Financial markets are filled with stories of bubbles, crashes, and periods of extreme optimism or pessimism. Yet human nature remains surprisingly constant, as we are prone to believe that “this time is different.” Sir John Templeton’s famous quote reminds investors that historical patterns, lessons, and cautionary tales are often ignored in the face of conviction, novelty, or excitement.
In this article, Hadrien Puche (ESSEC, Grande École, Master in Management, 2023 / 2027) comments on this quote, exploring why believing that history will not repeat itself can be one of the most dangerous biases in investing.

About Sir John Templeton
Sir John Templeton

Source: John Templeton Foundation
Sir John Templeton was a legendary investor and philanthropist, renowned for his disciplined approach to value investing, a strategy that involves seeking out companies, markets or assets that are deeply undervalued compared to their true long term potential. Rather than following the crowds, value investors analyze the fundamentals of companies (earnings, balance sheets, management…) to make investment decisions.
Born in 1912 in the United States, he built a global investment career by seeking opportunities where others saw only risk. In 1939, at the outbreak of WW2, he borrowed money to buy shares when the market was at its lowest, including shares in 34 bankrupted companies, only 4 of which turned out to be worthless. In 1954, he founded the Templeton Growth Fund, a diversified mutual fund that sought bargains in depressed markets around the world.
Although the exact origin of this quote is unclear, it reflects Templeton’s belief that market cycles tend to repeat themselves. Investors often dismiss historical lessons when conditions seem unprecedented. In periods of optimism, they believe innovation or policy changes make downturns impossible. But Templeton argued this mindset is even more dangerous during crises: each time recession, war or financial turmoil hits, people insist the situation is entirely different from past downturns and ignore proven patterns of recovery. This leads to panic selling and missed opportunities at the moment of greatest long term value. Markets may change, but human psychology and systemic risks tend to repeat in predictable ways.
Analysis of the quote
At the heart of Templeton’s statement lies a timeless observation about human behavior. Investors frequently convince themselves that new technologies, policies, or financial instruments render past risks irrelevant. They see bubbles in real time but rationalize them as unique and unrepeatable events.
This attitude is perilous. By assuming “it is different this time,” investors often take excessive risk, neglect proper analysis, and overvalue assets. History shows that the same patterns, including leverage, speculation, overconfidence, and panic, tend to recur regardless of the era or instrument. The global financial crisis of 2008, the dot com bubble of 2000, and the 1929 crash illustrate the consequences of ignoring these lessons.
Templeton’s advice is simple yet profound. Treat each investment with humility, respect historical precedents, and avoid the hubris of believing novelty exempts you from risk. Recognizing that “this time” may not be different is not a rejection of innovation or change. It is an acknowledgment of patterns, limits, and the laws of risk.
Economic and financial concepts related to the quote
Market cyclicity
Financial markets naturally tend to move in cycles. Bull markets are followed by corrections; recessions are followed by recoveries. This inherent cyclicity explains why Templeton’s warning is so critical: periods of euphoria are often followed by downturns regardless of how unique the circumstances appear.
This cyclical pattern is most vividly illustrated by the formation of financial bubbles; situations where asset prices rise far above their intrinsic value due to speculation and excessive optimism. Investors frequently underestimate these cycles when past trends have been unusually profitable. For example, during the dot com boom, many believed that technology’s growth would render traditional valuation metrics irrelevant. The result was a speculative bubble followed by a sharp market correction.
As documented by economist Charles P. Kindleberger in his classic work, Manias, Panics, and Crashes: A History of Financial Crises, these bubbles follow a predictable, recurring pattern.
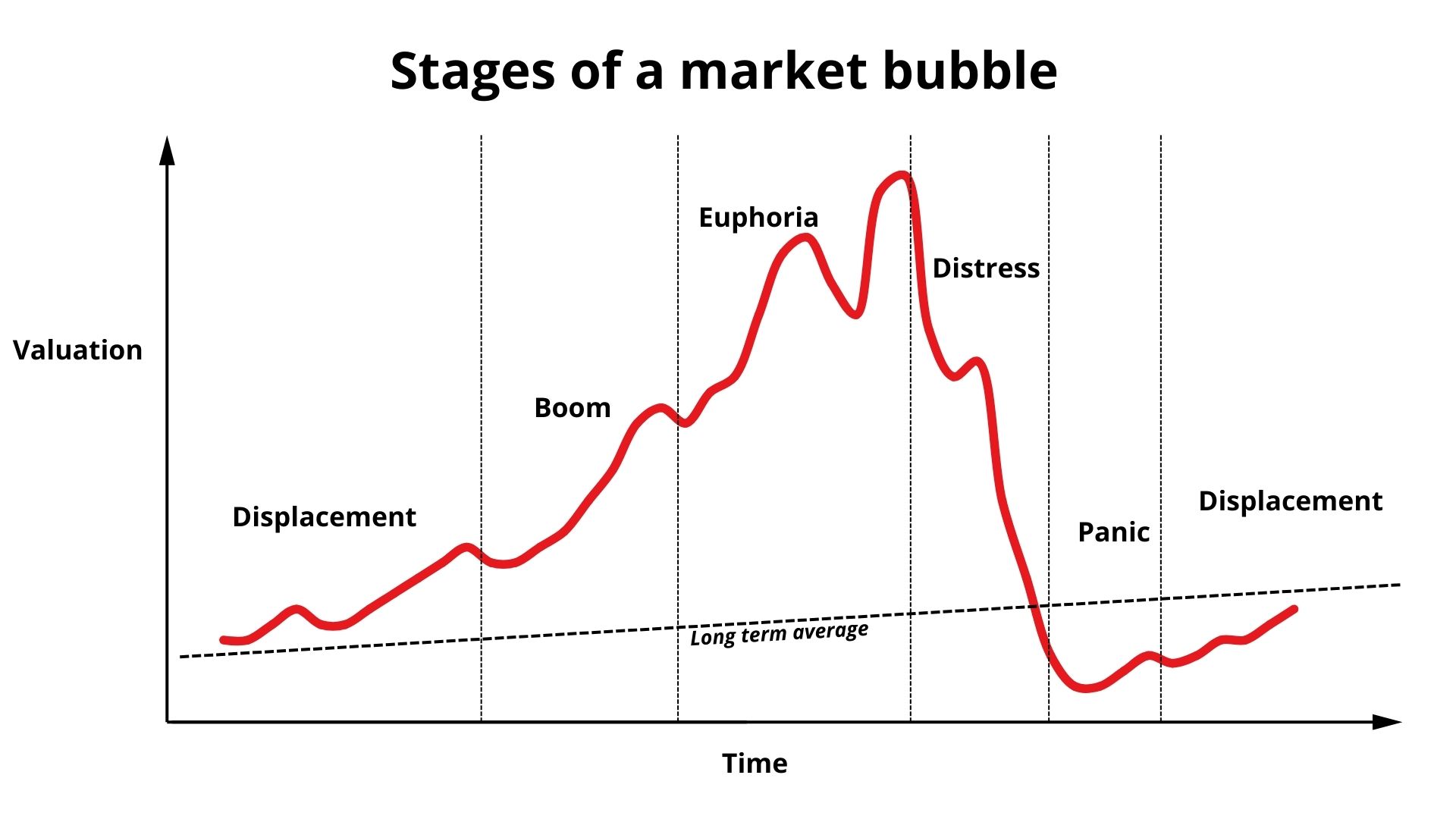
He argued that financial crises typically progress through phases of displacement, boom, euphoria, and eventually distress and panic. By ignoring history and assuming that novelty exempts them from these fundamental laws, investors risk participating in the formation and painful bursting of the bubble.
Understanding market cyclicity encourages investors to remain vigilant, diversify their holdings, and respect the natural flow of markets even when conditions seem unprecedented.
The Tranquility Paradox and Minsky’s Hypothesis
The tranquility paradox describes a simple but dangerous human habit: when the economy feels stable for long enough, we start believing that this stability will last forever. Rising markets, low volatility, and strong indicators give investors a sense of comfort. They begin to assume that risk has disappeared, that the system is safer than ever, and that the future will look just like the present.
This mindset is exactly what Templeton warned against, and it sits at the center of economist Hyman P. Minsky’s Financial Instability Hypothesis. Minsky’s core idea is counterintuitive: periods of stability create the conditions for instability. In other words, stability is not the end of risk, it’s the beginning of the next one.
The graph below illustrates this dynamic. When things look calm for long enough, investors slowly shift from safe financing to riskier forms, without even realizing it.
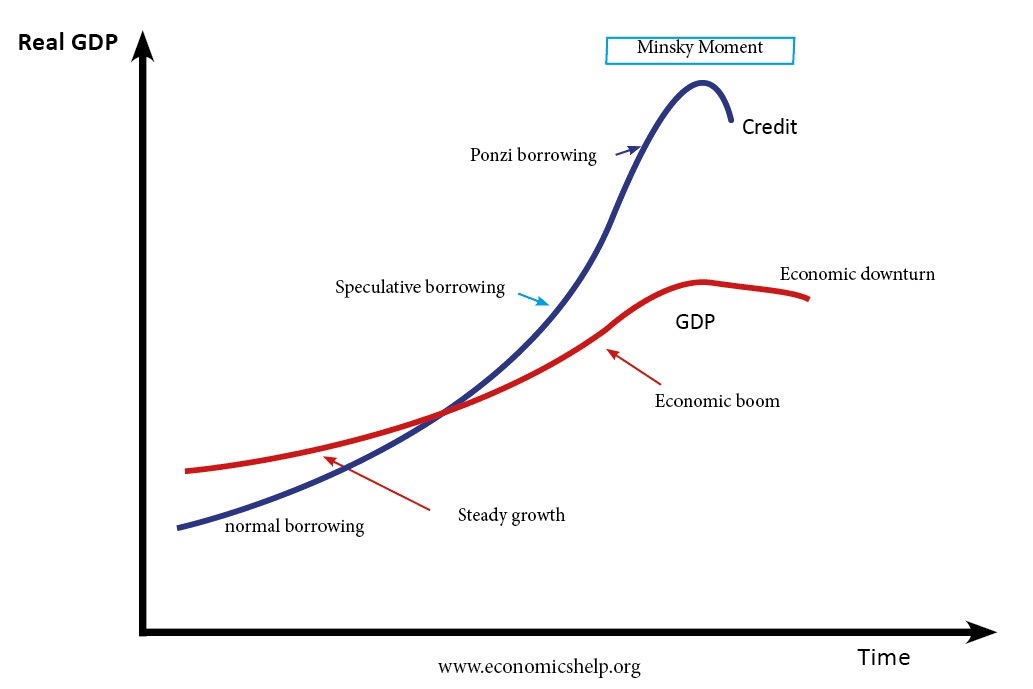
Minsky identified three stages:
- Hedge financing, the safe zone: Cash flow covers both interest and principal.
- Speculative financing, the risky zone: Cash flow covers interest only; principal is rolled over.
- Ponzi financing, the danger zone: Cash flow covers neither interest nor principal. Survival depends on continuous borrowing or rising asset prices.
Over time, more and more activity moves into those speculative and Ponzi stages, pushing the system closer to what Minsky called a Minsky Moment, the sudden realization that debts can’t be serviced, asset values drop, confidence collapses, and panic selling begins.
This is the heart of the paradox: calm markets create overconfidence, overconfidence leads to excessive risk taking, and excessive risk taking triggers the crisis. Understanding this pattern helps investors maintain discipline, stay cautious during good times, and avoid falling for the seductive idea that “this time is different.”
Historical bias in personal finance
Templeton’s warning is not limited to market professionals; personal finance and long term investing are equally susceptible to the belief that history will not repeat itself. This risk is rooted in historical bias, a cognitive shortcut where many individuals assume that high past returns on stock indexes, real estate, or other assets will continue indefinitely, often ignoring the possibility of lower future growth or structural changes in the economy.
This bias, a form of extrapolation bias, can be highly dangerous in retirement planning, risk allocation, and portfolio construction. Relying solely on historical equity returns may lead to severe overestimation of future wealth and underestimation of risks during periods of low growth or inflation.
As articulated by economist Burton Malkiel in A Random Walk Down Wall Street, the historical record provides valuable context, but it must not be treated as a definitive forecast. Malkiel’s work supports the idea that, in an efficient market, all available information is already reflected in current prices, meaning past price movements hold no predictive power for the future.
Therefore, Templeton encourages reflection: a disciplined investor balances cautious optimism about the future with a realistic understanding of historical realities, recognizing that past performance of market indexes does not guarantee future results.
My opinion about this quote
Templeton’s insight is essential for both students and seasoned professionals. It serves as a reminder that neither euphoria nor fear should dictate investment decisions. Markets will always fluctuate, and history often rhymes if it does not repeat exactly.
However, it is also true that sometimes conditions are different, and excessive caution can prevent individuals from capitalizing on genuine opportunities. Innovation, technological change, and macroeconomic shifts can justify deviations from historical trends. The challenge lies in distinguishing between real novelty and wishful thinking.
In personal finance, this principle is particularly relevant. Many investors assume that past returns on broad indexes such as the S&P 500 are a reliable guide for the future. Structural changes, low interest rates, and demographic shifts may produce different outcomes.
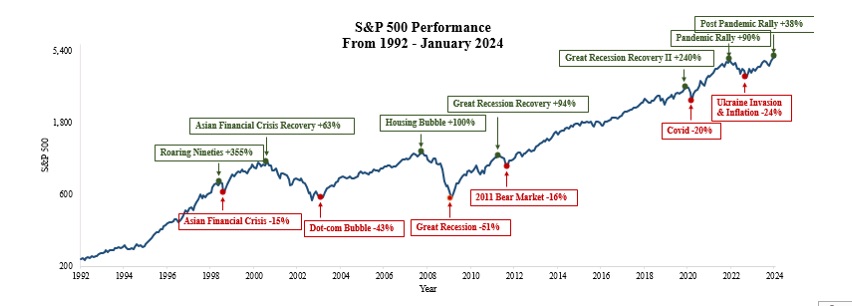
Balancing historical awareness with flexibility and critical thinking is the essence of sound investing.
Why should you be interested in this post?
Templeton’s warning is not only a lesson in investing. It is a lesson of humility, discipline, and critical thinking. Believing “this time is different” can blind both students and professionals to risks, patterns, and opportunities. Studying history, understanding cycles, and acknowledging psychological biases improves decision making in finance and beyond.
Whether you are building a portfolio, analyzing market trends, or planning for the future, this insight encourages you to respect the lessons of the past while remaining vigilant and adaptable.
Related posts
- All posts about quotes
- Behavioral finance and investment psychology
- In investing, what is comfortable is rarely profitable
Useful resources
Investment Wisdom & Discipline
These resources provide practical advice on long term, non emotional investing and avoiding market fads.
- Templeton, John. The Templeton Plan.
- Malkiel, Burton G. A Random Walk Down Wall Street.
History of Financial Crises
These essential books and papers explain why markets crash and the patterns those crises follow.
- Kindleberger, Charles P. (1978). Manias, Panics, and Crashes: A History of Financial Crises.
- Minsky, Hyman P. (1992). The Financial Instability Hypothesis, Working Paper No. 74, Jerome Levy Economics Institute.
Market Psychology & Valuation
These sources examine the role of human behavior, psychology, and valuation issues in speculative bubbles.
- Shiller, Robert. Irrational Exuberance.
- Blanchard, Olivier J., and Mark W. Watson. (1982). “Bubbles, Rational Expectations and Financial Markets.”
- Tirole, Jean. (1982). On the Possibility of Speculation under Rational Expectations, Econometrica, 50(5) 1163–1181.
About the Author
This article was written in December 2025 by Hadrien PUCHE (ESSEC Business School, Grande École Program, Master in Management, 2023-2027).
▶ Discover all articles by Hadrien PUCHE
