Regulations in financial markets
This article written by Akshit Gupta (ESSEC Business School, Master in Management, 2022) presents the regulations that exist in financial markets.
Definition of financial regulation
Financial regulation is a type of regulations or laws that help in maintaining the stability, integrity and transparency of the financial system of a country by subjecting financial institutions to several set of requirements, procedures and guidelines and ensuring adherence to such rules.
Supervision involves monitoring the performance and daily operations of the financial system in order to ensure its compliance with the rules and regulations specified under the financial framework and keep a check on the safety and financial health of the system. Thus, supervision is a part of the financial regulation framework and is needed to ensure the compliance of different parts present within the financial system including financial institutions, investment firms, banks etc. with the regulations.
Several kinds of financial regulations have been put into place by different countries in order to ensure fair and smooth functioning of the financial systems. The primary set of financial regulations includes:
Banking regulations
Banking regulations have been put into place to strengthen the global banking system and ensure its smooth and coordinated functioning. Basel Norms referred to as International banking regulations were introduced by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision as part of a coordinated effort to fulfil the gap between the different banking regulations and provide a platform for the respected parties to mitigate risk and ensure smooth functioning of the financial systems.
Preventing systematic risk
Systematic risk refers to the risk to the health of the entire financial system of an economy sparked by the failure of one or more financial institutions. With the global financial markets becoming more integrated, the financial institutions have become more inter-connected and dependent on each other. The complex financial structure of companies can be affected severely if a single company faces any disruption. Financial regulations are brought into enforcement to oversee and prevent such systematic risks from happening and affecting the health and integrity of the entire financial system.
Insider trading
Illegal Insider Trading refers to the use of material non-public information by an individual or a group of people to enter into unfair trades and gain illicit profits by breaching the trust and confidence of other investors. For example, Ivan Boesky, an infamous stock trader in the USA, was charged by SEC against allegations of trading in companies, that are about to undergo an M&A activity, with the use of insider information. He was sentenced to 3 years of imprisonment with a fine amounting to $100 million. Insider trading carries serious repercussions in today’s financial system, and stringent financial regulations have been implemented to avoid such incidents from happening.
Dispute resolution
Financial regulations help in the effective dispute resolutions between investors and entities or amongst entities in form of monetary and business disputes by means of arbitration processes. Several regulatory bodies like the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau in USA have been raised up within the financial regulation framework which acts as a mediation platform between different parties and help in implementing resolution controls and plans.
Investor protection
Financial regulations have been set up to protect the rights of every investor present in the financial system by bringing in better transparency and enhancing the quality of services offered to investors by different institutions. Standardized rules and procedures have been designed for the financial products offered by various investment management firms to offer investors with an equal base to evaluate the different product offerings. As part of a legislative framework to protect investor interest and promote transparency in the marketplace, Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MIFID II) was implemented by the European Union in 2018 to regulate the financial markets and ensure investor protection by safeguarding their rights. The regulation aims to promote better transparency by regularizing unorganized trading activities and transactions that were earlier not captured within the earlier financial system. Also, the directive aims to strengthen the potential risk mitigation strategies for investments done in the modern marketplace, using high frequency trading or algorithm-based trades, by means of implementing circuit breakers.
Objectives of financial regulation
Financial regulations serve as basic code of conduct that is required to be followed by all the market participants with a primary purpose of ensuring market integrity and stability. Different countries have several financial regulatory institutions that ensure that the markets function in a transparent way and the following objectives for setting up the regulations have been achieved:
- Maintaining stability and integrity
- Improving market confidence
- Bringing fairness and transparency
- Enhancing consumer protection
- Ensuring compliance with rules and procedures
- Preventing frauds
Structure of supervision
Over the past few decades, many reforms have been passed by different countries to ensure the smooth functioning of financial systems in this rapidly evolving and integrating global markets. The structure of supervision of the financial markets differ from country to country, but the broader framework behind the structure is primarily defined by unified global bodies (like the Basel Committee for supervision) and adherence to these structures is essential for every financial system.
We deal below with two examples: France and the United States of America.
Organization of financial regulation in France
In France, the following structure of hierarchy is followed to ensure smooth functioning of the financial system:
European Central Bank (ECB)
The European Central Bank has the primary responsibility to supervise all the 6000 banks operating in the euro zone within the defined framework of Single Supervisory Mechanism (SSM) under the European Union Law.
L’Autorité de contrôle prudentiel et de résolution (ACPR)
The ACPR is an institution integrated under the Banque de France and acts as a Lead Bank Supervisor for the French financial system. The ACPR has been set up with the primary function of supervising, monitoring and controlling the French financial system including its participants and ensuring stability therein. It has the authority to grant licenses to financial institutions and at the same time impose sanctions for any misconducts under the broad framework of its statutory powers.
L’Autorité des marchés financiers (AMF)
The AMF is an independent financial institution and administrative authority which possesses regulatory powers over the financial and banking industry in France. It was created under the Financial Security Act of 2003 with the primary purpose of ensuring protection of investor interest and smooth operations within the financial markets.
Organization of financial regulation in the United States of America
The figure below presents the structure for supervision within the United States of America. This figure illustrates the complexity of the supervision with many national and state regulators.
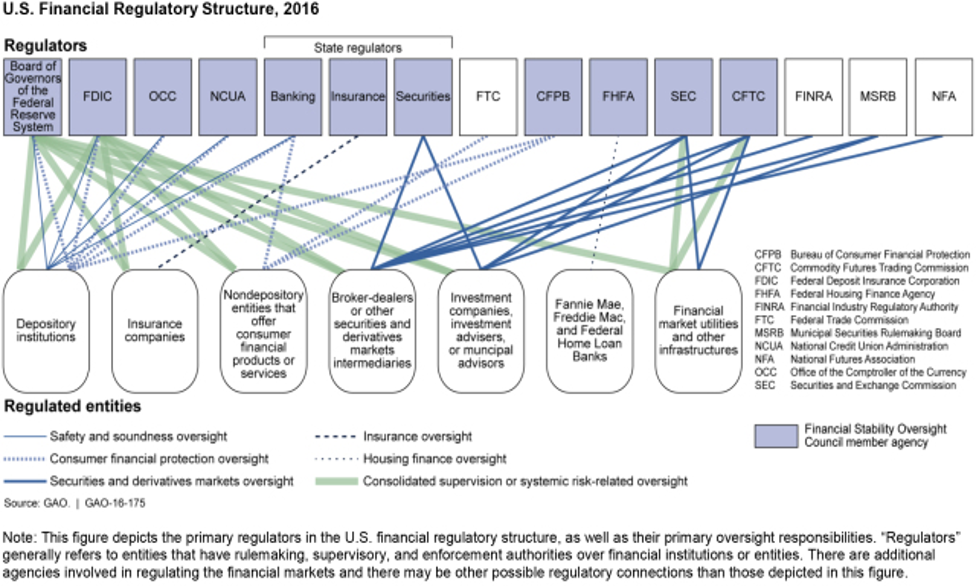
Source:https://blog.gao.gov/2016/07/21/6-years-after-dodd-frank-oversight-of-financial-services-industry-still-needs-streamlining/
Securities Exchange Commission (SEC)
The Securities and Exchange Commission is a federal agency responsible for overseeing and administering the financial market’s laws and regulations in United States of America. It was created in 1934 under the Securities Exchange Act as part of a response measure to revive the financial markets in USA following the Great Repression that took place after the stock market crash of 1929.
Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC)
The Commodity Futures Trading Commission was founded in 1975 as a federal agency regulating and supervising the activities in the commodity and the options market in the US financial industry. The commission was founded under the Commodity Futures Trading Commission Act of 1974 and has the primary objective of maintaining the integrity and efficiency of the commodity market in the USA. It is also embodied with the task of ensuring investor protection and safety from any illegal and fraudulent practices.
Movies about Financial Regulation In Financial Markets
The Wolf of Wall Street – Market Manipulation
The movie shows how Jordan Belfort, a famous stock broker, manipulates the market of penny stocks by spreading false information in the market and thereby operating a ‘Pump & Dump scheme’.
Trading Places (1983) – Insider Trading
The movie shows how the Duke Brothers made use of the insider information regarding the ‘Orange Crop Report’, which is set to be released by the United States Department of Agriculture, to manipulate the commodity futures markets.
Article written by Akshit Gupta (ESSEC Business School, Master in Management, 2022).

