Green bonds
This article written by Akshit GUPTA (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2019-2022) explains Green bonds traded in financial markets.
Introduction
A green bond is a fixed-income product that works like a conventional bond, except that the money invested in them is used exclusively to finance green projects that support environment preservation, sustainability and reduction of climate change (low-carbon economy). Green projects can include renewable energy such as solar and wind power, energy-efficient infrastructure, clean transportation and waste management and recycling.
In 2007, the European Investment Bank (EIB) issued the world’s first ever green bond under the name Climate Awareness Bond (CAB), which focused on renewable energy and energy efficiency projects. This was followed by the World Bank issuing its own green bonds, until 2012 when the first corporate green bond was issued. Since then the market for green bonds has grown tremendously creating all-time highs with every passing year. The greatest issuer of green bonds in 2020 was the French government with a combined issue size of nearly 13 billion USD.
Types of green bonds
Green bonds can be classified as the following: green “use of proceeds” bonds, green “use of proceeds revenue” bonds, green project bonds, and securitized green bonds.
Green “use of proceeds” bonds
The funds raised by these green bonds are invested in green projects but they are backed/secured by issuer’s assets. Hence, their ratings are the same as other debt instruments by the issuer. For instance, the Climate Awareness Bond issued by EIB is one such green bond.
Green “use of proceeds revenue” bonds
The funds raised are assigned to eligible green projects. However, bondholders have recourse to a specified revenue stream from the issuers which may or may not be related to the eligible green projects.
Green project bonds
Proceeds from green project bonds are used for specific projects, investors having a direct exposure to the green project itself.
Securitized green bonds
These bonds are backed by a large group of green projects or assets.
Benefits of investing in green bonds for issuers
Lower cost of capital
Green bonds help environment focused companies to raise large amount of initial and working capital at lower costs to fund their ESG activities which require heavy initial investments. For example, companies can raise capital to fund a project focused towards generating renewable energy.
Brand value
Companies issuing green bonds enjoy an increase in the brand value and favourable reputation amongst the investors, as they are becoming more inclined towards sustainability.
Benefits of investing in green bonds for investors
Diversification
Over the years, the financial markets have seen an increased demand for green bonds amongst investors. Various factors have contributed to this increase including portfolio diversification, focus on socially responsible investments opportunities, fulfilment of ESG mandates of the financial institutions, etc.
Tax benefits
Investors can enjoy tax incentives on the investments made in green bonds. The interest incomes generated on these bonds are generally tax exempt or provide tax reductions to the investors. Thus, the issuers also benefit from lower interest rates due to the tax benefits.
Increase in liquidity
As the market size for green bonds is increasing, investors can enjoy higher liquidity and can exit their positions as per their needs.
Examples
The image below shows the listing of green bonds on Euronext.
Listing of green bonds on Euronext.
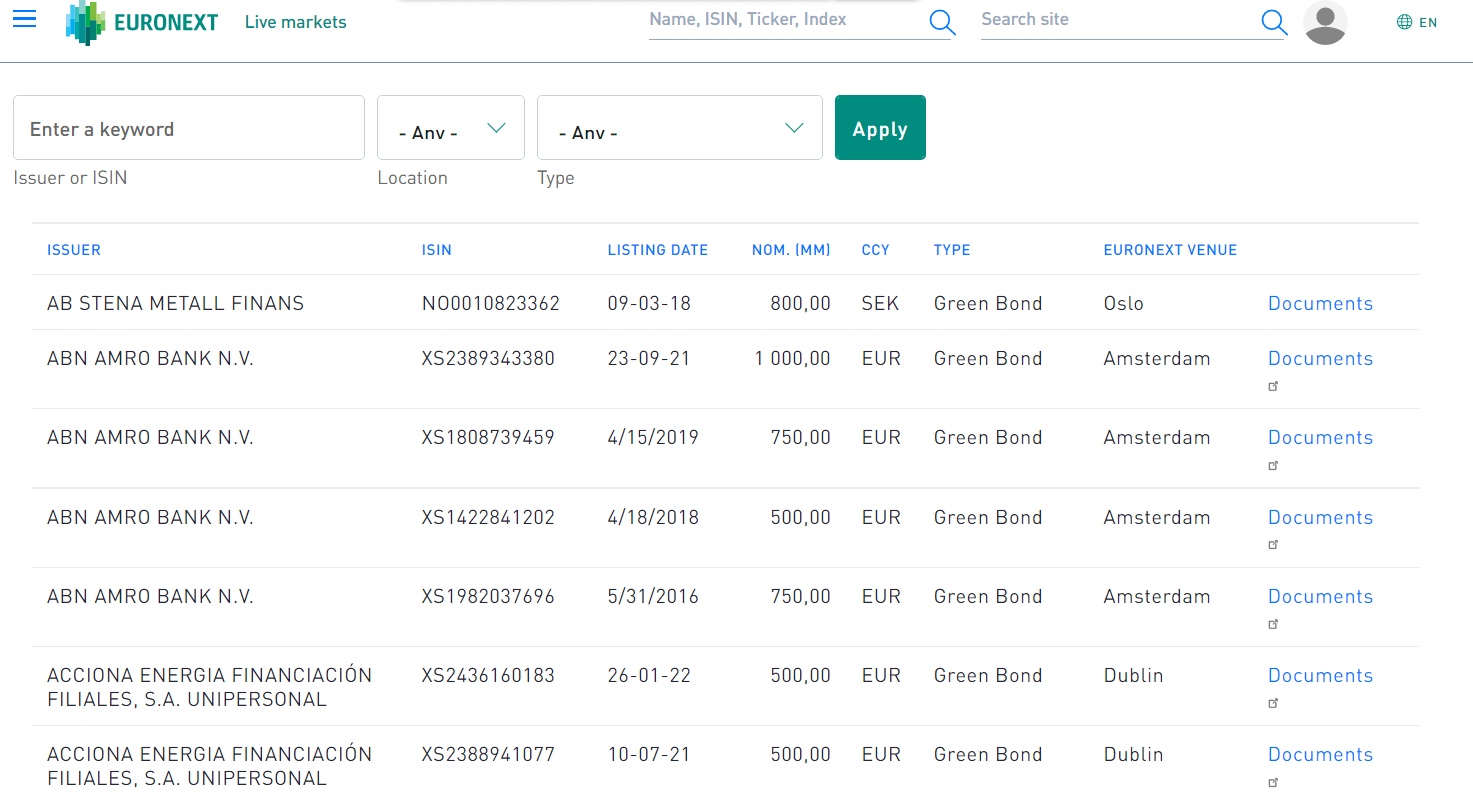
Source: Euronext.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ Akshit GUPTA Euro bonds
▶Jayati WALIA Fixed Income Products
▶ Jayati WALIA Credit Risk
Useful resources
Corporate Finance Institute Eurobonds
ICMA History of Eurobonds
Euronext Listing of green bonds
About the author
Article written in March 2022 by Akshit GUPTA (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2019-2022).


1 thought on “Green bonds”
Comments are closed.