Liabilities
In this article, Shruti CHAND (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2020-2022) elaborates on the concept of liabilities.
This read will help you get started with understanding the liability side of the balance sheet.
Introduction
A liability is an obligation that a company has in return of economic benefits that the company has received in the past. Any kind of obligation or risk that are due to a third party can be termed as liability.
Liabilities are recorded on the balance sheet can be short-term or long-term in nature.
Liability vs Expense
It is important to know that liability is not an expense for the business. An expense is the cost of operation for the business and is recorded on the income statement of a business. Liabilities on the other hand is what the business owes to another party already as the economic benefit has been transferred in the past. It is recorded in the balance sheet of the company.
Liabilities are very important for a business as they finance the daily operations of the business. For expansion activities, for instance if a business wants to expand overseas, liability in form of bank loans will help the business acquire assets to make the move to another location. This loan facilitated by a bank for example will be recorded in the liabilities section in the balance sheet.
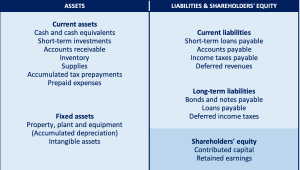
Structure of the Liabilities part of the balance sheet
The Liabilities part of the balance sheet can be structured as follows.
Current Liabilities
These are the company’s short-term obligation (Usually financial in nature) that are to be paid within a period of one year. Most noteworthy examples of current liabilities include:
- Wages Payable: The total amount of salaries that the company owes to its employees.
- Interest Payable: The credit that the business takes to finance short term needs of business operations accrues an interest. This interest in payable by the business in the short term and is recorded in the interest payable section of the balance sheet.
- Dividends Payable: The total amount of dividends that the company owes to the investors against the stocks issued to them.
These items help the readers understand the level of obligations on the businesses due in a short period of time.
Non-current liabilities
These are obligations that are owed in a period longer than a year. Long term bonds, loans, etc. are a part of long-term/non-current liabilities. Companies usually issue bonds fulfil their long-term capital needs which are very common type of non-current liability. Other common examples of long-term liabilities include:
- Debentures: Type of bond or debt instrument issued by the company unsecured against a collateral.
- Bonds Payable: Long term debt instrument issued by companies and government which is a promise to pay at a future date and is issued at a discount in the current period.
- Deferred tax liabilities: All that the company owed the government in the form of tax obligation that hasn’t been met yet by the company.
Final Word
Liability section of the balance sheet helps investors to assess the risk profile of a business. It is an important tool to measure the leverage taken by a firm to assess the risk level of the company within the industry and compare it with competitors in the same industry.
Relevance to the SimTrade certificate
This post deals with Liability side of the balance sheet, an important tool for investors to take investment decisions.
About theory
- By taking the SimTrade course, you will know more about how investors can use various strategies to invest in order to trade in the market.

About practice
- By launching the series of Market maker simulations, you can extend your learning about financial markets and trading approaches.

Related posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ Shruti CHAND Balance Sheet
▶ Shruti CHAND Long-Term Liabilities
▶ Shruti CHAND Accounts Payable
▶ Shruti CHAND Financial leverage
About the author
Article written by Shruti CHAND (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2020-2022).