Operating Profit
In this article, Bijal GANDHI (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2019-2022) explains the concept of Operating profit.
This read will help you understand in detail the meaning, components and formula for calculating operating profit along with relevant examples.
Operating Profit
Operating profit refers to the profit obtained from business operations before the deduction of interest and taxes. Operating profit is a good representation of the company’s profits as all the core expenses are taken into consideration except interest and tax. It is synonymously used with “EBIT” (Earnings before interest and taxes) and “operating income”. Although, EBIT may sometimes include non-operating revenue.
Components and Formula
Operating profit is equal to:
Operating revenue – COGS – Operating expenses – Depreciation –Amortization
- Gross profit: We know from the blog on revenue, gross profit equals revenue less COGS (cost of goods sold). Therefore, operating profit is often simplified as, Gross Profit – Operating expenses – Depreciation – Amortization.
- Operating expenses refers to the expenses that a business undertakes during its normal operations such as rent, electricity, salary, etc. These expenses are generally divided into broad categories in the income statement to make it concise. For example, in the LVMH example below, the operating expenses are divided into three broad categories like marketing and sales, general and administrative and other such costs.
- Depreciation refers to the value of the assets that have been used up every year. It is a method to allocate the cost of a physical asset over its useful life.
- Amortization refers to the accounting method of spreading the cost of an intangible asset over its useful life.
Example: LVMH
Let us once take the example of LVMH. The French multinational company LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton was founded in 1987. The company headquartered in Paris specializes in luxury goods and stands at a valuation (market capitalization in June 2021) of $329 billion. It is a consortium of 75 brands controlled under around 60 subsidiaries. Here, you can find a snapshot of LVMH Income statement for three years: 2018, 2019 and 2020.
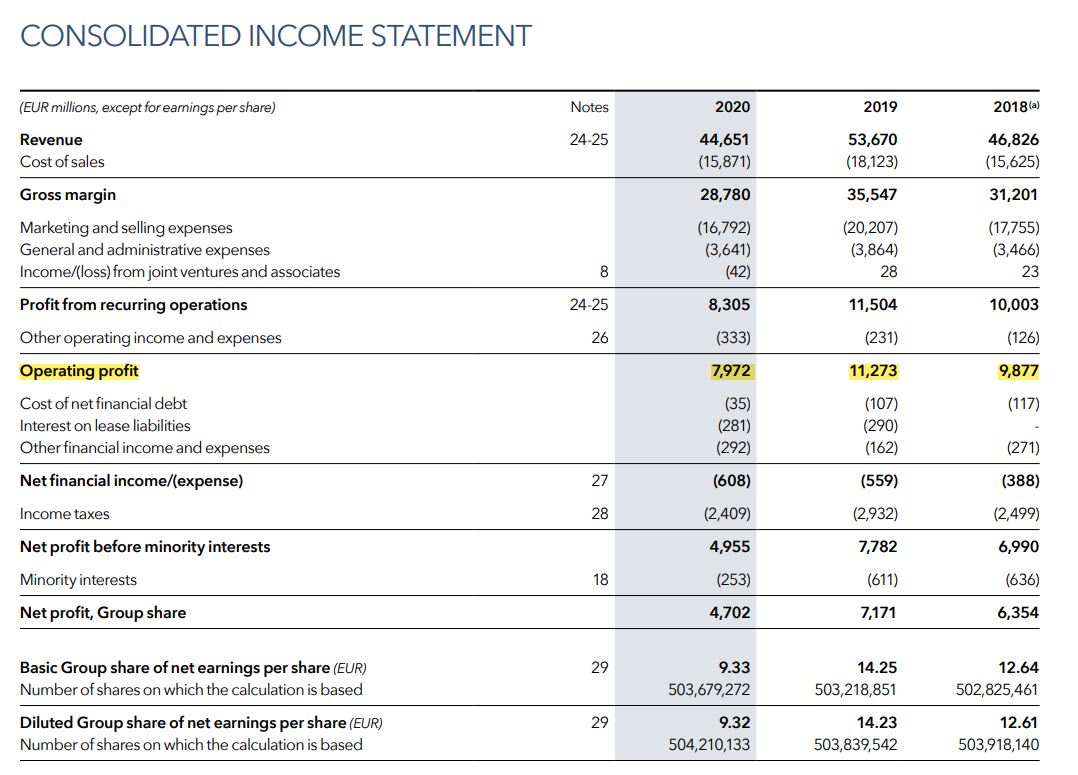
The operating profit for the year 2020 is 7,972 million euros. This means that from a revenue of 44,651 million euros in 2020, the company is now left with 7,972 million euros after deducting all expenses except interest and tax.
Operating profit vs Net profit
Net profit refers to the amount that a company is left with after deducting all expenses including interest and tax. For example, in the snapshot above, net profit is 4,702 million euros as compared to the operating profit of 7,972 million euros. This means that the total interest and tax expenses amounted to 7,972 less 4,702 million euros. Net profit which is also referred to as “bottom line” gives us a picture of the overall performance of the company and its management.
Exclusions from operating profit
There are several exclusions from operating profit because operating profit is calculated with the purpose of understanding the performance of a company’s core business only.
The revenue from the sale of an asset is not part of the operating profit. Similarly, investment income, interest income and debt interest expenses are not part of the company’s core business and therefore excluded from the calculation of operating profit.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ Bijal GANDHI Income statement
▶ Bijal GANDHI Revenue
▶ Bijal GANDHI Cost of goods sold
About the author
Article written in July 2021 by Bijal GANDHI (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2019-2022).


1 thought on “Operating Profit”
Comments are closed.