
In this article, Snehasish CHINARA (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2022-2024) explains the innovative world of Tron cryptocurrency, shedding light on its role in the evolution of decentralized applications and the broader blockchain ecosystem.
Historical context and background
Tron (TRX) was founded by Justin Sun in 2017, aiming to revolutionize the entertainment industry and decentralize the internet. The project’s initial coin offering (ICO) raised approximately $70 million, showcasing significant investor interest. Tron was designed as a decentralized platform to support smart contracts and high-throughput applications, providing an infrastructure that could handle a large volume of transactions efficiently.
Initially, Tron was launched as an ERC-20 token on the Ethereum blockchain. This allowed Tron to leverage Ethereum’s robust development community and infrastructure while developing its own blockchain. On June 25, 2018, Tron completed its mainnet launch, migrating from the Ethereum network to its proprietary blockchain, known as Odyssey. This transition marked Tron’s independence and its capability to support decentralized applications (dApps) natively.
The Tron ecosystem has expanded rapidly, integrating various blockchain-based projects and applications. In July 2018, Tron acquired BitTorrent, a popular peer-to-peer file-sharing protocol, further expanding its reach and application base. This acquisition was significant as it integrated BitTorrent’s extensive user base with Tron’s blockchain technology, exemplifying Tron’s vision of a decentralized internet.
Moreover, Tron’s commitment to fostering a decentralized web extends to its support for decentralized finance (DeFi). By providing a robust platform for creating and deploying decentralized applications, Tron has positioned itself as a key player in the DeFi space, enabling applications such as JustSwap, a decentralized exchange, and various other lending and borrowing platforms.
Tron Logo

Source: Tron.
Figure 1. Key Dates in Tron History

Source: Yahoo! Finance.
Key features
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) Consensus Mechanism
Tron’s blockchain utilizes the DPoS consensus algorithm, which enhances scalability and transaction speed. In this system, TRX holders vote for super representatives (SRs) who are responsible for validating transactions and securing the network. This method is more energy-efficient and faster compared to traditional Proof of Work (PoW) systems.
High Throughput and Scalability
Tron’s network is capable of processing up to 2,000 transactions per second (TPS), significantly higher than Bitcoin and Ethereum. This high throughput makes Tron suitable for a wide range of decentralized applications (dApps) that require rapid and efficient transaction processing.
Low Transaction Fees
Transaction fees on the Tron network are minimal, making it an attractive platform for developers and users alike. This cost-efficiency is crucial for microtransactions and frequent trading activities, which are common in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications.
Smart Contracts and dApps
Tron supports the development and deployment of smart contracts and decentralized applications. The Tron Virtual Machine (TVM) is fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), enabling developers to easily port their Ethereum-based dApps to Tron. This compatibility fosters a rich ecosystem of decentralized applications across various sectors.
TRC-20 and TRC-721 Tokens
Tron offers its own standards for tokens: TRC-20 for fungible tokens and TRC-721 for non-fungible tokens (NFTs). These standards are similar to Ethereum’s ERC-20 and ERC-721, respectively, allowing developers to create and manage a wide range of digital assets on the Tron network.
Decentralized Storage
Tron aims to decentralize the internet, and part of this vision includes decentralized storage solutions. By integrating BitTorrent technology, Tron provides a decentralized file sharing and storage system, enhancing data privacy and security.
Rich Developer Resources
Tron offers extensive resources for developers, including comprehensive documentation, development tools, and support programs. This robust support infrastructure encourages innovation and development within the Tron ecosystem.
Use cases
Decentralized Apps (dApps)
Tron is designed to support dApps across multiple sectors. These applications benefit from Tron’s high throughput and low transaction fees, making them more efficient and cost-effective. Popular dApps on Tron include games, social media platforms, and financial services.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Tron has become a significant player in the DeFi space, providing infrastructure for decentralized exchanges (DEXs), lending platforms, and stablecoins. JustSwap, Tron’s decentralized exchange, allows users to trade TRC-20 tokens without intermediaries. Additionally, platforms like JUST provide decentralized lending and borrowing services.
Digital Content and Entertainment
Tron’s primary mission is to decentralize the internet, particularly the digital content and entertainment industry. Platforms like TRON TV and BitTorrent integrate with Tron to offer decentralized content distribution, allowing content creators to share their work directly with consumers without intermediaries, ensuring fairer revenue distribution.
Supply Chain Management
Tron can be used to enhance transparency and traceability in supply chain management. By recording transactions and product movements on the blockchain, companies can ensure authenticity and reduce fraud. This use case is particularly relevant for industries like pharmaceuticals, food, and luxury goods.
Gaming
Tron’s blockchain supports various blockchain-based games that leverage the benefits of decentralized infrastructure. These games offer players true ownership of in-game assets, transparent reward systems, and the ability to trade items outside the game environment. Titles like WINk and others on the Tron platform showcase the potential for blockchain in gaming.
Voting and Governance
Tron’s DPoS consensus mechanism is an example of blockchain-based voting and governance in action. The Tron community votes for super representatives who validate transactions and make governance decisions. This model can be applied to other voting systems, including corporate governance, municipal voting, and organizational decision-making processes.
Data Storage and Sharing
Integrating BitTorrent with Tron provides a decentralized solution for data storage and sharing. This system allows users to store and share files securely without relying on centralized servers, enhancing privacy and reducing the risk of data breaches.
Technology and underlying blockchain
The Tron blockchain is a high-performance, decentralized platform designed to support a vast array of decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts. At its core, Tron utilizes a Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism, which enhances transaction throughput and network scalability. DPoS involves TRX holders voting for super representatives (SRs) who are responsible for validating transactions and maintaining the blockchain, ensuring efficient and democratic governance. Tron’s architecture includes the Tron Virtual Machine (TVM), which is fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). This compatibility enables seamless migration of dApps from Ethereum to Tron, fostering cross-chain interoperability. Tron’s blockchain can process up to 2,000 transactions per second (TPS), significantly outpacing many other blockchain networks, making it suitable for applications requiring high transaction volumes. Additionally, Tron supports the creation of custom tokens through its TRC-20 and TRC-721 standards, analogous to Ethereum’s ERC-20 and ERC-721, facilitating the development of fungible tokens and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). This robust infrastructure, combined with low transaction fees, makes Tron an attractive platform for developers and enterprises looking to build decentralized solutions.
Supply of coins
Tron (TRX) operates with a total maximum supply of 100 billion tokens. At its inception, Tron’s token allocation included 40% for initial token sale, 15% for the Tron Foundation, 35% for private placements, and 10% for the team. Over time, Tron’s supply distribution has undergone changes due to various factors such as token burns, airdrops, and network upgrades. Notably, Tron has implemented periodic token burns to reduce the circulating supply and increase scarcity, thereby potentially driving up the value of TRX. Additionally, the Tron Foundation periodically releases tokens from its allocated supply for ecosystem development, partnerships, and other strategic initiatives aimed at fostering the growth of the Tron network. Overall, Tron’s coin supply dynamics are managed with a focus on maintaining balance between liquidity, scarcity, and ecosystem development to support the long-term sustainability and adoption of the Tron blockchain.
Historical data for TRX (Tron)
How to get the data?
Tron is a popular cryptocurrency on the market, and historical data for the Tron such as prices and volume traded can be easily downloaded from the internet sources such as Yahoo! Finance, Blockchain.com & CoinMarketCap. For example, you can download data for Tron on Yahoo! Finance (the Yahoo! code for Tron is TRX-USD).How to get the data?
Figure 2. Tron data
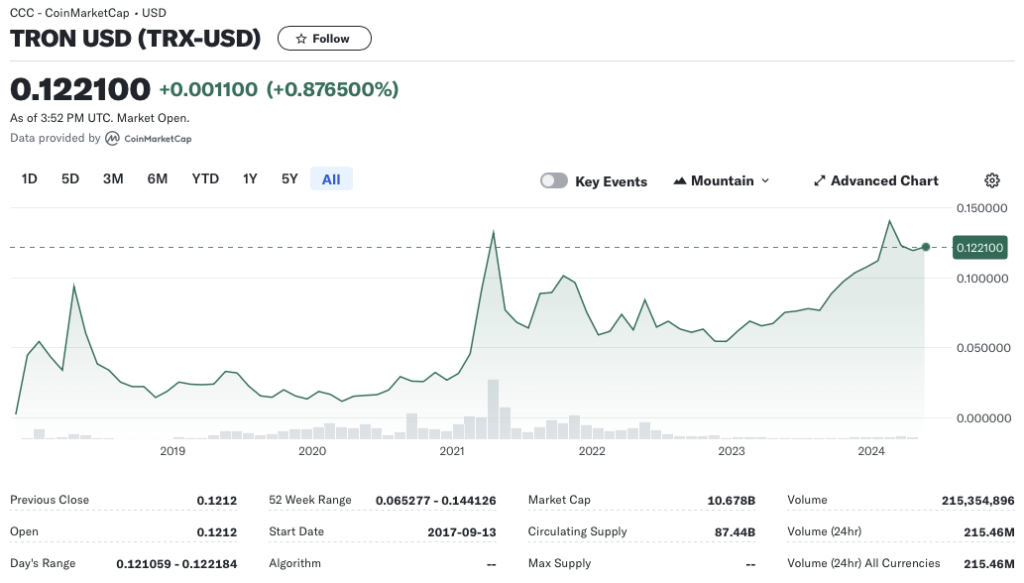
Source: Yahoo! Finance.
Historical data for the TRX (Tron) market prices
TRX (Tron) has experienced a dynamic evolution in its market prices since its inception in 2017. Initially introduced at a fraction of a cent, TRX quickly gained attention within the cryptocurrency community due to its ambitious vision and promising technology. The early months saw considerable volatility, with TRX experiencing rapid price fluctuations amid speculation and market sentiment. As Tron’s ecosystem matured and adoption grew, its market prices reflected both the broader trends in the cryptocurrency market and Tron-specific developments. Notable milestones, such as mainnet launches, strategic partnerships, and ecosystem expansions, often correlated with significant price movements. Despite periods of volatility, Tron’s market prices have shown resilience and a tendency to recover from downturns, reflecting investor confidence in its long-term potential. Over time, TRX has established itself as one of the prominent cryptocurrencies, with a growing user base and a diverse range of use cases. As the cryptocurrency market continues to evolve, Tron’s market prices are likely to reflect both internal and external factors, shaping its trajectory within the broader blockchain landscape.
Figure 3 below represents the evolution of the price of Tron (TRX) in US dollar over the period November 2017 – May 2024 . The price corresponds to the “closing” price (observed at 10:00 PM CET at the end of the month).
Figure 3. Evolution of Tron price
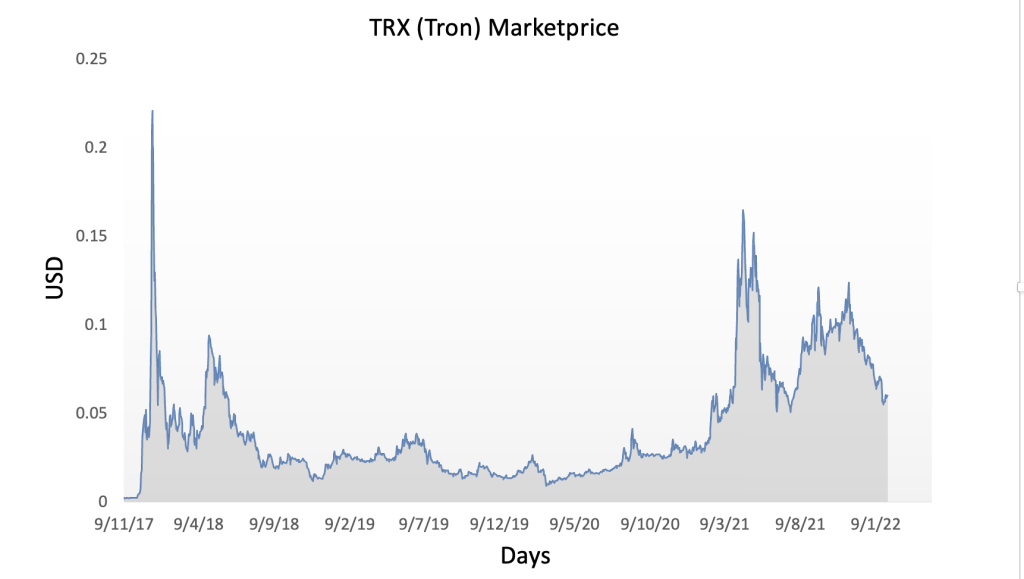
Source: Yahoo! Finance.
R program
The R program below written by Shengyu ZHENG allows you to download the data from Yahoo! Finance website and to compute summary statistics and risk measures about the Tron (TRX).

Data file
The R program that you can download above allows you to download the data for Tron from the Yahoo! Finance website. The database starts on November 2017.
Table 1 below represents the top of the data file for the Tron (TRX) downloaded from the Yahoo! Finance website with the R program.
Table 1. Top of the data file for Tron (TRX)
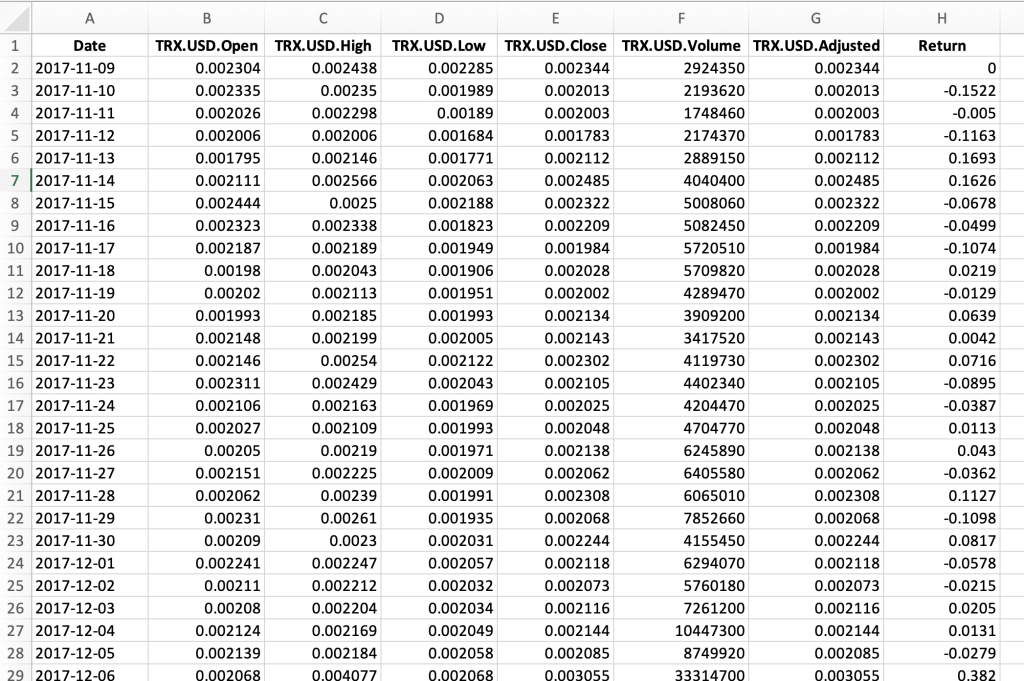
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
Python code
You can download the Python code used to download the data from Yahoo! Finance.

Python script to download Tron (TRX) historical data and save it to an Excel sheet:
import yfinance as yf
import pandas as pd
# Define the ticker symbol for Iron
Tron_ticker = “TRX -USD”
# Define the date range for historical data
start_date = “2017-05-30”
end_date = “2024-04-30”
# Download historical data using yfinance
Tron_data = yf.download(Tron_ticker, start=start_date, end=end_date)
# Create a Pandas DataFrame from the downloaded data
Tron_df = pd.DataFrame(Tron_data)
# Define the Excel file path
excel_file_path = “Tron_historical_data.xlsx”
# Save the data to an Excel sheet
Tron_df.to_excel(excel_file_path, sheet_name=”Tron Historical Data”)
print(f”Data saved to {excel_file_path}”)
# Make sure you have the required libraries installed and adjust the “start_date” and “end_date” variables to the desired date range for the historical data you want to download.
Evolution of the TRX (Tron)
Figure 4 below gives the evolution of the TRX (Tron) on a daily basis.
Figure 4. Evolution of the TRX (Tron)
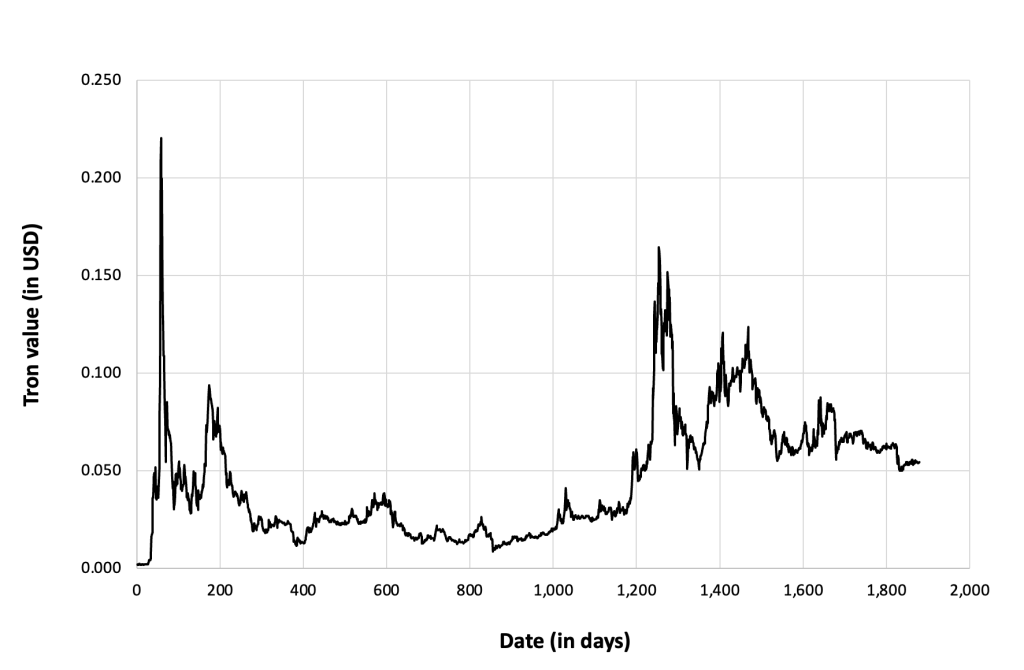
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
Figure 5 below gives the evolution of the TRX (Tron) returns from May 2017 to May 2024 on a daily basis.
Figure 5. Evolution of the TRX (Tron) returns.

Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
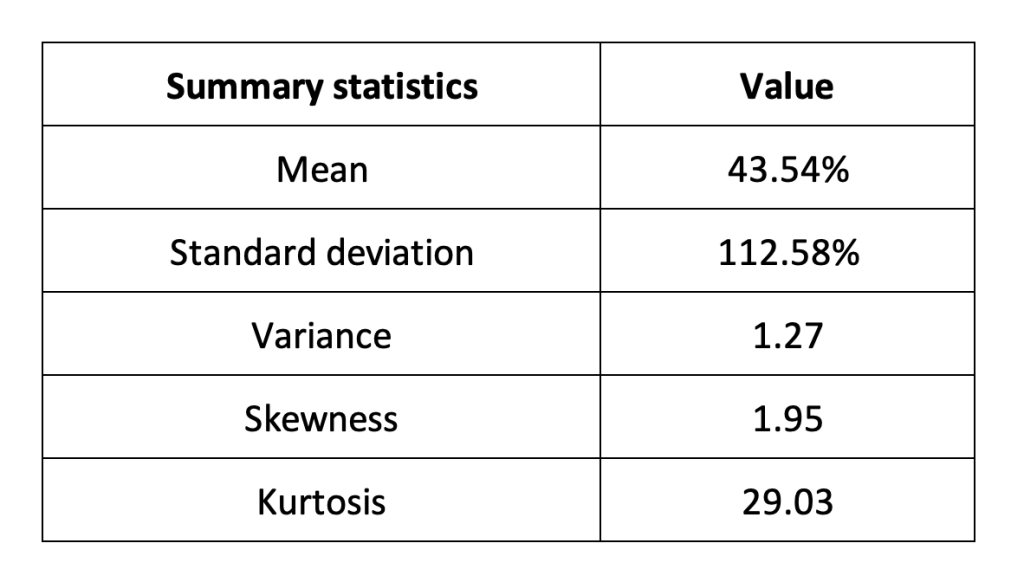
Summary statistics for the TRX (Tron)
The R program that you can download above also allows you to compute summary statistics about the returns of the TRX (Tron).
Table 2 below presents the following summary statistics estimated for TRX (Tron):
- The mean
- The standard deviation (the squared root of the variance)
- The skewness
- The kurtosis.
The mean, the standard deviation / variance, the skewness, and the kurtosis refer to the first, second, third and fourth moments of statistical distribution of returns respectively.
Table 2. Summary statistics for TRX (Tron)
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
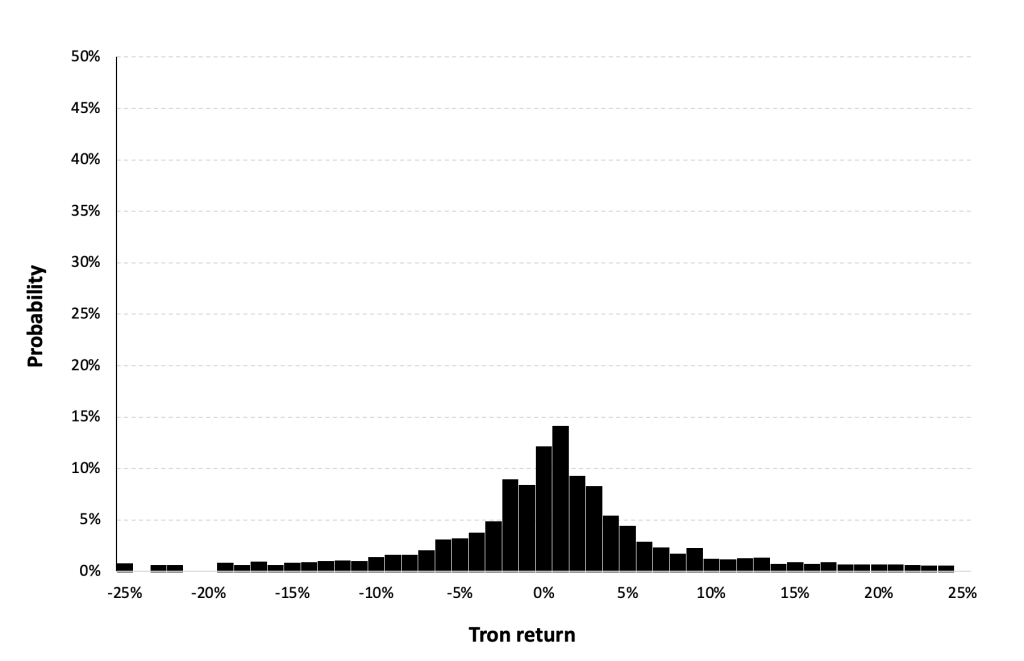
Statistical distribution of the TRX (Tron) returns
Historical distribution
Figure 6 represents the historical distribution of the TRX (Tron) daily returns for the period from May 2017 to May 2024.
Figure 6. Historical distribution of TRX (Tron) returns.
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
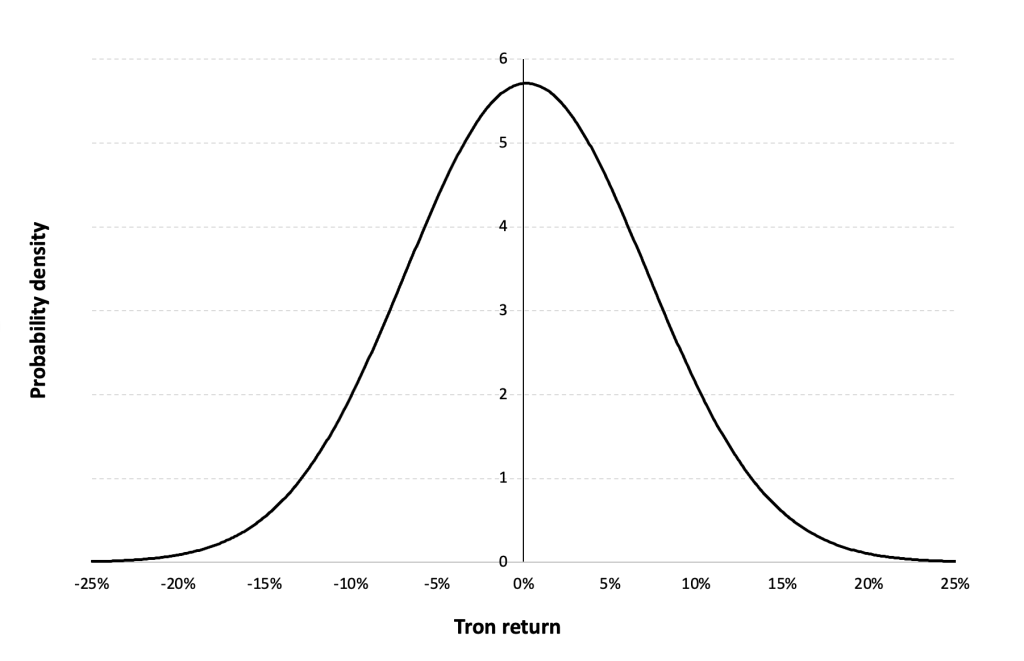
Gaussian distribution
The Gaussian distribution (also called the normal distribution) is a parametric distribution with two parameters: the mean and the standard deviation of returns. We estimated these two parameters over the period from May 2017 to May 2024.
Figure 7 below represents the Gaussian distribution of the TRX (Tron) daily returns with parameters estimated over the period from May 2017 to May 2024.
Figure 7. Gaussian distribution of the TRX (Tron) returns.
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
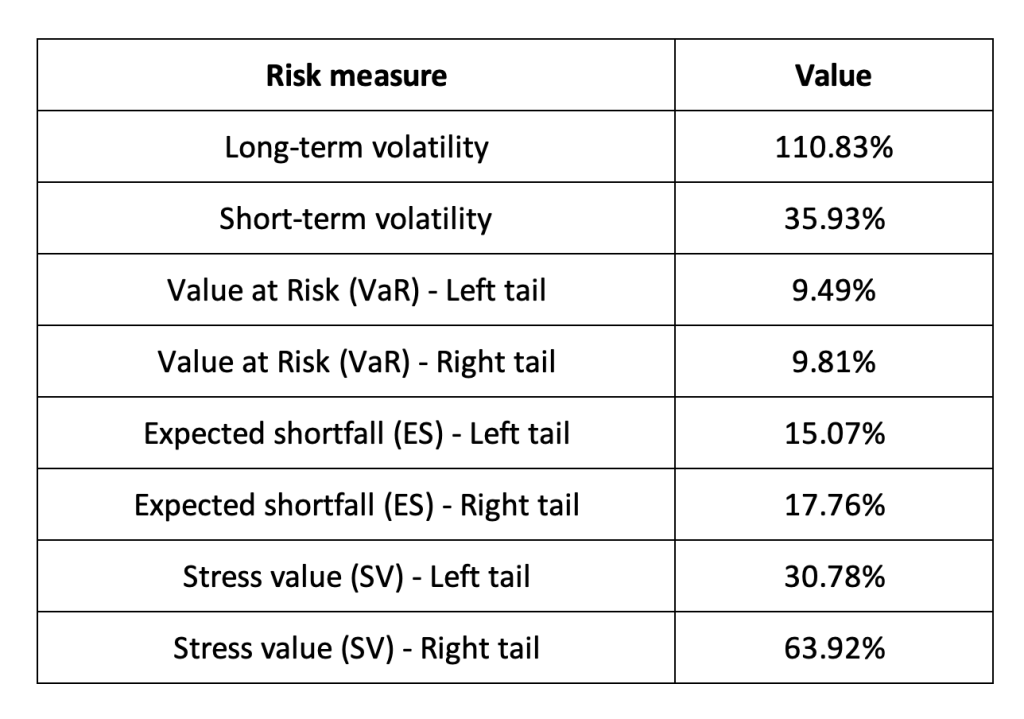
Risk measures of the TRX (Tron) returns
The R program that you can download above also allows you to compute risk measures about the returns of the TRX (Tron).
Table 3 below presents the following risk measures estimated for the TRX (Tron):
- The long-term volatility (the unconditional standard deviation estimated over the entire period)
- The short-term volatility (the standard deviation estimated over the last three months)
- The Value at Risk (VaR) for the left tail (the 5% quantile of the historical distribution)
- The Value at Risk (VaR) for the right tail (the 95% quantile of the historical distribution)
- The Expected Shortfall (ES) for the left tail (the average loss over the 5% quantile of the historical distribution)
- The Expected Shortfall (ES) for the right tail (the average loss over the 95% quantile of the historical distribution)
- The Stress Value (SV) for the left tail (the 1% quantile of the tail distribution estimated with a Generalized Pareto distribution)
- The Stress Value (SV) for the right tail (the 99% quantile of the tail distribution estimated with a Generalized Pareto distribution)
Table 3. Risk measures for the TRX (Tron)
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
The volatility is a global measure of risk as it considers all the returns. The Value at Risk (VaR), Expected Shortfall (ES) and Stress Value (SV) are local measures of risk as they focus on the tails of the distribution. The study of the left tail is relevant for an investor holding a long position in the TRX (Tron) while the study of the right tail is relevant for an investor holding a short position in the TRX (Tron).
Why should I be interested in this post?
This post provides an engaging exploration of Tron cryptocurrencies, tailored to both newcomers and seasoned crypto enthusiasts alike. It delves into Tron’s innovative blockchain technology and its transformative impact across diverse industries, from entertainment to decentralized finance. By delving into Tron’s underlying technology, consensus mechanism, and ecosystem development, readers can grasp the potential of Tron to revolutionize decentralized applications, scalability, and cross-chain interoperability. Furthermore, the post examines Tron’s historical price trends, market dynamics, and community governance structure, offering valuable insights for investors, traders, and ecosystem participants. Whether you’re curious about cutting-edge blockchain solutions or searching for investment opportunities in the crypto market, this post provides comprehensive insights into the significance and potential of Tron in shaping the future of decentralized technologies.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
About cryptocurrencies
▶ Snehasish CHINARA Bitcoin: the mother of all cryptocurrencies
▶ Snehasish CHINARA How to get crypto data
▶ Alexandre VERLET Cryptocurrencies
▶ Youssef EL QAMCAOUIDecentralised Financing
▶ Hugo MEYERThe regulation of cryptocurrencies: what are we talking about?
About statistics
▶ Shengyu ZHENG Moments de la distribution
▶ Shengyu ZHENG Mesures de risques
▶ Jayati WALIA Returns
Useful resources
Academic research about risk
Longin F. (2000) From VaR to stress testing: the extreme value approach Journal of Banking and Finance, N°24, pp 1097-1130.
Longin F. (2016) Extreme events in finance: a handbook of extreme value theory and its applications Wiley Editions.
Data
Yahoo! Finance Historical data for Tron
CoinMarketCap Historical data for Tron
About the author
The article was written in May 2024 by Snehasish CHINARA (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2022-2024).
