
In this article, Emmanuel CYROT (ESSEC Business School, Global Bachelor in Business Administration (GBBA), 2021-2026) introduces the ELTIF 2.0 Evergreen Fund.
Introduction
The asset management industry is pivoting to democratize private market access for the wealth segment. We are moving from the rigid Capital Commitment Model (the classic “blind pool” private equity structure) to the flexible NAV-Based Model, an open-ended structure where subscriptions and redemptions are executed at periodic asset valuations rather than through irregular capital calls. For technical product specialists, the ELTIF 2.0 regulation isn’t just a compliance update, it’s the architectural blueprint for the democratization of private markets. Here is the deep dive into how these “Semi-Liquid” or “Evergreen” structures actually work, the European landscape, and the engineering behind them.
The Liquidity Continuum: Solving the “J-Curve” Problem
To understand the evergreen structure, you have to understand what it fixes. In a traditional Closed-End Fund (the “Old Guard”):
- The Cash Drag: You commit €100k, but the manager only calls 20% in Year 1. Your money sits idle.
- The J-Curve: You pay fees on committed capital immediately, but the portfolio value drops initially due to costs before rising (the “J” shape).
- The Lock: Your capital is trapped for 10-12 years. Secondary markets are your only (expensive) exit.
The Evergreen / Semi-Liquid Solution represents the structural convergence of private market asset exposure with an open-ended fund’s periodic subscription and redemption framework.
- Fully Invested Day 1: Unlike the Capital Commitment model, your capital is put to work almost immediately upon subscription.
- Perpetual Life: There is no “end date.” The fund can run for 99 years, recycling capital from exited deals into new ones.
- NAV-Based: You buy in at the current Net Asset Value (NAV), similar to a mutual fund, rather than making a commitment.
The difference in investment processes between evergreen funds and closed ended funds
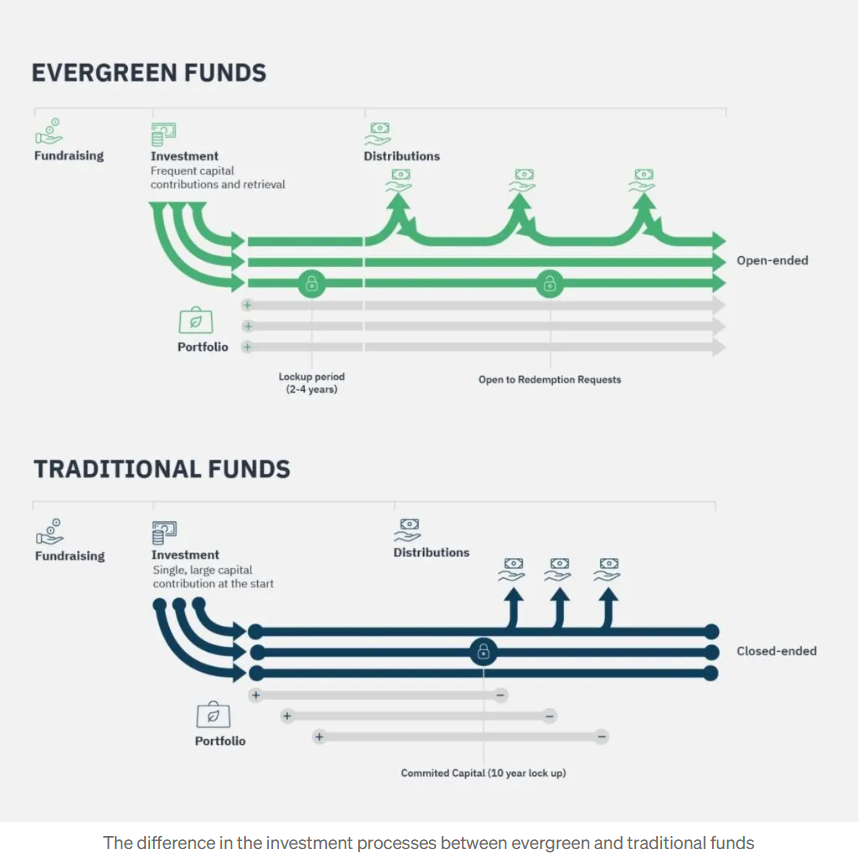
Source: Medium.
The European Landscape: The Rise of ELTIF 2.0
The “ELTIF 2.0” regulation (Regulation (EU) 2023/606) is the game-changer. It removed the extra local rules that held the market back in Europe. These rules included high national minimum investment thresholds for retail investors and overly restrictive limits on portfolio composition and liquidity features imposed by national regulators.
Market Data as of 2025 (Morgan Lewis)
- Volume: The market is rapidly expanding, with over 160+ registered ELTIFs now active across Europe as of 2025.
- The Hubs: Luxembourg is the dominant factory (approx. 60% of funds), followed by France (strong on the Fonds Professionnel Spécialisé or FPS wrapper) and Ireland.
- The Arbitrage: The killer feature is the EU Marketing Passport. A French ELTIF can be sold to a retail investor in Germany or Italy without needing a local license. This allows managers to aggregate retail capital on a massive scale.
Structural Engineering: Liquidity
This section delves into the precise engineering required to reconcile the illiquidity of the underlying assets with the promise of periodic investor liquidity in Evergreen/Semi-Liquid funds. This is achieved through a combination of Asset Allocation Constraints and robust Liquidity Management Tools (LMTs).
The primary allocation constraint is the “Pocket” Strategy, or the 55/45 Rule. The fund is structurally divided into two distinct components. First, the Illiquid Core, which must represent greater than 55% of the portfolio, is the alpha engine holding long-term, illiquid assets such as Private Equity, Private Debt, or Infrastructure. Notably, ELTIF 2.0 has broadened the scope of this core to include newer asset classes like Fintechs and smaller listed companies. Second, the Liquid Pocket, which can be up to 45%, serves as the fund’s buffer, holding easily redeemable, UCITS-eligible assets like money market funds or government bonds. While the regulation permits a high 45% pocket, efficient fund operation typically keeps this buffer closer to 15%–20% to mitigate performance-killing “cash drag”.
Crucial to managing liquidity risk is the Gate Mechanism. Although the fund offers conditional liquidity (often quarterly), the Gate prevents a systemic crisis if many investors attempt to exit simultaneously. This mechanism works by capping redemptions at a specific percentage of the Net Asset Value (NAV) per period, commonly set at 5%. If aggregate redemption requests exceed this threshold (e.g., requests total 10%), all withdrawing investors receive a pro-rata share of the allowable 5% and the remainder of their request is deferred to the next liquidity window.
Finally, managers utilize Anti-Dilution Tools like Swing Pricing to protect the financial interests of the long-term investors remaining in the fund. In a scenario involving heavy redemptions, where the fund manager is forced to sell assets quickly and incur high transaction costs, Swing Pricing adjusts the NAV downwards only for the exiting investors. This critical mechanism ensures that those demanding liquidity—the “leavers”—bear the transactional “cost of liquidity,” thereby insulating the NAV of the “stayers” from dilution.
Why should I be interested in this post?
Mastering ELTIF 2.0 architecture offers a definitive edge over the standard curriculum. With the industry pivoting toward the “retailization” of private markets, understanding the engineering behind evergreen funds and liquidity gates demonstrates a level of practical sophistication that moves beyond theory—exactly what recruiters at top-tier firms like BlackRock or Amundi are seeking for their next analyst class.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ David-Alexandre BLUM The selling process of funds
Useful resources
Société Générale Fonds Evergreen et ELTIF 2 : Débloquer les Marchés Privés pour les Investisseurs Particuliers
About the author
The article was written in December 2025 by Emmanuel CYROT (ESSEC Business School, Global Bachelor in Business Administration (GBBA), 2021-2026).
▶ Read all articles by Emmanuel CYROT.
