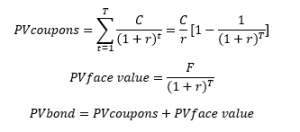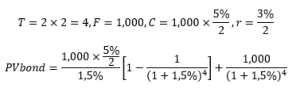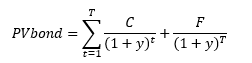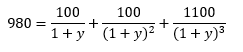In this article, Nithisha CHALLA (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management (MiM, 2021-2024) gives a comprehensive overview of U.S. Treasury bonds, covering their features, benefits, risks, and how to invest in them.
Introduction
Treasury bonds, often referred to as T-bonds, are long-term debt securities issued by the U.S. Department of the Treasury. They are regarded as one of the safest investments globally, offering a fixed interest rate and full backing by the U.S. government. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of Treasury bonds, from their basics to advanced concepts, making it an essential read for finance students and professionals.
What Are Treasury Bonds?
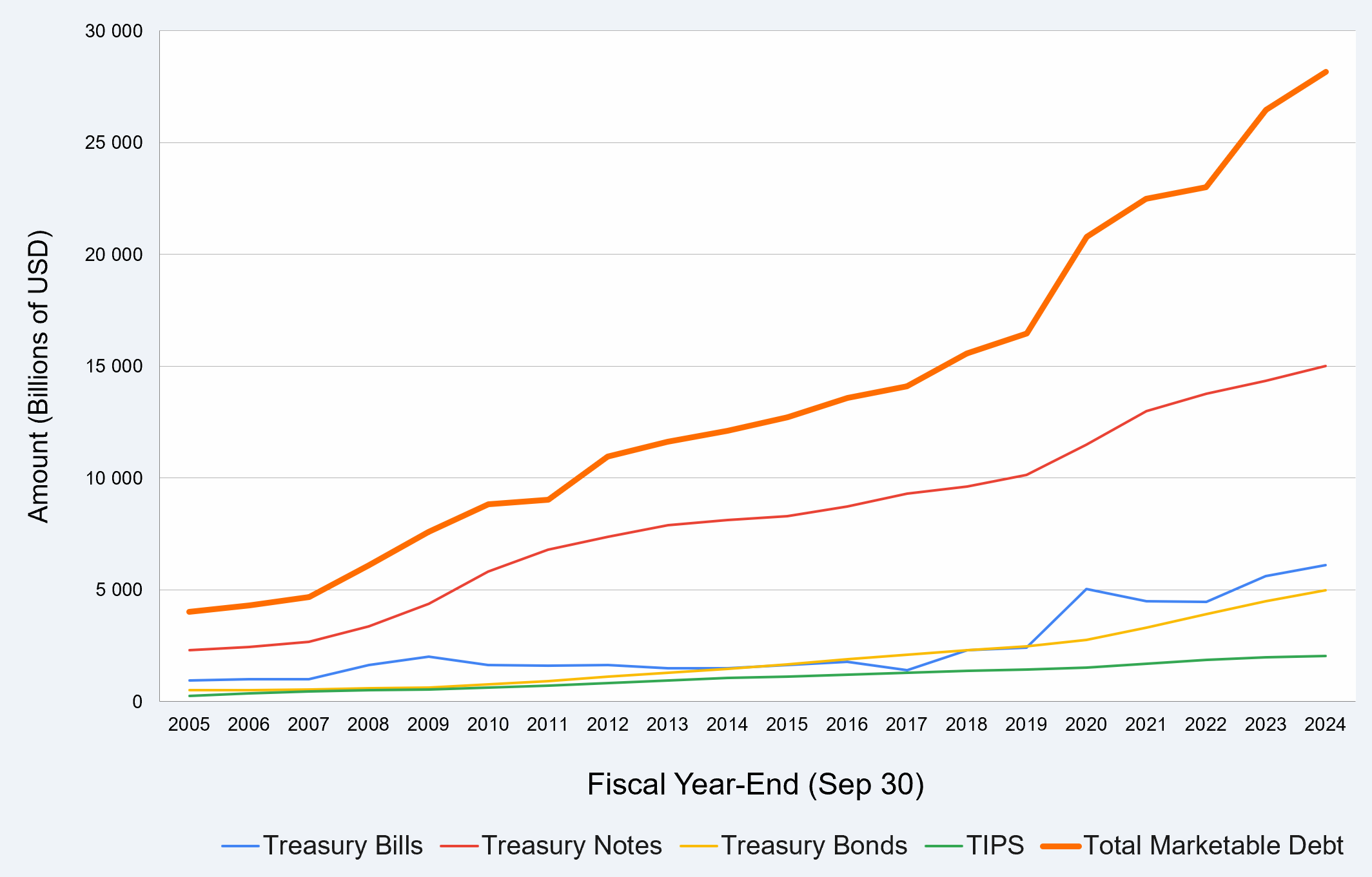
Treasury bonds are government debt instruments with maturities ranging from 10 to 30 years. Investors receive semi-annual interest payments and are repaid the principal amount upon maturity. Due to their low credit risk, Treasury bonds are a popular choice for conservative investors and serve as a benchmark for other interest-bearing securities.
Types of Treasury Securities
Treasury bonds are part of a broader category of U.S. Treasury securities, which include:
- Treasury Bills (T-bills): Short-term securities with maturities of one year or less, sold at a discount and matured at face value.
- Treasury Notes (T-notes): Medium-term securities with maturities between 2 and 10 years, offering fixed interest payments.
- Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS): Securities adjusted for inflation to protect investors’ purchasing power.
- Treasury Bonds (T-bonds): Long-term securities with maturities of up to 30 years, ideal for investors seeking stable, long-term income.
Historical Performance of Treasury Bonds
Historically, Treasury bonds have been a cornerstone of risk-averse portfolios. During periods of economic uncertainty, they act as a haven, preserving capital and providing reliable income. For instance, during the 2008 financial crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic, Treasury bond yields dropped significantly as investors flocked to their safety.
Despite their stability, T-bonds are sensitive to interest rate fluctuations. When interest rates rise, bond prices typically fall, and vice versa. Over the long term, they have delivered modest returns compared to equities but excel in capital preservation.
Investing in Treasury Bonds
Investing in Treasury bonds can be done through various channels like Direct Purchase, Brokerage Accounts, Mutual Funds and ETFs, and Retirement Accounts:
- Direct Purchase: Investors can buy T-bonds directly from the U.S. Treasury via the TreasuryDirect website.
- Brokerage Accounts: Treasury bonds are also available on secondary markets through brokers.
- Mutual Funds and ETFs: Investors can gain exposure to Treasury bonds through funds that focus on government securities.
- Retirement Accounts: T-bonds are often included in 401(k) plans and IRAs for diversification.
Factors Affecting Treasury Bond Prices
Several factors influence the prices and yields of Treasury bonds such as Interest Rates, Inflation Expectations, Federal Reserve Policy, and Economic Conditions:
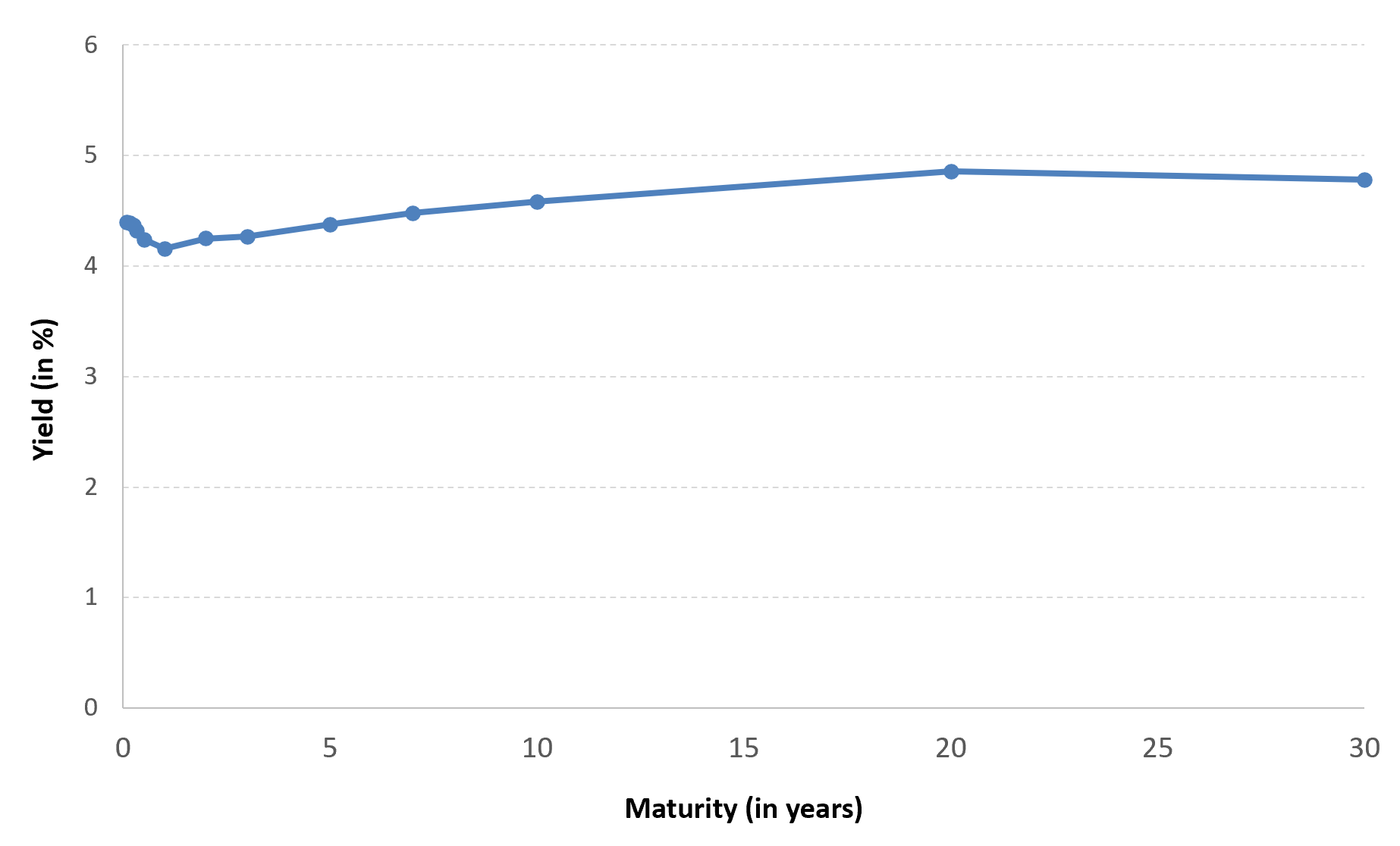
- Interest Rates: An inverse relationship exists between bond prices and interest rates.
- Inflation Expectations: Higher inflation erodes the real return on bonds, causing prices to drop.
- Federal Reserve Policy: The Federal Reserve’s actions, such as changing the federal funds rate or engaging in quantitative easing, directly impact Treasury yields.
- Economic Conditions: In times of economic turmoil, demand for Treasury bonds increases, driving up prices and lowering yields.
Relationship between bond price and current bond yield
Let us consider a US Treasury bond with nominal value M, coupon C, maturity T, and interests paid twice a year every semester. The coupon (or interest paid every period) is computed with the coupon rate. The nominal value is reimbursed at maturity. The current yield is the market rate, which may be lower or greater than the rate at the time of issuance of the bond (the coupon rate used to compute the dollar value of the coupon). The formula below gives the formula for the price of the bond (we consider a date just after the issuance date and different yield rates.
Formula for the price of the bond
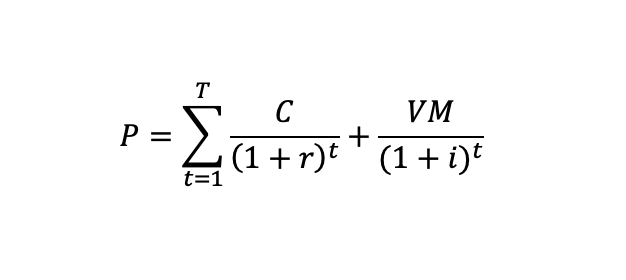
Source: The author
Relationship between bond price and current bond yield
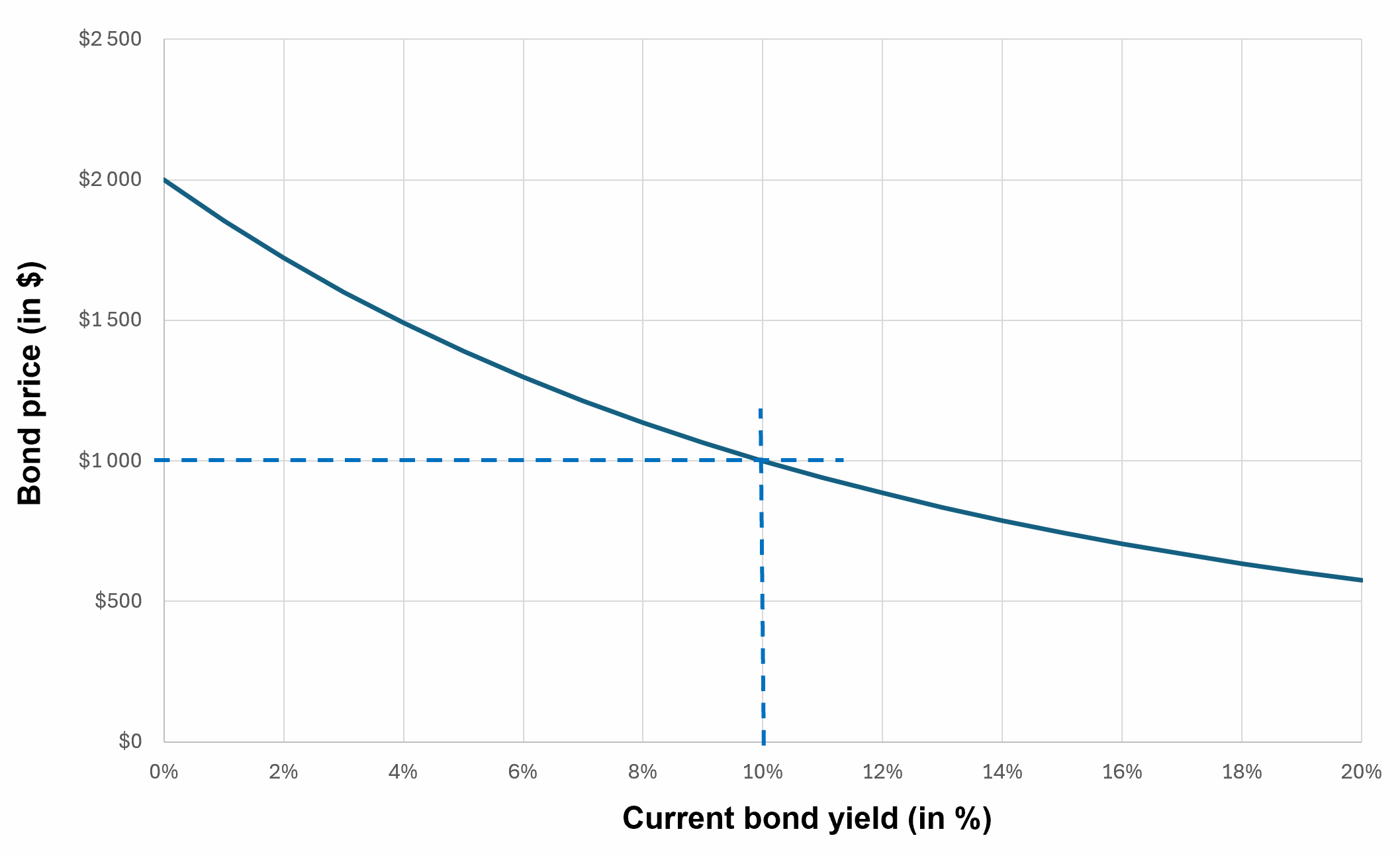
Source: The author
You can download below the Excel file for the data used to build the figure for the relationship between bond price and current bond yield.
Risks and Considerations
While Treasury bonds are low-risk investments, they are not entirely risk-free, there are several factors to consider, such as Interest Rate Risk (Rising interest rates can lead to capital losses for bondholders), Inflation Risk (Fixed payments lose purchasing power during high inflation periods), Opportunity Cost (Low returns on T-bonds may be less attractive compared to higher-yielding investments like stocks).
Treasury Bond Futures
Treasury bond futures are standardized contracts that allow investors to speculate on or hedge against future changes in bond prices. These derivatives are traded on exchanges like the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) and are essential tools for managing interest rate risk in sophisticated portfolios.
Treasury Bonds in the Global Market
The U.S. Treasury market is the largest and most liquid government bond market worldwide. It plays a pivotal role in the global financial system:
- Reserve Currency: Many central banks hold U.S. Treasury bonds as a key component of their foreign exchange reserves.
- Benchmark for Other Securities: Treasury yields serve as a reference point for pricing other debt instruments.
- Foreign Investment: Countries like China and Japan are significant holders of U.S. Treasury bonds, underscoring their global importance.
Conclusion
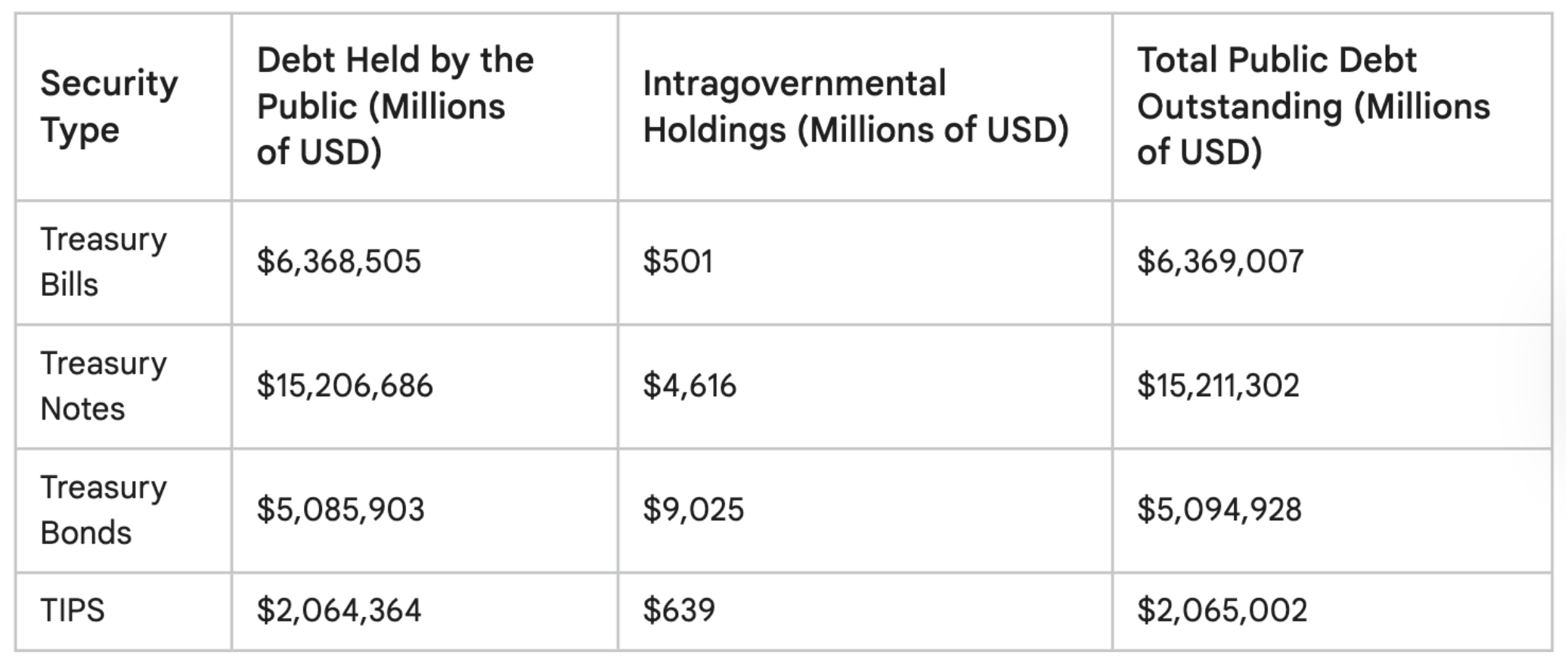
Treasury bonds are fundamental to the financial landscape, offering safety, stability, and insights into broader economic dynamics. Whether you are a finance student building foundational knowledge or a professional refining investment strategies, understanding Treasury bonds is indispensable. As of 2023, the U.S. Treasury market exceeds $24 trillion in outstanding debt, reflecting its vast scale and importance. By mastering the nuances of Treasury bonds, you gain a competitive edge in navigating the complexities of global finance.
Why should I be interested in this post?
Understanding Treasury bonds is crucial for anyone pursuing a career in finance. These instruments provide insights into Monetary Policy, Fixed-Income Analysis, Portfolio Management, and Macroeconomic Indicators.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ Nithisha CHALLA Datastream
Useful resources
Treasury Direct Treasury Bonds
Fiscal data U.S. Treasury Monthly Statement of the Public Debt (MSPD)
Treasury Direct Understanding Pricing and Interest Rates
About the author
The article was written in October 2025 by Nithisha CHALLA (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management (MiM), 2021-2024).