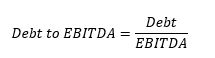Corporate debt
In this article, Rodolphe Chollat-Namy (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole – Master in Management, 2019-2023) introduces you to corporate debt.
Investors seek to determine how the different characteristics of a bond can influence its intrinsic value in order to know whether it is a good investment or not. To do this, they will look at the theoretical value of a bond, i.e. its present value. How can this be determined? How to interpret it?
Composition of a company’s debt
The debt of a company is composed of short-term liabilities and of long-term liabilities.
Short-term liabilities: accounts payable, deferred revenues, wages payable, short-term notes, current portion of long-term debt.
Long-term liabilities: Bonds payable, capital leases, long-term loans, pension liabilities, deferred compensation, deferred income taxes.
Let us have a look to the long-term liabilities:
- Bonds payable: A bond payable is a form of long-term debt issued by the company.
- Capital leases: A capital lease is a contract entitling a renter to the temporary use of an asset.
- Long-term loans: A long-term loan involve borrowing money over a specified period with a pre-planned payment schedule.
- Pension liabilities: A pension liability is the difference between the total amount due to retirees and the actual amount of money the company has on hand to make those payments.
- Deferred compensation: Deferred compensation is an arrangement in which a portion of an employee’s income is paid out at a later date after which the income was earned.
- Deferred income taxes: Deferred income taxes result from a difference in income recognition between tax laws and the company’s accounting methods.
When looking at a company’s debt, analysts often look at net debt. It is equal to the sum of the short-term liabilities and of the long-term liabilities minus the cash and the cash equivalents, that are liquid investments with a maturity of 90 days (certificates of deposit, treasury bills, commercial paper, …). It is a metric that measures a company’s ability to bay all its debts if they were due today.
For example, assume that a company has a line of credit of $5,000, a current portion of long-term debt of $25,000, a $60,000 long-term bank loan, and $40,000 in bonds. Moreover it has $10,000 in cash and $5,000 in Treasury bills.
The short-term debt would be equal to $5,000 + $25,000 = $30,000
The long-term debt would be equal to $60,000 + $40,000 = $100,000
And the cash and cash equivalents would be equal to $10,000 + $5,000 = 15,000
So the net debt of the company would be equal to $115,000.
Debt Ratios
Nevertheless, an absolute value will not give us much indication of the health of the company. In order to understand the company’s indebtedness, we need to compare the amount of debt with other metrics. To do this, we will use what are called ratios.
We will focus here on three important ratios: the debt-to-equity ratio, the EBIT-to-interest expenses ratio and the debt-to-EBITDA ratio.
Debt-to-equity ratio (D/E)
The D/E ratio, also known as gearing, is a ratio that measures the level of debt of a company in relation to its equity. Simply put, it tells us about the financial structure of the company.
Changes in long-term liabilities have more influence on the D/E ratio than changes in short-term liabilities. Thus, investors will use other ratios if they want information on short-term liabilities.
The higher the ratio, the more indebted the company is. The risk is therefore higher. Between 0 and 0.1, the ratio is theoretically excellent. Above 1, the ratio is theoretically bad.
Beware, this ratio has its limitations. First of all, the reading of this ratio depends on the industries. Capital intensive industries, such as TMT or oil and gas, will tend to have higher ratios. It is therefore necessary to compare the ratios of companies in the same sector. On the other hand, a low D/E ratio can also mean that a company is afraid to invest. In the long run, this can present a risk of downgrading compared to its competitors.
It is therefore important to keep in mind, and this is also true for other ratios, that it is one indicator among others and that it cannot be perfect. It is important to put it into context and to compare comparable companies.
Interest Coverage ratio (ICR)
The ICR is the ratio of financial expenses to operating income. It measures a company’s ability to pay the interest on its debt.
A low ICR means that less profit is available for interest payments and that the company is more vulnerable to rising interest rates.
Usually, the ICR is considered low when it is below 3. However, it varies according to the type of industry. On the other hand, we can also look at the trends that are emerging. A falling ICR is worrying for investors.
Debt-to-EBIDTA ratio
This ratio measures the company’s ability to repay its debt with the money generated by its activity. It tells us how many years of profit it would take to pay off the entire debt. It is often referred to as leverage.
Analysts often use this ratio, which is easy to calculate. The lower the ratio, the healthier the company. A good ratio is between 2 and 4. However, again, it depends on the industry.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ Rodolphe CHOLLAT-NAMY Why do companies issue debt?
▶ Rodolphe CHOLLAT-NAMY Corporate debt
▶ Louis DETALLE A quick review of the DCM (Debt Capital Market) analyst’s job…
About the author
Article written in May 2021 by Rodolphe Chollat-Namy (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole – Master in Management, 2019-2023).