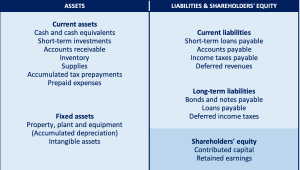
Assets
In this article, Shruti CHAND (ESSEC Business School, Master in Management, 2020-2022) elaborates on the concept of assets.
This read will help you get started with understanding Assets side on the balance sheet of a company.
Introduction
An asset can be defined as anything that has an economic value or future benefit. Assets are an important part of the balance sheet of a firm as it reports all that a business owns at a given point of time. Assets are economic resources that will generate cash flows in the future. Examples of assets include machinery, building, accounts receivable, etc.
All the value of assets that one sees on the balance sheet are typically recorded on historical cost, adjusted from time to time based on depreciation. The Assets side of the balance sheet states all the assets in the order of their liquidity, i.e., ease with which they can be converted into cash. Hence, current assets such as cash or cash equivalents, short-term investments, etc. are listed first followed by fixed non-liquid assets at the end (with the US and international framework).
Structure of the Assets part of the Balance Sheet
Types of Assets on the Balance Sheet:
Current Assets:
Any asset that can be converted into cash with ease (Typically within a timeframe of 1 year) is known as Current Asset.
Most common current assets on a balance sheet include cash and cash equivalents, inventory, accounts receivable, and other prepaid expenses.
Fixed Assets:
Fixed assets are resources that the business owns which cannot be converted into cash immediately. Most noteworthy fixed assets on a balance sheet include plants, buildings, machinery and equipment. There is a constant adjustment that is made to the value of these assets from time to time to reflect their current value.
Financial Assets:
This asset class represents the securities, corporate bonds, preferred equity and all other hybrid equity that is financial in nature that the business owns.
Intangible Assets:
These assets have no physical existence whatsoever, but since they still have value attached to it and generate benefit for the business, they are categorized as Intangible Assets. Examples of intangible assets include patents, copyrights, trademarks, goodwill and other intellectual property owned by the business.
Note that with the French presentation of the balance sheet, the least liquid assets appear in the top while the more liquid assets appear in the bottom of the balance sheet), and similarly the shareholders’ equity and the long-term liabilities appear in the top while the short-term liabilities appear in the bottom of the balance sheet.
Final Word:
Investors use the Assets side of the balance sheet to check the financial health of the business (profitability of the investments). One common way to assess the performance is to find out Asset turnover ratio which measures the revenues generated form the use of assets against sales.
The amount of which type of asset a business owns is dependent upon its area of operations. Some businesses are more capital intensive than others which might require them to have more fixed assets than others. Equipment manufacturers are going to have large number of fixed assets such as machinery while a tech business have almost no fixed assets (except intellectual property assessed over time accounted in intangibles).
Relevance to the SimTrade certificate
This post deals with Asset side of the balance sheet, an important tool for investors to take investment decisions.
About theory
- By taking the SimTrade course, you will know more about how investors can use various strategies to invest in order to trade in the market.

About practice
- By launching the series of Market maker simulations, you can extend your learning about financial markets and trading approaches.

About the author
Article written by Shruti Chand (ESSEC Business School, Master in Management, 2020-2022).