
In this article, Snehasish CHINARA (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2022-2024) explains the intricate workings and transformative potential of Binance Coin (BNB), exploring its origins, utility, market dynamics, and future prospects of this cornerstone of the digital economy.
Historical context and background
Binance Coin (BNB) is one of the most prominent cryptocurrencies in the market, known for its unique utility and its connection to the world’s largest cryptocurrency exchange, Binance. Binance, founded by Changpeng Zhao (CZ) in 2017, quickly rose to prominence as one of the leading cryptocurrency exchanges globally. Its rapid growth can be attributed to several factors, including its user-friendly interface, wide range of supported cryptocurrencies, and a robust security system. Binance gained significant traction during the bull run of 2017, becoming the go-to platform for traders and investors seeking to capitalize on the burgeoning cryptocurrency market.
In July 2017, Binance conducted an Initial Coin Offering (ICO) to raise funds for the development of its platform and ecosystem. During the ICO, the exchange issued its native cryptocurrency, Binance Coin (BNB), which operates on the Ethereum blockchain as an ERC-20 token. The ICO was a massive success, raising $15 million within just a few weeks.
BNB was initially designed as a utility token to facilitate transactions on the Binance platform, offering users various benefits such as discounted trading fees and participation in token sales hosted on the exchange. Binance committed to using a portion of its profits to buy back and burn BNB tokens periodically, reducing the overall supply over time and potentially increasing its value.
As Binance continued to expand its services and offerings, the utility of BNB expanded beyond just a means of reducing trading fees. BNB became an integral part of the Binance ecosystem, serving as the native currency for various applications and services, including Binance Launchpad, Binance Smart Chain, Binance DEX (decentralized exchange), and Binance NFT marketplace, among others.
The introduction of Binance Smart Chain (BSC) in 2020 further elevated the importance of BNB in the cryptocurrency space. BSC, a blockchain platform compatible with Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), was developed to provide an alternative to Ethereum for decentralized finance (DeFi) applications and decentralized applications (DApps). BNB serves as the native currency of BSC, powering transactions and fueling the ecosystem’s growth.
BNB Logo

Source: Binance.
Figure 1. Key Dates in BNB History

Source: Yahoo! Finance.
Key features
- The mean
- The standard deviation (the squared root of the variance)
- The skewness
- The kurtosis.
- The long-term volatility (the unconditional standard deviation estimated over the entire period)
- The short-term volatility (the standard deviation estimated over the last three months)
- The Value at Risk (VaR) for the left tail (the 5% quantile of the historical distribution)
- The Value at Risk (VaR) for the right tail (the 95% quantile of the historical distribution)
- The Expected Shortfall (ES) for the left tail (the average loss over the 5% quantile of the historical distribution)
- The Expected Shortfall (ES) for the right tail (the average loss over the 95% quantile of the historical distribution)
- The Stress Value (SV) for the left tail (the 1% quantile of the tail distribution estimated with a Generalized Pareto distribution)
- The Stress Value (SV) for the right tail (the 99% quantile of the tail distribution estimated with a Generalized Pareto distribution)
Utility Token
BNB was initially designed as a utility token to facilitate transactions on the Binance platform. Users can utilize BNB to pay for trading fees, exchange fees, and various other services offered by Binance.
Discounted Fees
One of the primary benefits of holding BNB on the Binance exchange is the opportunity to receive discounts on trading fees. Binance offers users who pay their trading fees with BNB a significant discount, incentivizing its use within the platform.
Token Burn
Binance commits to using a portion of its profits to buy back and burn BNB tokens regularly. This token burning mechanism reduces the total supply of BNB over time, potentially increasing its scarcity and value.
Multiple Use Cases
BNB has expanded beyond its original utility and is now used for various purposes within the Binance ecosystem. It serves as the native currency for token sales on Binance Launchpad, transaction fees on Binance DEX, and participation in Binance NFT marketplace, among other applications.
Binance Smart Chain (BSC)
BNB is the native cryptocurrency of Binance Smart Chain, a blockchain platform compatible with Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). BSC offers low transaction fees and high throughput, making it an attractive option for decentralized applications (DApps) and decentralized finance (DeFi) projects.
Governance
BNB holders have the opportunity to participate in the governance of the Binance ecosystem. They can vote on proposals and decisions related to the development and direction of Binance, providing a degree of decentralization and community involvement.
Staking and Yield Farming
BNB holders can participate in staking and yield farming programs, allowing them to earn rewards or yield by locking up their BNB tokens and contributing to the security and operation of the network.
Use cases
Participation in Token Sales
BNB holders often have exclusive access to token sales hosted on the Binance Launchpad platform. These sales allow users to invest in promising blockchain projects at an early stage, with BNB serving as the primary currency for participation.
Payment Method
BNB can be used as a payment method for various goods and services, both online and offline. Several merchants and businesses accept BNB as a form of payment, enabling users to utilize their cryptocurrency holdings for everyday transactions.
Binance Ecosystem Services
BNB is utilized within various services and applications offered by the Binance ecosystem. This includes decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), non-fungible token (NFT) marketplaces, and more. BNB serves as the native currency for transactions, governance, and incentives within these platforms.
Cross-Chain Compatibility
With the introduction of Binance Smart Chain (BSC), BNB gained cross-chain compatibility, enabling it to be used in decentralized applications (DApps) and DeFi protocols across different blockchain networks. This expansion of utility enhances the interoperability and flexibility of BNB as a cryptocurrency.
Technology and underlying blockchain
Binance Coin (BNB) operates on two primary blockchain networks: the Ethereum blockchain and the Binance Smart Chain (BSC). Initially launched as an ERC-20 token on the Ethereum blockchain, BNB has since undergone a significant expansion with the introduction of the Binance Smart Chain. The Ethereum-based BNB tokens are utilized for various functions within the Binance ecosystem, including trading fee discounts, participation in token sales, and payments. However, to address scalability and transaction cost concerns, Binance developed the Binance Smart Chain, a parallel blockchain compatible with Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). BSC combines high performance with low transaction fees, offering a viable alternative for decentralized applications (DApps) and decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols. BNB serves as the native currency of BSC, facilitating transactions, powering smart contracts, and providing liquidity across the Binance Smart Chain ecosystem. BSC employs a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, where validators stake BNB to secure the network and validate transactions. This hybrid approach leverages the benefits of both decentralization and efficiency, making BNB and the Binance Smart Chain integral components of the rapidly evolving blockchain landscape.
Supply of coins
The total supply of Binance Coin (BNB) is capped at 200 million tokens. However, BNB’s initial distribution was structured to release a portion of this supply gradually over time. During its initial coin offering (ICO) in July 2017, Binance allocated 50% of the total token supply to the public sale, representing 100 million BNB tokens. The remaining 50% was split among the Binance team, early investors, and strategic partners, with a significant portion earmarked for ecosystem development and marketing efforts. Notably, Binance committed to periodic token burns, where a portion of BNB tokens used to pay for trading fees on the Binance exchange is systematically removed from circulation and permanently destroyed. These token burns serve to reduce the overall supply of BNB over time, potentially increasing its scarcity and value. As of [current date], multiple token burns have occurred, steadily decreasing the circulating supply of BNB and contributing to its deflationary nature. Additionally, BNB’s migration from the Ethereum blockchain to its own blockchain, Binance Chain, introduced a new mechanism for token issuance and governance, further shaping the supply dynamics of BNB within the Binance ecosystem.
Historical data for Binance Coin (BNB)
How to get the data?
The Binance Coin (BNB) is popular cryptocurrency on the market, and historical data for the Binance Coin (BNB) such as prices and volume traded can be easily downloaded from the internet sources such as Yahoo! Finance, Blockchain.com & CoinMarketCap. For example, you can download data for Binance Coin (BNB) on Yahoo! Finance (the Yahoo! code for Binance Coin is BNB-USD).
Figure 2. Binance Coin (BNB) data
Source: Yahoo! Finance.
Historical data for Binance Coin (BNB) market prices
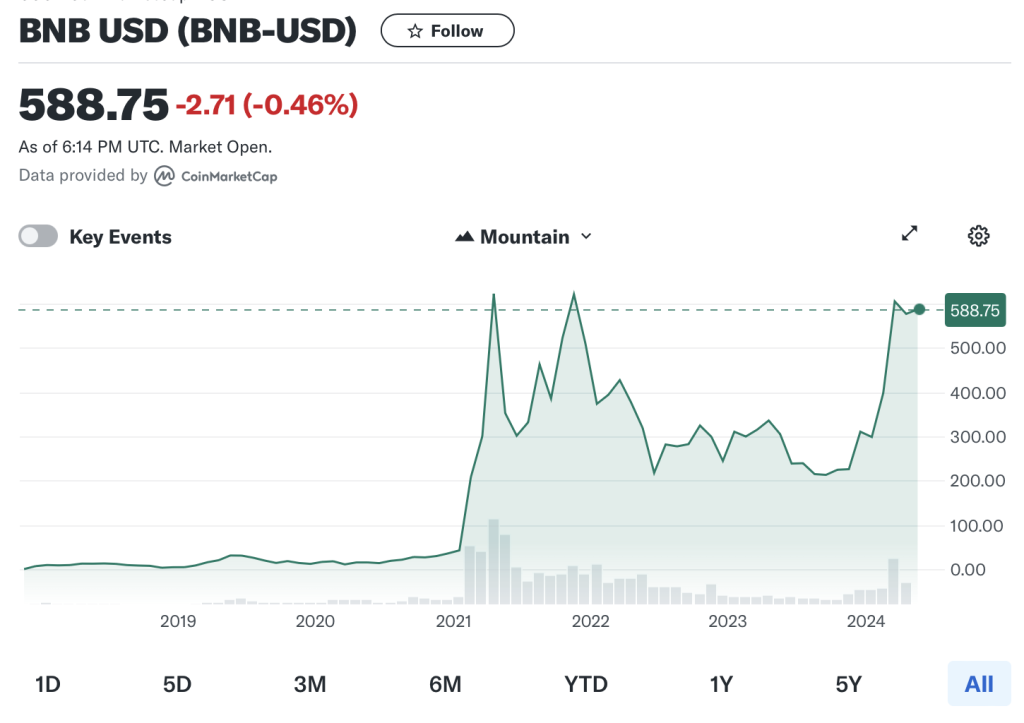
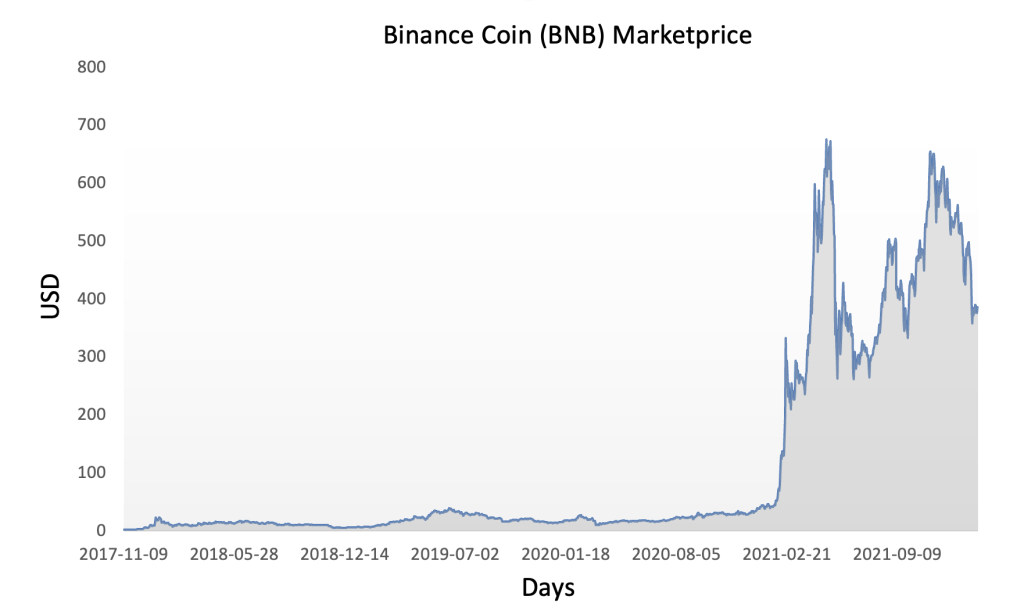
Binance Coin (BNB) has experienced significant volatility and price fluctuations since its inception in 2017. Initially launched at a price of around $0.10 during its ICO, BNB quickly gained traction and surged to an all-time high of over $40 in January 2018, fueled by the widespread adoption of the Binance exchange and the overall bullish sentiment in the cryptocurrency market at the time. However, like many other cryptocurrencies, BNB subsequently underwent a prolonged bear market, with its price plummeting to single-digit levels by the end of 2018. The following years saw periods of both growth and consolidation for BNB, with its price closely tied to developments within the Binance ecosystem, regulatory developments, and broader market trends. Notable milestones, such as the launch of Binance Smart Chain (BSC) and the subsequent rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, have often coincided with bullish movements in BNB’s price. As of the latest data, BNB has demonstrated resilience and continued to maintain its position among the top cryptocurrencies by market capitalization, reflecting its enduring relevance and utility within the digital asset landscape.
Figure 5 below represents the evolution of the price of Binance Coin (BNB) in US dollar over the period November 2017 – May 2024. The price corresponds to the “closing” price (observed at 10:00 PM CET at the end of the month).
Figure 3. Evolution of Binance Coin (BNB) price.
Source: Yahoo! Finance.
R program
The R program below written by Shengyu ZHENG allows you to download the data from Yahoo! Finance website and to compute summary statistics and risk measures about the Binance Coin (BNB).

Data file
The R program that you can download above allows you to download the data for the Binance Coin (BNB) from the Yahoo! Finance website. The database starts on November, 2017.
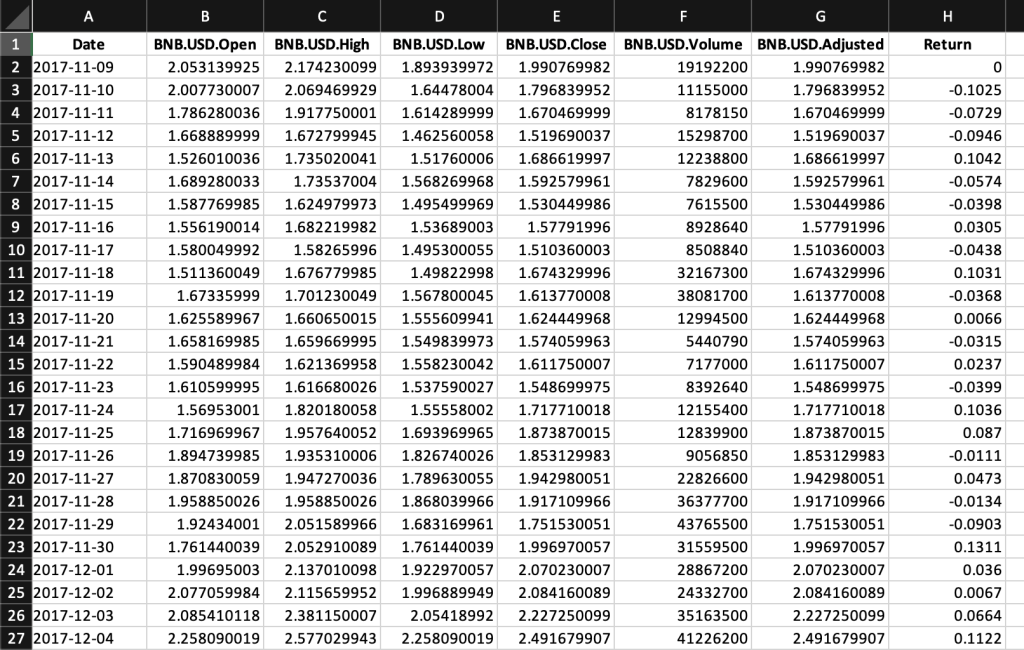
Table 1 below represents the top of the data file for the Binance Coin (BNB) downloaded from the Yahoo! Finance website with the R program.
Table 1. Top of the data file for the Binance Coin (BNB)
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
Python code
You can download the Python code used to download the data from Yahoo! Finance.

Python script to download Binance Coin (BNB) historical data and save it to an Excel sheet::
import yfinance as yf
import pandas as pd
# Define the ticker symbol for Binance Coin (BNB)
Binance_ticker = “BNB-USD”
# Define the date range for historical data
start_date = “2020-01-01”
end_date = “2022-01-01”
# Download historical data using yfinance
Binance_data = yf.download(Binance_ticker, start=start_date, end=end_date)
# Create a Pandas DataFrame from the downloaded data
Binance_df = pd.DataFrame(Binance_data)
# Define the Excel file path
excel_file_path = “Cardano _historical_data.xlsx”
# Save the data to an Excel sheet
Binance_df.to_excel(excel_file_path, sheet_name=” Binance Historical Data”)
print(f”Data saved to {excel_file_path}”)
# Make sure you have the required libraries installed and adjust the “start_date” and “end_date” variables to the desired date range for the historical data you want to download.
Evolution of the Binance Coin (BNB)
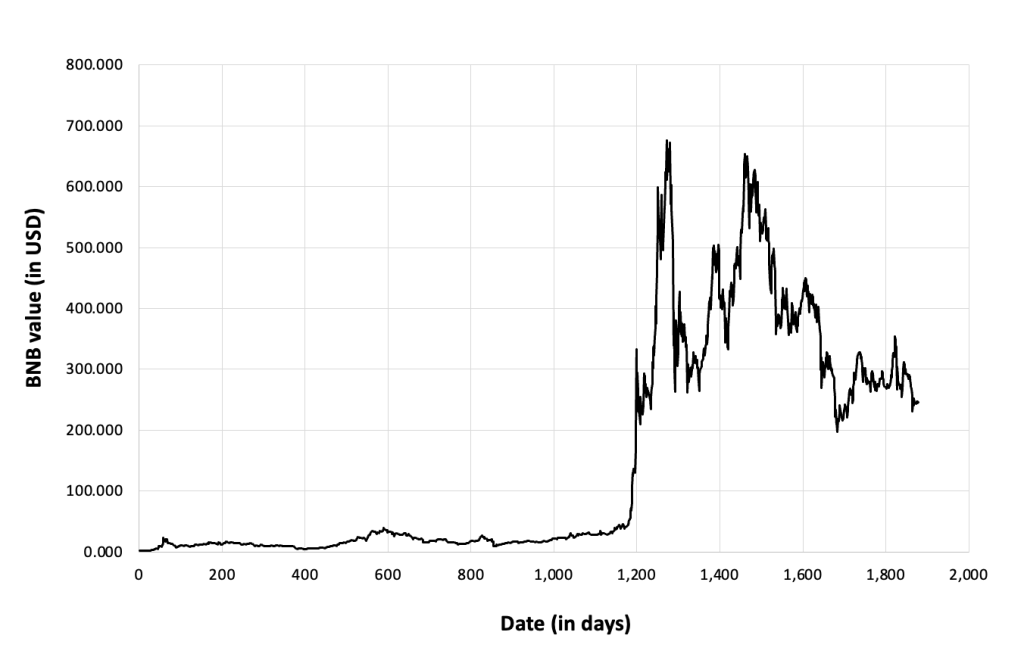
Figure 4 below gives the evolution of the Binance Coin (BNB) on a daily basis.
Figure 4. Evolution of the Binance Coin (BNB)
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
Figure 5 below gives the evolution of the Binance Coin (BNB)returns from November, 2017 to May, 2024 on a daily basis.
Figure 5. Evolution of the BNB returns.

Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
Summary statistics for the Binance Coin (BNB)
The R program that you can download above also allows you to compute summary statistics about the returns of the Binance Coin (BNB).
Table 2 below presents the following summary statistics estimated for Binance Coin (BNB):
The mean, the standard deviation / variance, the skewness, and the kurtosis refer to the first, second, third and fourth moments of statistical distribution of returns respectively.
The mean, the standard deviation / variance, the skewness, and the kurtosis refer to the first, second, third and fourth moments of statistical distribution of returns respectively.
Table 2. Summary statistics for Binance Coin (BNB).
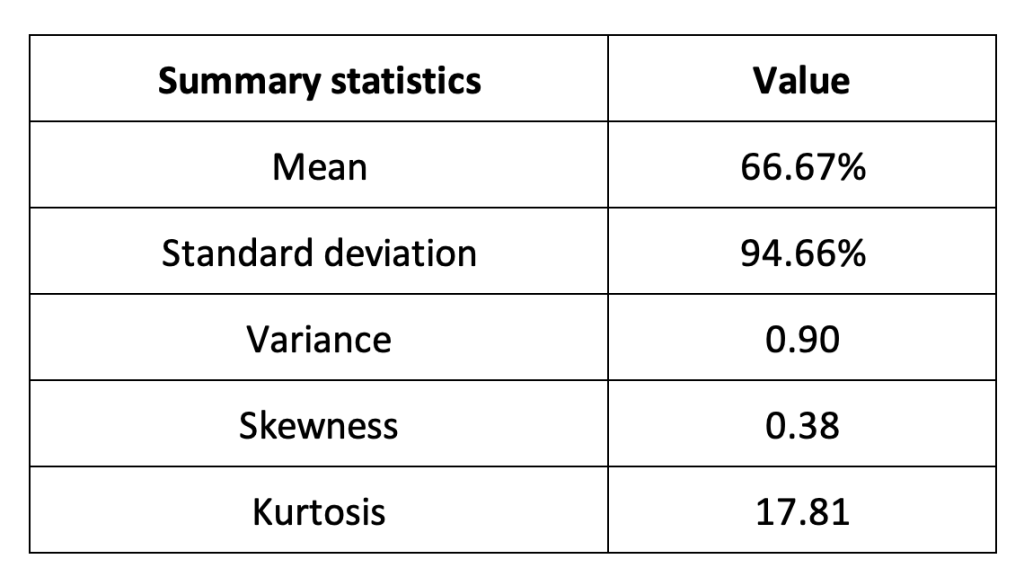
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
Statistical distribution of the Binance Coin (BNB) returns
Historical distribution
Figure 6 represents the historical distribution of the Binance Coin (BNB) daily returns for the period from November, 2017 to May, 2024.
Figure 6. Historical BNB distribution of the returns.
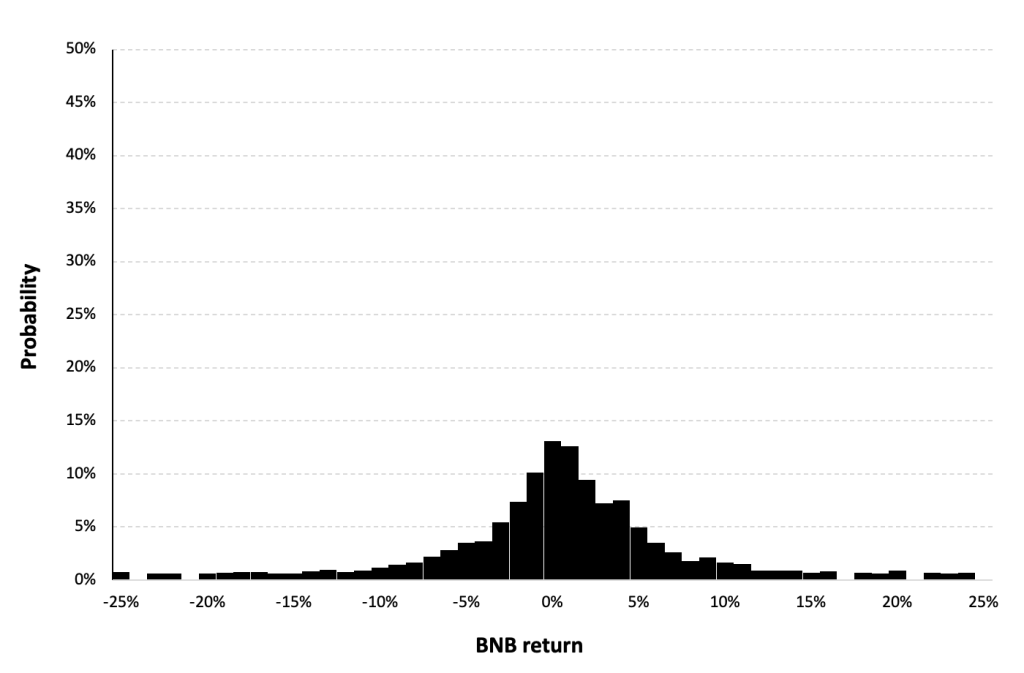
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
Gaussian distribution
The Gaussian distribution (also called the normal distribution) is a parametric distribution with two parameters: the mean and the standard deviation of returns. We estimated these two parameters over the period from November 2017 to May 2024.
Figure 7 below represents the Gaussian distribution of the Binance Coin (BNB)daily returns with parameters estimated over the period from November 2017 to May 2024.
Figure 7. Gaussian distribution of Binance Coin (BNB) returns.
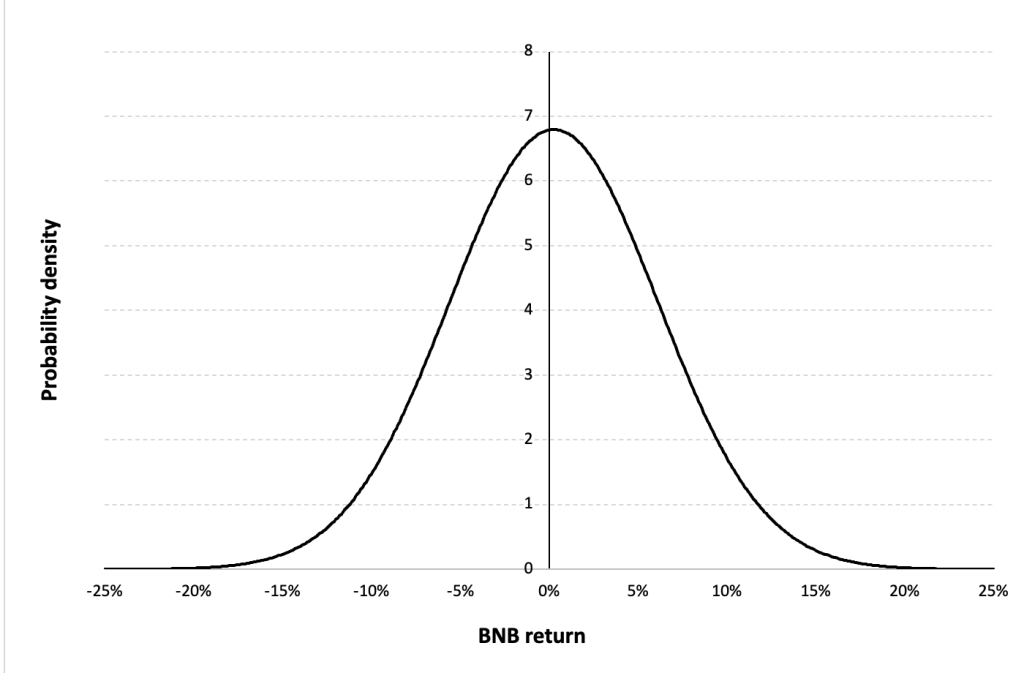
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
Risk measures of the Binance Coin (BNB)returns
The R program that you can download above also allows you to compute risk measures about the returns of the Binance Coin (BNB).
Table 3. Risk measures for Binance Coin (BNB).
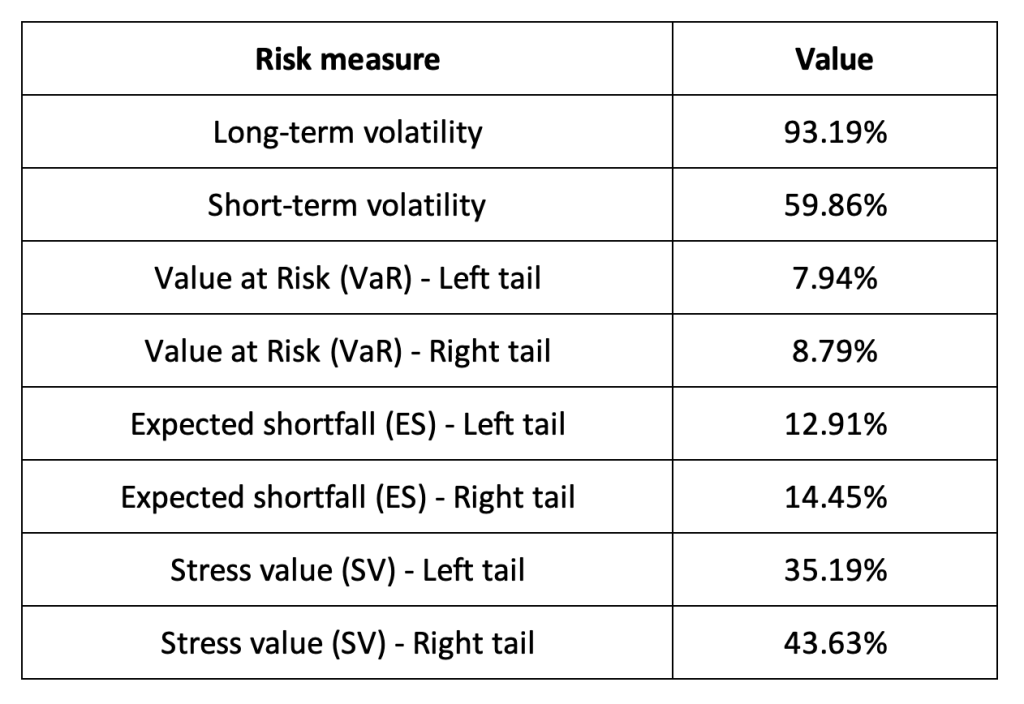
Source: computation by the author (data: Yahoo! Finance website).
The volatility is a global measure of risk as it considers all the returns. The Value at Risk (VaR), Expected Shortfall (ES) and Stress Value (SV) are local measures of risk as they focus on the tails of the distribution. The study of the left tail is relevant for an investor holding a long position in the Binance Coin (BNB)while the study of the right tail is relevant for an investor holding a short position in the Binance Coin (BNB).
Why should I be interested in this post?
This post offers a captivating exploration of Binance Coin (BNB), tailored for both newcomers to the cryptocurrency realm and seasoned enthusiasts alike. It delves into the innovative utility and multifaceted ecosystem surrounding BNB, shedding light on its pivotal role within the Binance platform and beyond. By dissecting BNB’s diverse applications, including trading fee discounts, participation in token sales, and ecosystem services like decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs), readers can grasp the breadth of opportunities presented by this digital asset. Additionally, the post delves into the historical price data and supply dynamics of BNB, providing valuable insights for investors, traders, and stakeholders navigating the volatile cryptocurrency market. Whether you’re intrigued by the potential of utility tokens or seeking to harness the power of the Binance ecosystem, this post offers an insightful journey into the significance and possibilities of Binance Coin in shaping the future of decentralized finance and digital economies.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
About cryptocurrencies
▶ Snehasish CHINARA Bitcoin: the mother of all cryptocurrencies
▶ Snehasish CHINARA How to get crypto data
▶ Alexandre VERLET Cryptocurrencies
About statistics
▶ Shengyu ZHENG Moments de la distribution
▶ Shengyu ZHENG Mesures de risques
▶ Jayati WALIA Returns
Useful resources
Academic research about risk
Longin F. (2000) From VaR to stress testing: the extreme value approach Journal of Banking and Finance, N°24, pp 1097-1130.
Longin F. (2016) Extreme events in finance: a handbook of extreme value theory and its applications Wiley Editions.
Data
Yahoo! Finance Historical data for Binance Coin (BNB)
CoinMarketCap Historical data for Binance Coin (BNB)
About the author
The article was written in May 2024 by Snehasish CHINARA (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2022-2024).
