Decentralized finance (DeFi)
In this article, Youssef EL QAMCAOUI (ESSEC Business School, Master in Strategy & Management of International Business (SMIB), 2020-2021) discusses decentralized finance (DeFi).
From cryptocurrencies to decentralized finance
As you may know, Bitcoin is a form of money (cryptocurrency) that isn’t controlled by any central bank or government. It can be transferred to anyone from anyone around the world, without the need of a bank or a financial institution. Bitcoin is decentralized money.
However, transferring money is only the first of many building blocks in a financial system. Aside from sending money to one another, there are a variety of financial services we use today. For example, loans, saving plans, insurance and stock markets are all services that are built around money and together create our financial system.
Today, our financial system and all its services are completely centralized. Banks, stock markets, insurance companies and other financial institutions all have someone in charge, whether it be a company or a person, that controls and offers these services. This centralized financial system has its risks – mismanagement, fraud and corruption to name a few. But what if we could decentralize the financial system as a whole in the same way Bitcoin decentralized money?
That’s exactly what DeFi is all about. DeFi is a term given to financial services that have no central authority or someone in charge. Using decentralized money, like some cryptocurrencies, that can also be programmed for automated activities, we can build exchanges, lending services, insurance companies and other organizations that don’t have any owner and aren’t controlled by anyone.
How to build decentralized finance
Platform based on Ethereum
In order to create a decentralized financial system, the first thing we need is an infrastructure for programming and running decentralized services. That is the main objective of Ethereum. Ethereum is a Do-It-Yourself platform for writing decentralized programs also known as decentralized apps. By using Ethereum we can write automated code, also known as smart contracts, that manage any financial service we’d like to create in a decentralized manner. This means that we determine the rules as to how a certain service will work, and once we deploy those rules on the Ethereum network, we no longer have control over them – they are immutable.
Once we have a system in place like Ethereum for creating decentralized apps, we can start building our decentralized financial system.
Now let’s take a look at some of the building blocks that comprise it. The first thing any financial system needs is of course money. “why not use Bitcoin or Ether, which is Ethereum’s currency?” Whilst Bitcoin is indeed decentralized, it has only very basic programmable functionality and is not compatible with the Ethereum platform. Ether, on the other hand, is compatible and programmable. However, it is also highly volatile.
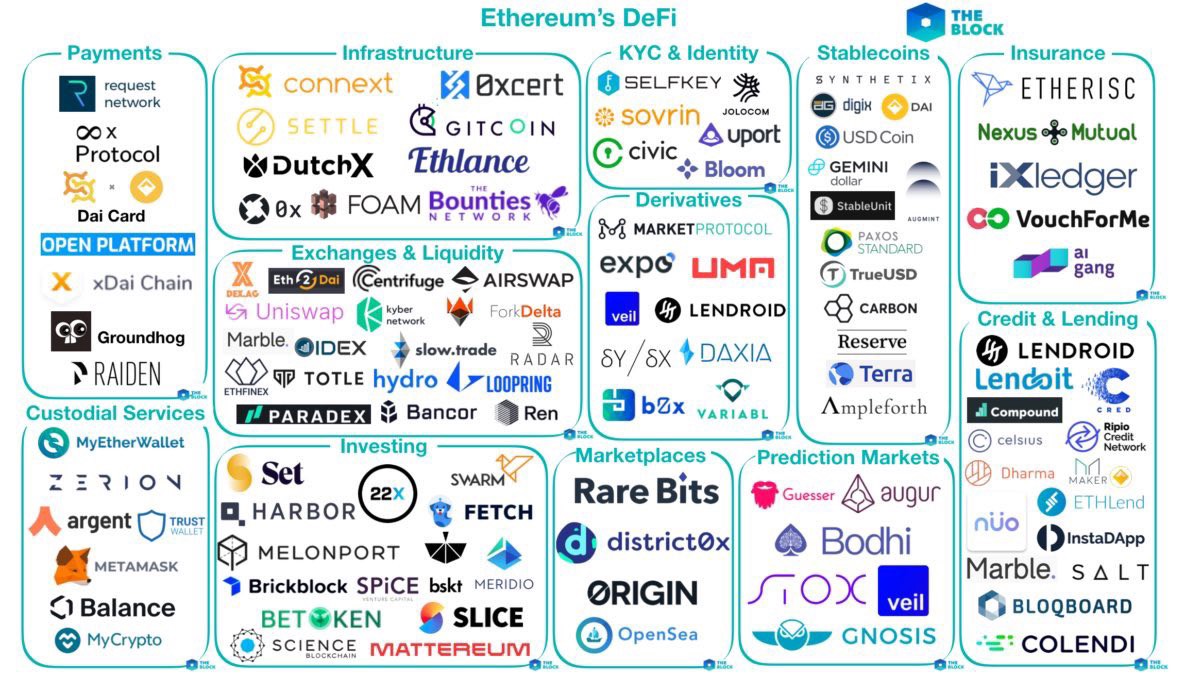
Figure 1 presents a map of the DeFi ecosystem broken down by category: payments, custodial services, infrastructure, exchanges and liquidity, investing, know you customer (KYC) and identity, derivatives, marketplaces, stablecoins, prediction markets, insurance, and credit and lending.
Stablecoins
If we’re looking to build reliable financial services that people will want to use, we’ll need a more stable currency to operate within this system. This is where stablecoins come in. Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies that are pegged to the value of a real-world asset, usually some major currency like the US dollar.
For the purpose of DeFi, we’ll want to use a stablecoin that doesn’t use fiat money reserves for maintaining a peg, since this will require some sort of central authority. This is where the stablecoin DAI comes into play. DAI is a decentralized cryptocurrency pegged against the value of the US dollar, meaning one DAI equals one US dollar. Unlike other popular stablecoins whose value is backed directly by US Dollar reserves, DAI is backed by crypto collaterals that can be viewed publicly on the Ethereum blockchain. DAI is over collateralized, meaning if you lock up in a deposit $1 worth of Ether, you can borrow 66 cents worth of DAI. As soon as you want your Ether back, just pay back the DAI you borrowed and the Ether will be released.
If you don’t have any Ether to lock up as collateral, you can just buy DAI on an exchange. Because DAI is over collateralized, even if Ether’s price becomes extremely volatile, the value of the locked Ether backing the DAI in circulation will most likely still remain at 100% or more. In essence, the DAI stablecoin is actually also a smart contract that resides on the Ethereum platform. This makes DAI a truly a decentralized stablecoin which cannot be shut down nor censored, hence it’s a perfect form of money for other DeFi services.
Financial ecosystem
Now that our decentralized financial system has stable decentralized money, it’s time to create some additional services. The first use case that we’ll discuss is the decentralized exchange (DEX). DEXes operate according to a set of rules, or smart contracts, that allow users to buy, sell, or trade cryptocurrencies. Just like DAI they also reside on the Ethereum platform which means they operate without a central authority. When you trade on a DEX, there is no exchange operator, no sign-ups, no identity verification, and no withdrawal fees. Instead, the smart contracts enforce the rules, execute trades, and securely handle funds when necessary. Also, unlike a centralized exchange, there’s often no need to deposit funds into an exchange account before conducting a trade. This eliminates the major risk of exchange hacking which exists for all centralized exchanges. But the range of decentralized financial services doesn’t stop there. When it comes to decentralized money markets – services that connect borrowers with lenders – Compound is an Ethereum based borrowing and lending decentralized app. This means you can lend your crypto out and earn interest on it. Alternatively, maybe you need some money to pay the rent or buy groceries, but the only funds you have are cryptocurrencies. If that’s the case you can deposit your crypto as collateral and borrow against it. The Compound platform automatically connects the lenders with borrowers, enforces the terms of the loans, and distributes the interest. The process of earning interest on cryptocurrencies has become extremely popular lately, giving rise to “yield farming” – A term given to the effort of putting crypto assets to work while seeking to generate the most returns possible.
So we have decentralized stablecoins, decentralized exchanges and decentralized money markets.
How about decentralized insurance?
All of these new financial products definitely entail some risks. That is where insurance comes in in case something goes wrong: a decentralized platform that connects people who are willing to pay for insurance with people who are willing to insure them for a premium, while everything happens autonomously without any insurance company or agent in the middle, DeFi services work in conjunction with one another, making it possible to mix and match different services to create new and exciting opportunities.
DeFi: money legos
The term ‘money legos’ has been coined to refer to DeFi services as it reminds of building structures out of Lego blocks. For example, you can build the following service from different money legos:
- You start out by using a decentralized exchange aggregator to find the exchange with the best rate for swapping Ether for DAI.
- You then select the DEX you want and conduct the trade. Then you lend the DAI you received to borrowers to earn interest.
- Finally, you can add insurance to this process to make sure you’re covered in case anything goes wrong.
That’s just one example out of the many opportunities DeFi offers. Some of the main advantages that have driven interest towards DeFi are understandably transparency, interoperability, decentralization, free for all services and flexible user experience, among others. However, there are also some risks you should be aware of. The most important risk is that DeFi is still in its infancy, and this means that things can go wrong due to operational risks. Smart contracts have had issues in the past where people didn’t define the rules for certain services correctly and hackers found creative ways to exploit existing loopholes in order to steal money.
Additionally, you should remember that a system is decentralized only as its most central component. This means that some services may be only partially decentralized while still keeping some centralized aspects that can act as a weakness to the project. It’s important to understand exactly how a product or service works before investing in it so you can be aware of any issues that may come up.
Conclusion
To sum it up, it seems that the DeFi revolution has reached its early adopter stage and the coming years will tell if it manages to cross the chasm into mainstream adoption. There’s no doubt that a decentralized financial system can benefit a huge portion of the population that currently suffers from financial discrimination, high fees, and inefficiencies in managing their funds.
Why should I be interested in this post?
This might be of interest to you if you are trying to get to know the ecosystem of Decentralized Finance and you are interested in cryptocurrencies and getting slowly your assets out of the traditional centralized finance (banks, fund managements, etc.).
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ Alexandre VERLET Cryptocurrencies
▶ Alexandre VERLET The NFTs, a new gold rush?
Useful resources
Forbes Decentralized finance will change your understanding of financial systems
Investopedia Decentralized finance
The conversation What is decentralized finance? An expert on bitcoins and blockchains explains the risks and rewards of DeFi
The Financial Times (29/12/2019) DeFi movement promises high interest but high risk
About the author
The article was written in October 2021 by Youssef EL QAMCAOUI (ESSEC Business School, Master in Strategy & Management of International Business (SMIB), 2020-2021).

