Hedging Strategies – Equities
This article written by Akshit GUPTA (ESSEC Business School, Master in Management, 2019-2022) presents the different hedging strategies based on option contracts.
Introduction
Hedging is a risk mitigation strategy used by investors reduce the risk in an existing investment. In financial markets, hedging is used as an effective tool by investors to minimize the risk exposure and maximize the returns for any investment in securities. Equity options are commonly used by investors / traders as hedging mechanisms due to their great flexibility (in terms of expiration date, moneyness, liquidity, etc.) and availability. Hedging does not eliminate the entire risk for any investment but often limits the potential losses that the investor can incur. Positions in equity options are used to offset the risk exposure in the underlying equity, another option contract or in any other derivative contract.
Different strategies used in hedging
There are many ways to hedge the exposure in any given security. Some of the most used hedging strategies for an exposure in equity includes the following:
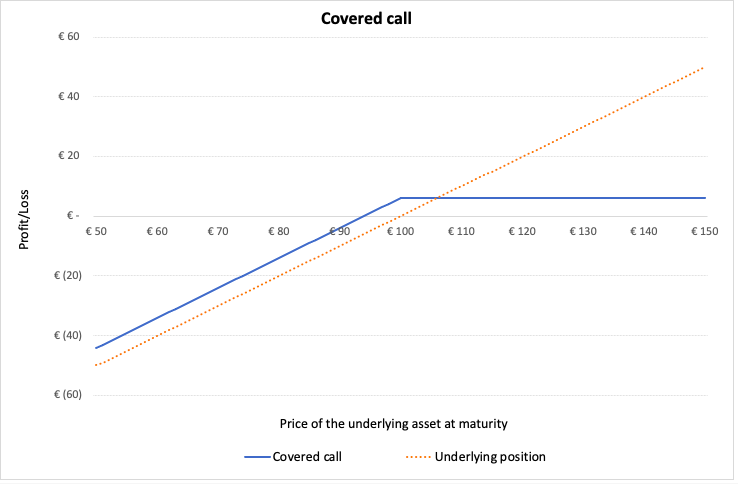
Writing a covered call
A call option gives the buyer of the option, the right but not the obligation, to buy a security at a fixed date and price defined in the contract. In a covered call, the investor writes (sells) a call option on the stock he holds in his portfolio. He earns the premium by writing the call option. Investors execute this strategy when they are bullish about the stock. The maximum payoff potential from this strategy is limited but the potential downside/losses is can be quite high (although limited).
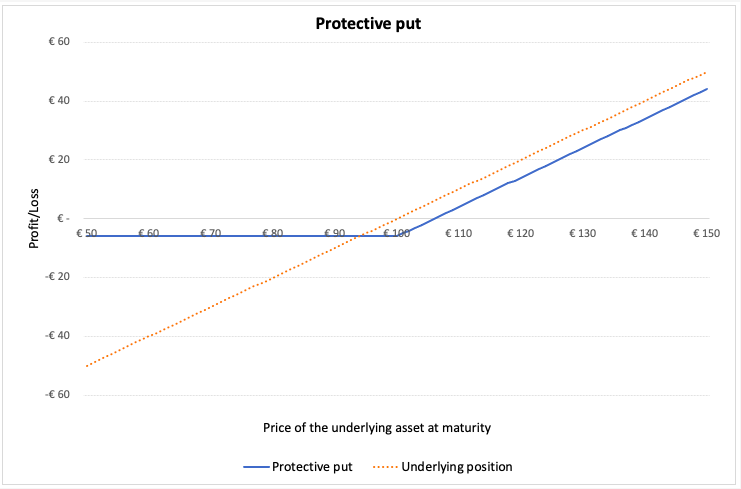
Buying a protective put
A put option gives the buyer of the option, the right but not the obligation, to sell a security at a fixed date and price defined in the contract. In a protective put, the investor buys a put option on the stock she holds in her portfolio. She pays the premium by buying the put option. Investors execute this strategy when they are bearish about the stock. The maximum payoff potential from this strategy is unlimited but the potential downside/losses is limited.
Spreads
Spreads are option hedging strategies where the investor/trader will take positions in multiple options of the same type (either call options or put options on the same underlying). The different types of spreads are mentioned below:
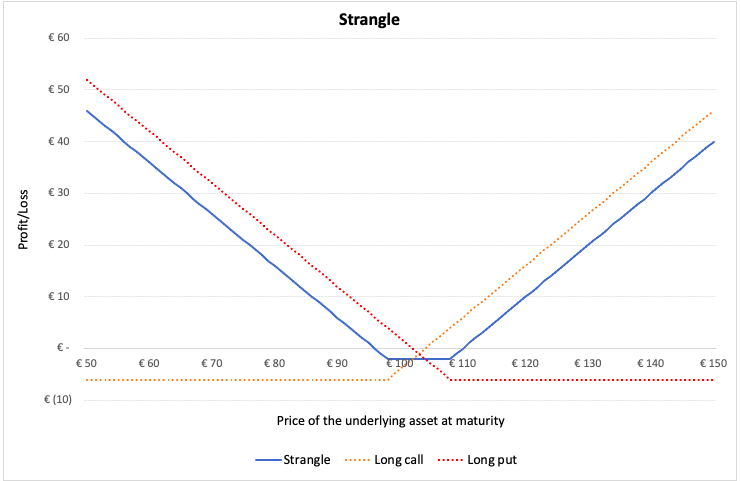
Strangle and Straddle
In a strangle, the investor buys a European call and a European put option, both at the same expiration date but different strike prices. To benefit from this strategy, the price of the underlying asset must move further away from the central value in either direction i.e., increase or decrease. If the stock prices stay at a level closer to the central value, the investor will incur losses. This strategy is suitable for investors who expect a huge price movement but are unsure of the direction of the movement.
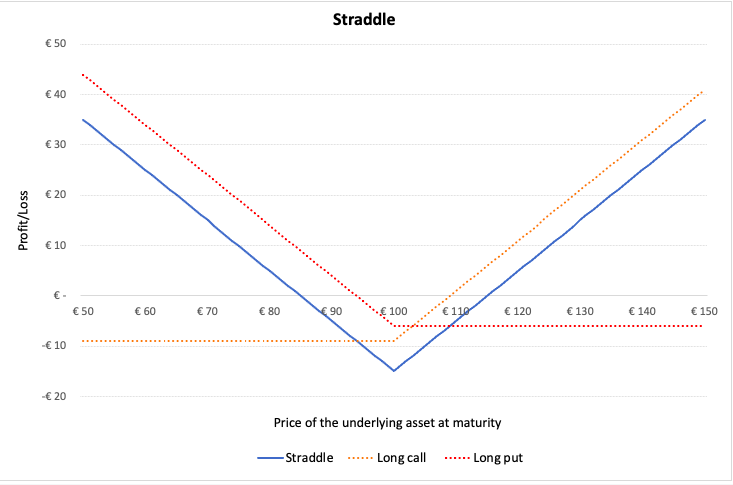
In a straddle, the investor buys a European call and a European put option, both at the same expiration date and at the same strike price. This strategy works in a similar manner like a strangle. However, the potential losses are a bit higher than incurred in a strangle if the stock price remains near the central value at expiration date.
Bull and Bear spreads
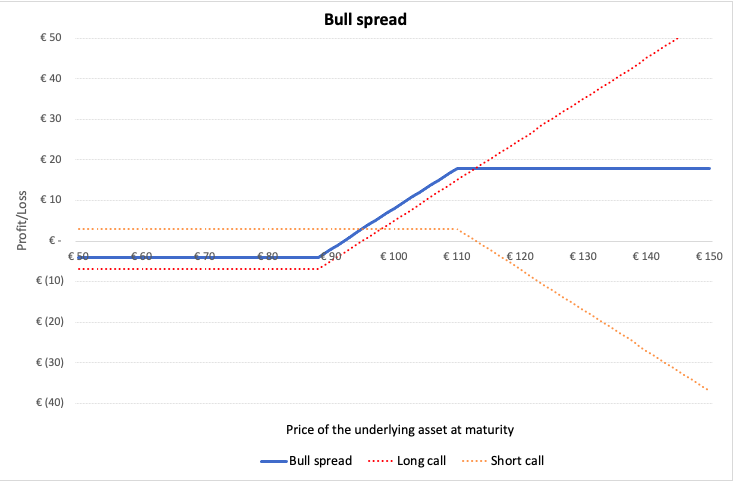
In a bull spread, the investor buys a European call option on a stock with strike price K1 and sells a call option on the same stock at strike price K2 (which is higher than K1) at the same expiration date. The investor forecasts the prices to go up and is bullish about the stock. The spread limits the potential downside risk on buying the call option, but also limits the potential profit by capping the upside. It Is used as an effective hedge to limit the losses.
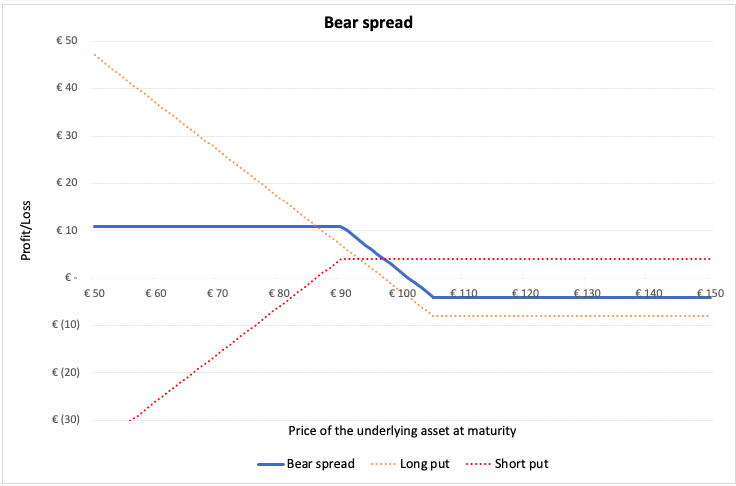
In a bear spread, the investor expects the prices of the stock to decline. In order to hedge against the downside, the investor buys a put option at strike price K2 and sells a put option at strike price K1, where K1 < K2. Initially, this strategy leads to a cash outflow since the put option is sold at a lower strike price, which results in lower premium.
Useful Resources
Hull J.C. (2015) Options, Futures, and Other Derivatives, Ninth Edition, Chapter 10 – Trading strategies involving Options, 276-295.
Investopedia Using Options as a Hedging Strategy
Related Posts
▶ Gupta A. Option Greeks – Delta
▶ Gupta A. History of Options markets
▶ Gupta A. Option Trader – Job description
▶ Gupta A. Options
About the author
Article written in September 2021 by Akshit GUPTA (ESSEC Business School, Master in Management, 2019-2022).

