
In this article, SHIU Lang Chin (ESSEC Business School, Global Bachelor in Business Administration (GBBA), 2024-2026) explains the time value of money, a simple but fundamental concept used in all areas of finance.
Overview of the time value of money
The time value of money (TVM) is the idea that one euro today is worth more than one euro in the future because today’s money can be invested to earn interest. In other words, receiving cash earlier gives more opportunities to save, invest, and grow wealth over time. This principle serves as the foundation for valuing loans, bonds, investment projects, and many everyday financial decisions.
To work with TVM, finance uses a few key tools: present value (the value today of future cash flows), future value (the value in the future of money invested today),etc. With these elements, it becomes possible to compare different cash-flow patterns that occur at various dates consistently.
Future value
The future value (FV) of money answers the question: if I invest a certain amount today at a given interest rate, how much will I have after some time? Future value uses the principle of compounding, which means that interest earns interest when it is reinvested.
For a simple case with annual compounding, the formula is:
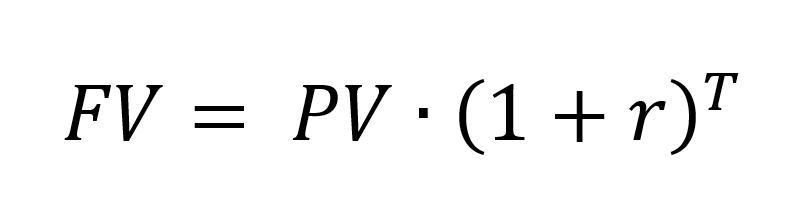
where PV is the amount invested today, r is the annual interest rate, and T is the number of years.
For example, if 1,000 euros are invested at 5% per year for 3 years, the future value is FV = 1,000 × (1.05)^3 = 1,157.63 euros. This shows how even a modest interest rate can increase the value of an investment over time.
Compounding frequency can also change the result. If interest is compounded monthly instead of annually, the formula is adjusted to use a periodic rate and the total number of periods. The more frequently interest is added, the higher the future value for the same nominal annual rate, illustrating why compounding is such a powerful mechanism in long-term investing.
Compounding mechanism with monthy and annual compounding.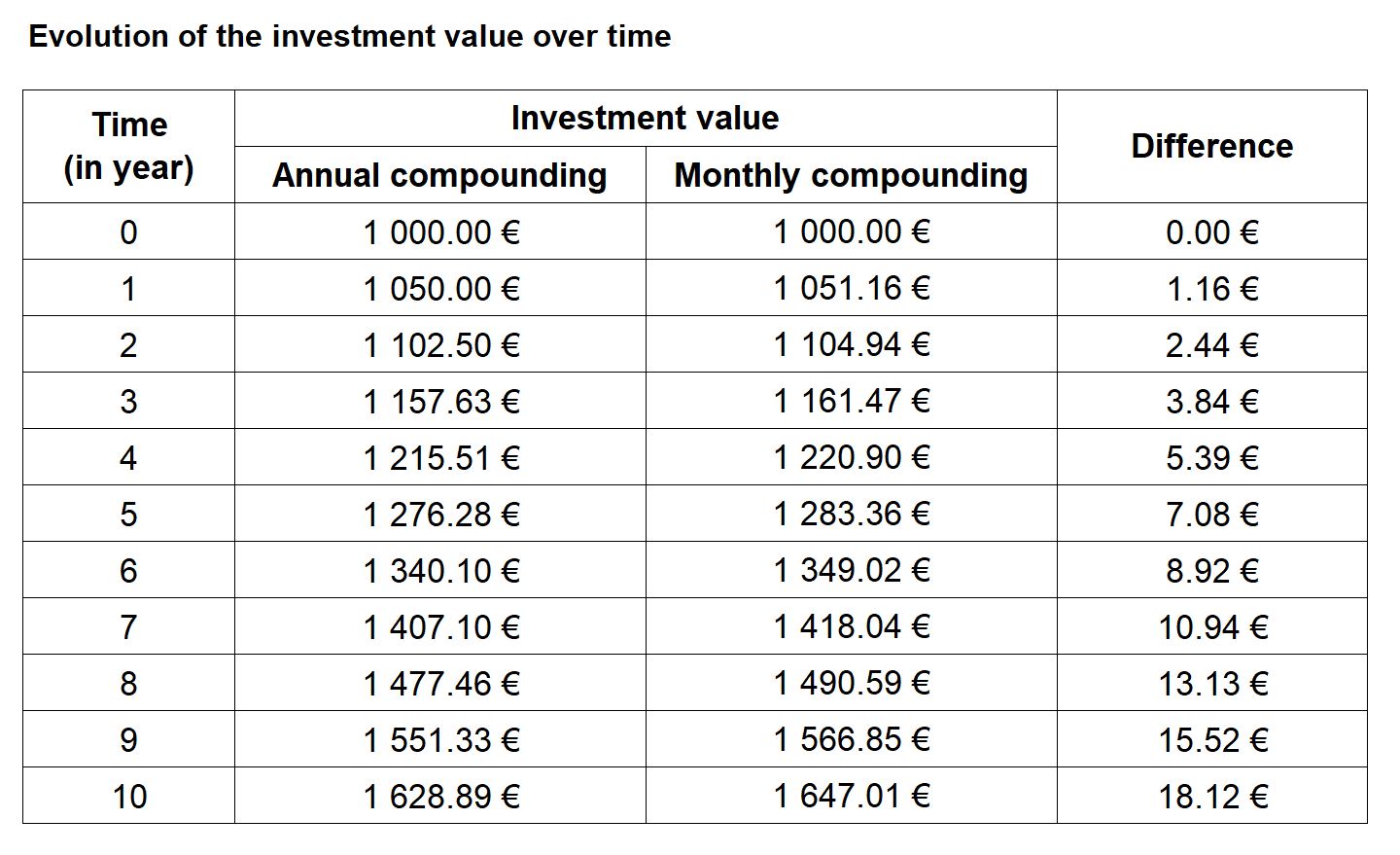
Compounding mechanism with monthy and annual compounding.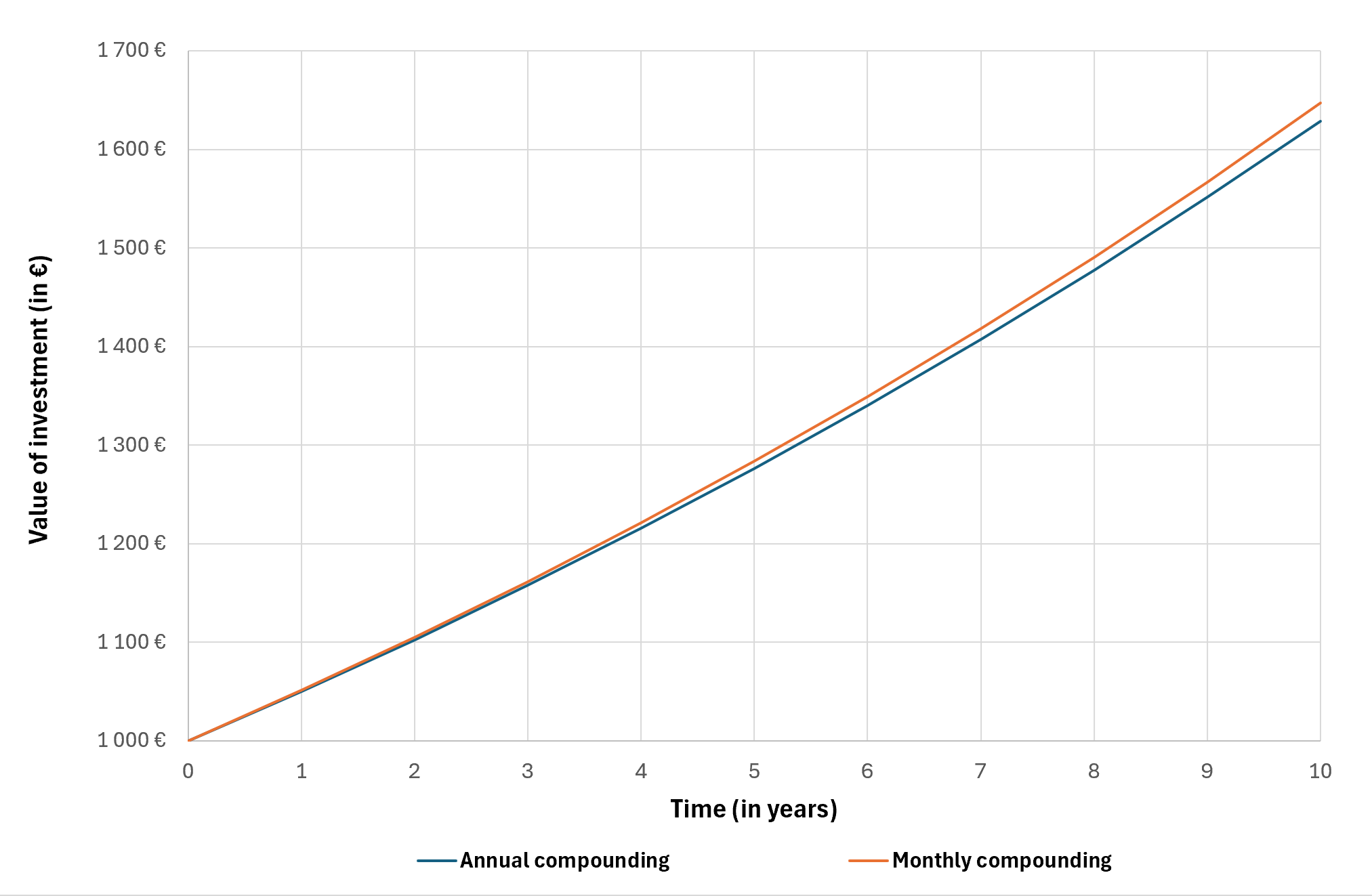
You can download the Excel file provided below, which contains the computation of an investment to illustrate the impact of the frequency on the compounding mechanism.
Present value
Present value (PV) is the reverse operation of future value and answers the question: how much is a future cash flow worth today? To find PV, the future cash flow is “discounted” back to today using an appropriate discount rate that reflects opportunity cost, risk and inflation.
For a single future cash flow, the present value formula is:
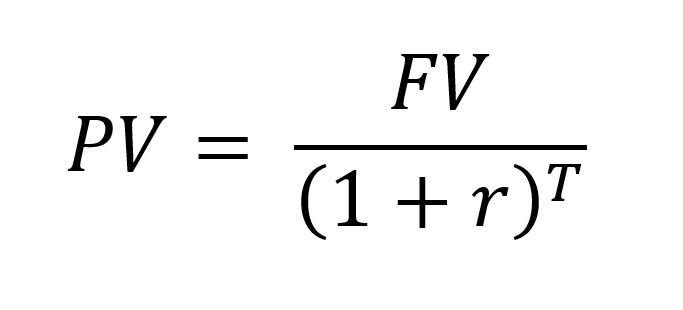
Where FV is the future amount, r is the discount rate per period, and T is the number of periods.
For example, if an investor expects to receive 1,000 euros in 2 years and the discount rate is 5% per year, the present value is PV = 1,000 / (1.05)^2 = 907.03 euros. This means the investor would be indifferent between receiving 907.03 euros today or 1,000 euros in two years at that discount rate.
Choosing the discount rate is a key step: for a safe cash flow, a risk-free rate such as a government bond yield might be used, while for a risky project, a higher rate reflecting the required return of investors would be more appropriate. A higher discount rate reduces present values, making future cash flows less attractive compared to money today.
Applications of the time value of money
The time value of money is used in almost every area of finance. In corporate finance, it forms the basis of discounted cash-flow (DCF) analysis, where the expected future cash flows of a project or company are discounted to estimate the net present value. Investment decisions are typically made by comparing the present value to the initial cost.
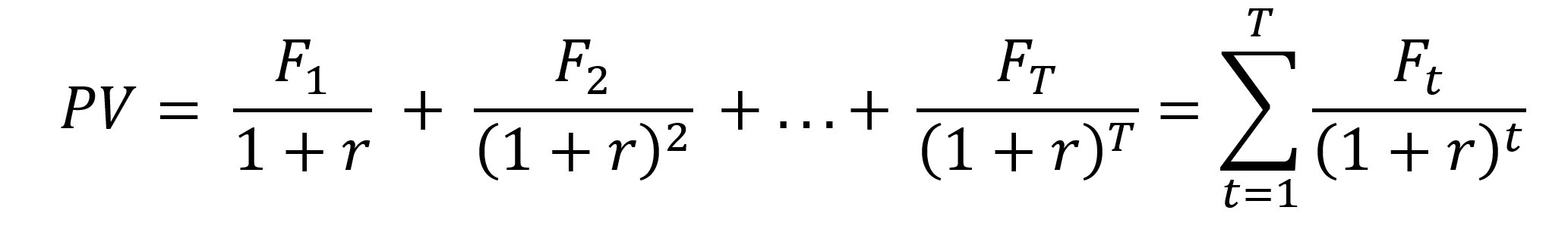
In banking and personal finance, TVM is essential to design and understand loans, deposits and retirement plans. Customers who understand how interest rates and compounding work can better compare offers, negotiate terms and plan their savings. In capital markets, bond pricing, yield calculations and valuation of many other instruments depend directly on discounting streams of cash flows.
Even outside professional finance, TVM helps individuals answer simple but important questions: is it better to take a lump sum now or a stream of payments later, how much should be saved each month to reach a future target, or what is the true cost of borrowing at a given interest rate? A good intuition for TVM improves financial decision-making in everyday life.
Why should I be interested in this post?
As a university student, understanding TVM is essential because it underlies more advanced techniques such as discounted cash-flow (DCF) valuation, bond pricing and project evaluation. It is usually one of the first technical topics taught in introductory corporate finance and quantitative methods courses.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ All posts about Financial techniques
▶ Hadrien PUCHE The four most dangerous words in investing are, it’s different this time
▶ Hadrien PUCHE Remember that time is money
Useful resources
Harvard Business School Online Time value of money
Investing.com Time value of money: formula and examples
About the author
The article was written in December 2025 by SHIU Lang Chin (ESSEC Business School, Global Bachelor in Business Administration (GBBA), 2024-2026).
▶ Read all articles by SHIU Lang Chin.

