The GameStop saga
In this article, Alexandre VERLET (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2019-2022) explains the GameStop saga. Why does the app “Robinhood” bears its name so well? Did hedge funds actually kneeled down before a bunch of Reddit users? What is a short squeeze? Let’s find out!
Speculation on GameStop
For some, it is a massive collusion that dangerously overvalued a firm, for others, forum users beat the greedy Wall Street hedge funds at their own game and allowed millions of ordinary millennials to make money. GameStop, which is now being referred to as the MOASS (the Mother of All Short Squeezes), is a financial drama that challenged Wall Street players and public regulators and a premise of the major shifts that amateur investing will impose upon financial markets. It all started on the Reddit forum called “WallStreetBets” in early January 2021, where amateur investors were merely sharing hinches and posting memes about their latest profits or losses. It became much more than that the day some users started to take personally the short selling of GameStop, a video games firm that had been a part of their teenage years and that they considered seriously undervalued. That was the spark that triggered a massive buy trend on the GameStop stock, to both support GameStop and to make money out of the big funds that seemed to always win on the markets. Then, a speculation bubble grew as the media started to report what was happening, amateur investors betting that millions of others would join the party, making money out of it and beating the hedge funds at their own game. The GameStop share rose from around $20 in early January to $480 in late January, a 2,300% increase that caused the short-selling hedge funds in what is known as a short squeeze position.
Figure 1. GameStop share price.
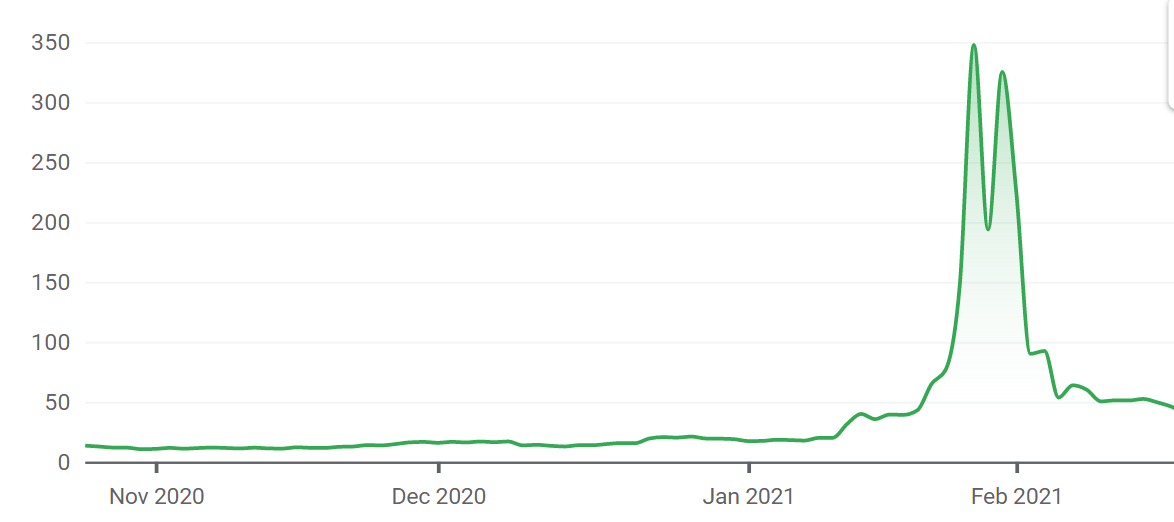
Source: Source: Google Finance.
Short selling
In order to understand what a short squeeze is, you must first get familiar with the concept of shorting. The simplest definition of shorting a stock would be to bet against that stock, meaning that one anticipates the stock price will drop at some point and wishes to make a profit out of that fall. Usually, an investor can either buy or sell a stock to respectively bet it will go up or down, but selling a stock implies the investor owns that stock. Although that sounds rather obvious, selling without owning a stock at all is actually possible – it is known as a “naked short”-, but it is theoretically illegal to do so in the USA. What investors do when they want to bet against a stock but do not own it, which is by far the most common case, is to place a “covered short”, meaning they borrow the stock from a broker in exchange for a commission, sell it for its current market price at time t, and buy it later once the price has fallen, say, at t+1. The current market price at time t minus the market price at time t+1 minus the broker’s commission is the investor’s profit. That is what happens when the investor is right. When he or she is wrong, things get trickier. Investing on financial markets is by definition risky, but buying shares only exposes the investor to lose the money invested. On the other hand, short-selling exposes to a loss that is theoretically limitless: a share price is bounded by 0 for a caller, but could rise to levels that could send the short seller to bankruptcy. That is what the short squeeze is all about: if the share price at time t+1 is much higher than at time t, buying the shares would mean a massive loss for the investor.
Now, the obvious question would be: why on earth would an investor sell at time t+1 and expose himself to massive losses, and not just wait for the share price to go down later? The first reason is that the investor pays fees to the broker that work like an adjustable interest rate, meaning the price rise will also drive the brokers fees up to the point that the investor might lose big, especially if he or she has to wait long enough for the price to go back to its selling price (and even lower than that to compensate the broker’s fees paid in-between). Second, the regulator, in our case the clearing house, ensures the solvability of investors by demanding they either refund their margin account or liquidate assets to make sure they are able to face their financial obligations towards the broker – this process is known as a “margin call”. The short squeeze happens when the investor is forced to buy back the shares he borrowed and sold initially, at a price that is much higher, which further drives the share price up in the case of a big investor.
In the case of GameStop, the short sellers were indeed big investors, with at least the two hedge funds Melvin Capital and Citron Capital short squeezed only a couple of weeks after the frenzy began. Since those investors short sold the stocks for around 20$, you can easily imagine that being forced to sell around 350$ costed huge amounts of money to those firms- up to $5 billion. What is brand new about GameStop, is the fact that the short squeeze was orchestrated by a group of amateur investors with no connections in Wall Street and using a public internet forum. The fact that it happened in 2021 is not so random. In recent years, social networks laid the ground for collusion at large scale, “free” trading apps such as Robinhood made investing as easy as a game, and the lockdowns imposed in 2020 boosted amateur investing activity. Considering the dreadful reputation of hedge funds, particularly since the 2008 crisis, such news was welcomed with much enthusiasm on the internet and beyond.
Political issues and future challenge for regulators
Consequently, when GameStop trading was frozen on the investing apps, the issue became political: “People on Wall Street only care about the rules when they’re the ones getting hurt. It’s time for SEC and Congress to make the economy work for everyone” said US Senator Sherrod Brown (Chairman of the Senate Banking Committee). Investor populism gained support on both sides of the political scene, as exemplified by the similar positions held by the Democrat AOC and the Republican Ted Cruz in favor of the amateur investors. Unfortunately, the reality is more complex than just GameStop being a victory for the democratization of finance where the mob overthrows the big players who run Wall Street. The SEC is currently investigating where the profits of the short squeeze went, and ironically a significant part of it might have been generated by innovative hedge funds who anticipated the trends by tracking forums and app data. Therefore, if financial markets keep attracting amateur investors people in the coming years, and they most likely will, a huge challenge awaits financial regulators. Meanwhile, AMC and Blackberry’s shares have been the next targets of the Reddit traders, and there is no doubt that the MOASS will engender many more financial dramas. To be continued…
 Source: GameStop
Source: GameStopRelated posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ Shruti CHAND WallStreetBets
▶ Raphaël ROERO DE CORTANZE Gamestop: how a group of nostalgic nerds overturned a short-selling strategy
▶ Raphaël ROERO DE CORTANZE How do “animal spirits” shape the evolution of financial markets?
Useful resources
GameStop (GME) (Yahoo Finance)
About the author
This article was written in April 2021 by Alexandre VERLET (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2019-2022).


1 thought on “The GameStop saga”
Comments are closed.