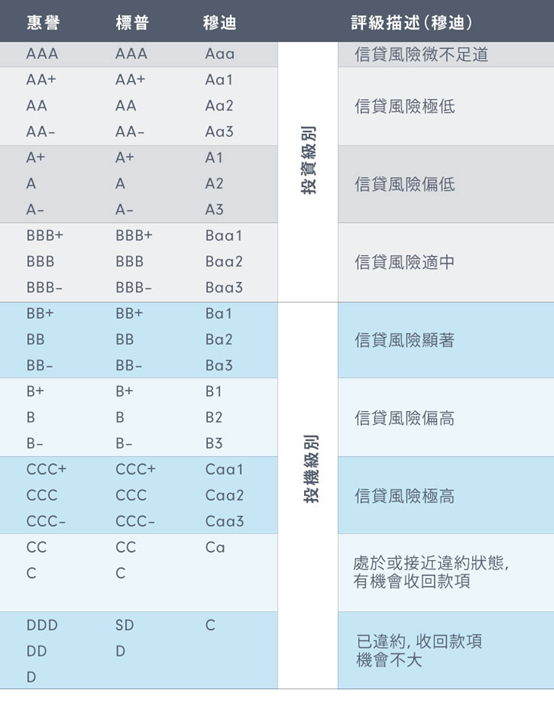
Source: the company.
My internship
From August to November 2023, I worked as an Analyst Assistant at the Investment Service Department. The experience allowed me to gain deep exposure to China’s local government financing system and understand how professional credit evaluations are produced from both data and policy perspectives.
My missions
My primary mission was to support the team in building and maintaining credit evaluation databases for local governments and urban investment enterprises. I conducted detailed research on more than 130 companies across the Sichuan and Chongqing regions, analyzing their business structures, investment pipelines, guarantee arrangements, and key financial items. I helped calculate funding gaps and conducted preliminary assessments of repayment risk.
I also created and updated database templates using Excel, SQL, and internal analytical tools to maintain credit evaluation data for local governments, urban investment enterprises, and bond issuance activities. This included compiling statistics on local government bonds and special refinancing bond issuances.
Another major part of my mission was to verify and cross-check corporate operational and financial data to support fundamental research. I helped review over 60 debt financing reports and credit analysis documents, ensuring accuracy and consistency across key metrics. Through this work, I learned how rating agencies ensure data reliability before forming credit opinions.
Required skills and knowledge
This internship required strong analytical thinking, attention to detail, and the ability to manage large volumes of financial data. Hard skills such as Excel modeling, SQL queries, statistical analysis, and familiarity with financial statements were essential. Equally important were soft skills such as communication, logical reasoning, and the ability to organize information from inconsistent disclosures.
Given the diversity of local government financing practices across regions, I needed to quickly understand differences in fiscal structures, reporting standards, and project pipelines. The role required not only technical ability but also a policy-oriented mindset to interpret the implications of debt levels, off-balance-sheet risks, and industry trends.
What I learned
Through the database reconstruction and indicator standardization work, I gained a systematic understanding of credit risk assessment and the financial mechanisms behind China’s local government financing vehicles (LGFVs). I developed the ability to assess repayment capacity based on funding gaps, cash flow projections, and guarantee relationships.
My contribution helped improve the efficiency of data extraction and cross-validation, significantly reducing the time required for report preparation. During the internship, I also discovered several enterprises exhibiting liquidity pressure and implicit debt risks. These findings supported the final credit rating conclusions.
Overall, this internship strengthened my skills in data management, logical analysis, and risk identification. It also deepened my understanding of how rating agencies support bond market stability through standardized evaluation and high-quality information disclosure.
Financial concepts related to my internship
I present below three financial concepts related to my internship: credit risk assessment, local government implicit debt, and refinancing pressure.
Credit risk assessment
Credit risk assessment is the foundation of the bond market. My work involved analyzing financial ratios, debt structures, liquidity indicators, and funding gaps to determine whether an issuer has adequate repayment capacity. These assessments directly influence credit rating outcomes and bond pricing.
Local government implicit debt
Urban investment companies often carry implicit debt obligations on behalf of local governments. Understanding the link between fiscal revenues, government guarantees, and off-balance-sheet debt was crucial to evaluating the financial sustainability of LGFVs.
Refinancing and liquidity pressure
Many LGFV issuers face refinancing pressure as their short-term borrowings accumulate. By tracking debt maturities and analyzing cash flow projections, I learned how rating agencies evaluate the risk of default and identify early signals of liquidity stress.
Why should I be interested in this post?
This post is relevant for students interested in fixed-income research, credit analysis, bond markets, or public finance in China. Working in a rating agency provides exposure to the fundamentals behind bond pricing, the interaction between public policy and financial markets, and the analytical rigor required to evaluate complex debt structures.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
Professional experiences
▶ All posts about Professional experiences
▶ Snehasish CHINARA My Apprenticeship Experience as Customer Finance & Credit Risk Analyst at Airbus
▶ Samia DARMELLAH My Experience as a Credit Risk Portfolio Analyst at Société Générale Private Banking
▶ Matthieu MENAGER My professional experience as a credit analyst at Targobank
▶ Aamey MEHTA My experience as a credit analyst at Wells Fargo
▶ Jayati WALIA My experience as a credit analyst at Amundi Asset Management
Financial techniques
▶ Jayati WALIA Credit risk
▶ Raphaël ROERO DE CORTANZE Credit Rating Agencies
▶ Bijal GANDHI Credit Rating
▶ Dawn DENG Assessing a Company’s Creditworthiness: Understanding the 5C Framework and Its Practical Applications
Useful resources
China Central Depository & Clearing Co., Ltd.
About the author
The article was written in November 2025 by Tianyi WANG (ESSEC Business School, Global Bachelor in Business Administration (GBBA), 2022-2026).