

In this article, William LONGIN (Sorbonne School of Economics, Master in Money Banking Finance Insurance, 2024-2026) and Kilien DUPAYRAT (IESEG School of Management, Grande Ecole Program, Entrepreneurship, 2022-2027) discusses “free” video game business models and uses the case studies of League of Legends, Candy Crush, and Axie Infinity as an illustration.
Introduction
There is “no such thing as a free lunch” but somehow the early 21th century has been marked by the emergence of games that don’t need to be purchased to be played.
The video game market matters! It is the biggest entertainment related industry in the world. According to Access Creative College (2022) “the game industry is worth almost double the film and music industry, combined”. In 2022, the global market size of the video game industry was estimated at 217 billion USD and expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13% between 2023 and 2030 according to Grand View Research (2022).
Since its inception in the late 20th century, the video game industry has rapidly evolved from arcade games to immersive experiences across devices. The industry keeps growing and is driven by changing consumer preferences and new technologies. At its disposal is an array of strategies to be profitable. The ways of playing and technologies also evolved with it, from the basic arcade games where you needed to insert a coin to play, to the most advanced business models like blockchain games where the content is made of NFTs. Companies in today’s revenue models master the balance between paying and non-paying players as well as understanding the latest trends.
In this article, we will look at why so many video game companies make their games free and how these new revenue models are the most popular. As a reminder, the revenue model is part of the business model and focuses on how the company makes money by monetizing its products.
Free-to-play (F2P) revenue model
The free-to-play (F2P) revenue model offers free download video games. Their method to generate revenue is through in-game purchases of virtual items for cosmetic, boosting or convenience purposes. The bought items don’t influence the gameplay but can appeal to a desire to design and customize (costumes, colors, etc.) The free-to-play revenue model initially wasn’t popular with investors and companies due to the dominance of traditional premium models, where games were purchased to download. The lack of upfront cost has allowed these sorts of games to reach a larger audience. The F2P model has proven to be highly effective, contributing significantly to the popularization of video games in general. In 2020, Free to play games accounted for “78% of the digital games market revenue” (Davidovici-Nora, 2013).
League of Legends case study
The spread of F2P revenue models came with the rise of online games such as “League of Legends,” free to download but with costly in-game items. The in-game currency is called “Riot Points, RP’s” and can be traded for cosmetic items (skins, wards, emotes) and other non-essential enhancements (event passes, rune pages). Purchases don’t give a gameplay advantage to paying players vs nonpaying players. Therefore, by eliminating barriers to entry to play the game significantly increased its reach. Consider here under the process map of typical experience for a player of “League of Legends” and where transactions take place.
Figure 1 below presents the flow chart “from download to purchase” for the case of League of Legends.
Figure 1. Flow chart from download to purchase: the case of League of Legends.
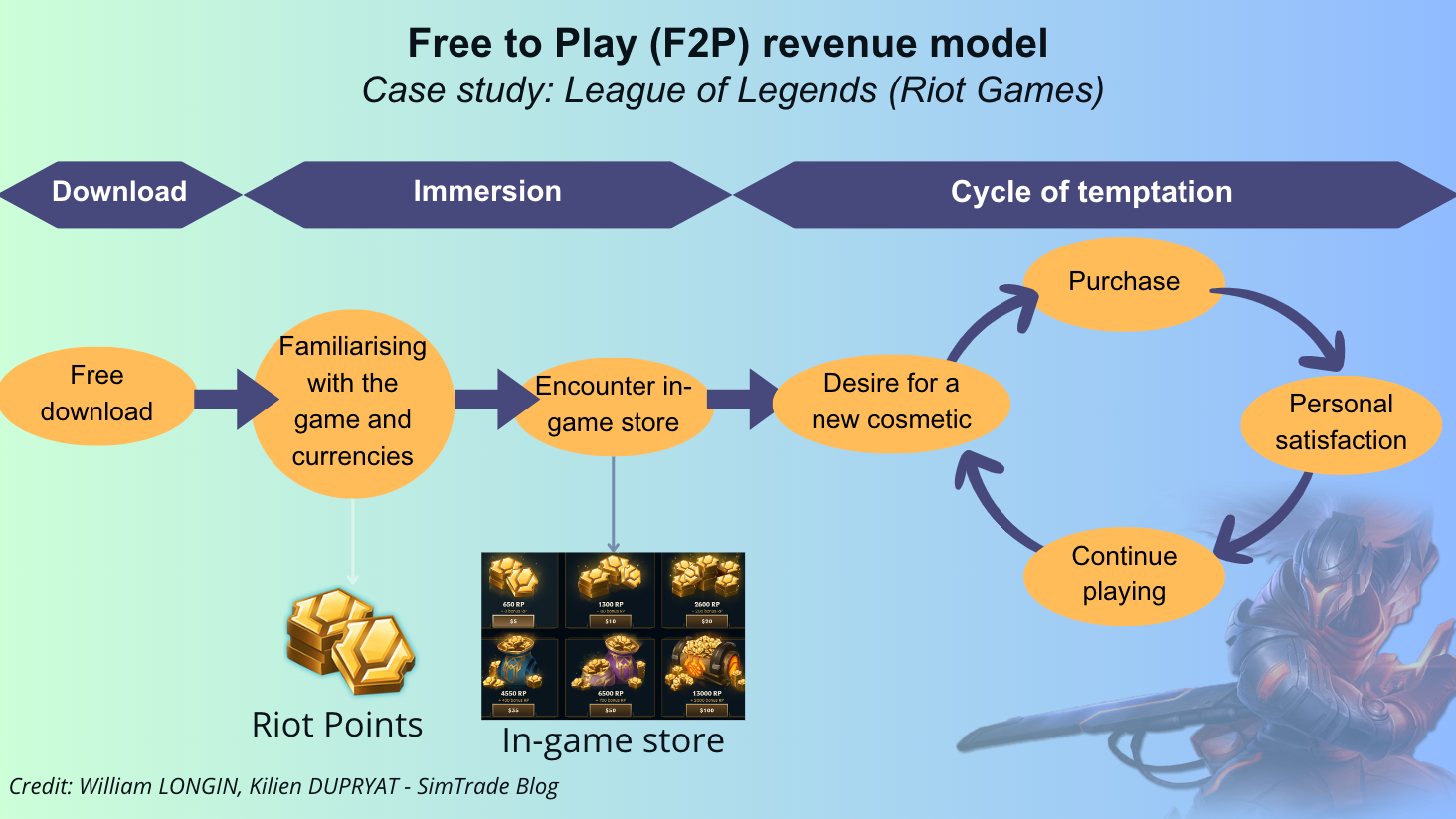
Source: the authors.
Freemium revenue model
The freemium revenue model offers free-to-download video games like F2P games but it doesn’t offer access to the entire game. The differences between both business models are subtle. The gaming experience is incomplete (store purchases include game extensions at a premium). Thus, the name “freemium” is a combination of “free”, the core gaming experience is free and “premium” as the game extensions are purchasable at a premium. In this revenue model there is also possibility to purchase cosmetic items, boosters and convenience improvers.Candy Crush case study
Candy Crush is an example using the freemium model because it is free to download and begin playing but encourages players to pay for certain enhancements or additional content to improve or expedite their gameplay experience. While the core mechanics—matching candies, progressing through levels, and competing with friends—are accessible at no initial cost, the game limits play sessions through mechanisms like lives (which refill slowly over time) and imposes difficulty spikes on certain levels. Players looking to bypass these limitations, access extra levels more quickly, or gain advantageous power-ups and boosters can purchase them through in-app transactions. These premium offerings are not strictly necessary to play the game, but they greatly enhance or complete the experience, making Candy Crush a clear example of the “freemium” model: the main game is free, yet the most streamlined, convenient, or extended version of play comes at a premium.Figure 2 below presents the flow chart “from download to purchase” for the case of Candy Crush.
Figure 2. Flow chart from download to purchase: the case of Candy Crush Saga.
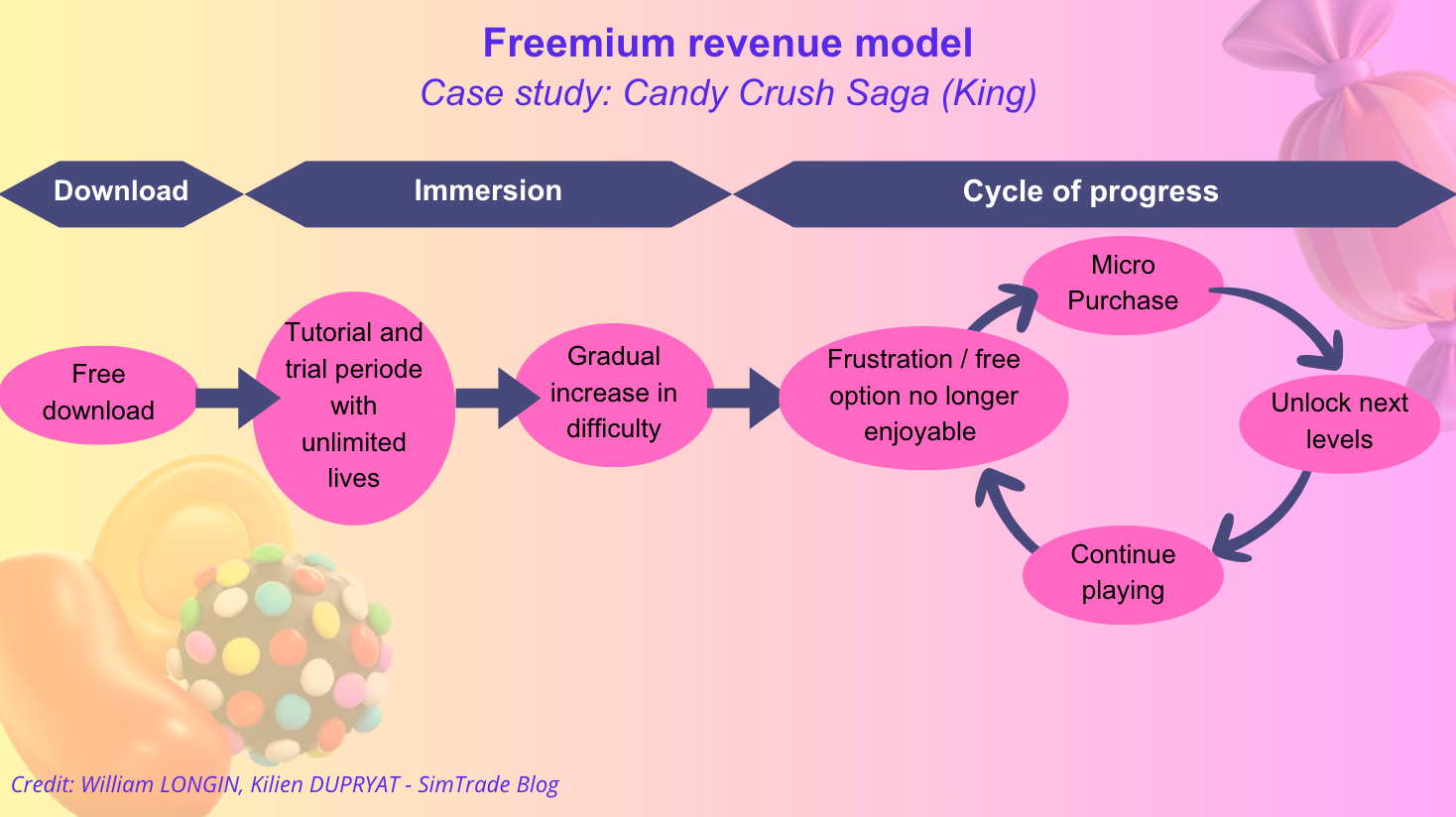
Source: the authors.
The flow chart above illustrates how the freemium revenue model typically unfolds for a game like Candy Crush Saga. Initially, players are enticed by the free download and ease of access. After installing, they enter a tutorial or trial phase where resources such as lives are abundant, allowing them to experience the game’s mechanics without frustration. As players progress, the difficulty gradually increases, eventually reaching levels at which winning without purchasing boosts or extra lives becomes challenging. This leads to a point of dissatisfaction or frustration, where the game’s free option feels less enjoyable or even stalled. In response, many players opt to make micro-purchases—buying boosters, additional moves, or unlocking new levels—to overcome obstacles and continue playing seamlessly. This cycle repeats, encouraging ongoing engagement and revenue generation through periodic spending.
Play-to-earn (P2E) revenue model
Revenue Model
The blockchain revenue model is known as the play-to-earn (P2E). These games use blockchain technology to create decentralized gaming ecosystems where players can earn real-world value through in-game activities. Although counterintuitive, this business model brings value to players and to the video game creators at the same time. This model represents a significant shift from traditional gaming paradigms by integrating financial incentives directly into gameplay.
Axie Infinity case study
The game Axie Infinity is a blockchain game and is an example of a P2E game. The game studio charges a rate between transactions in the game economy. “Sky Mavis charges a 4.25% fee to players when they trade Axies on its marketplace.” according to wikipedia.
Figure 3 below presents the flow chart “from download to purchase” for the case of Axie Infinity.
Figure 3. Flow chart from download to purchase: the case of Axie Infinity.
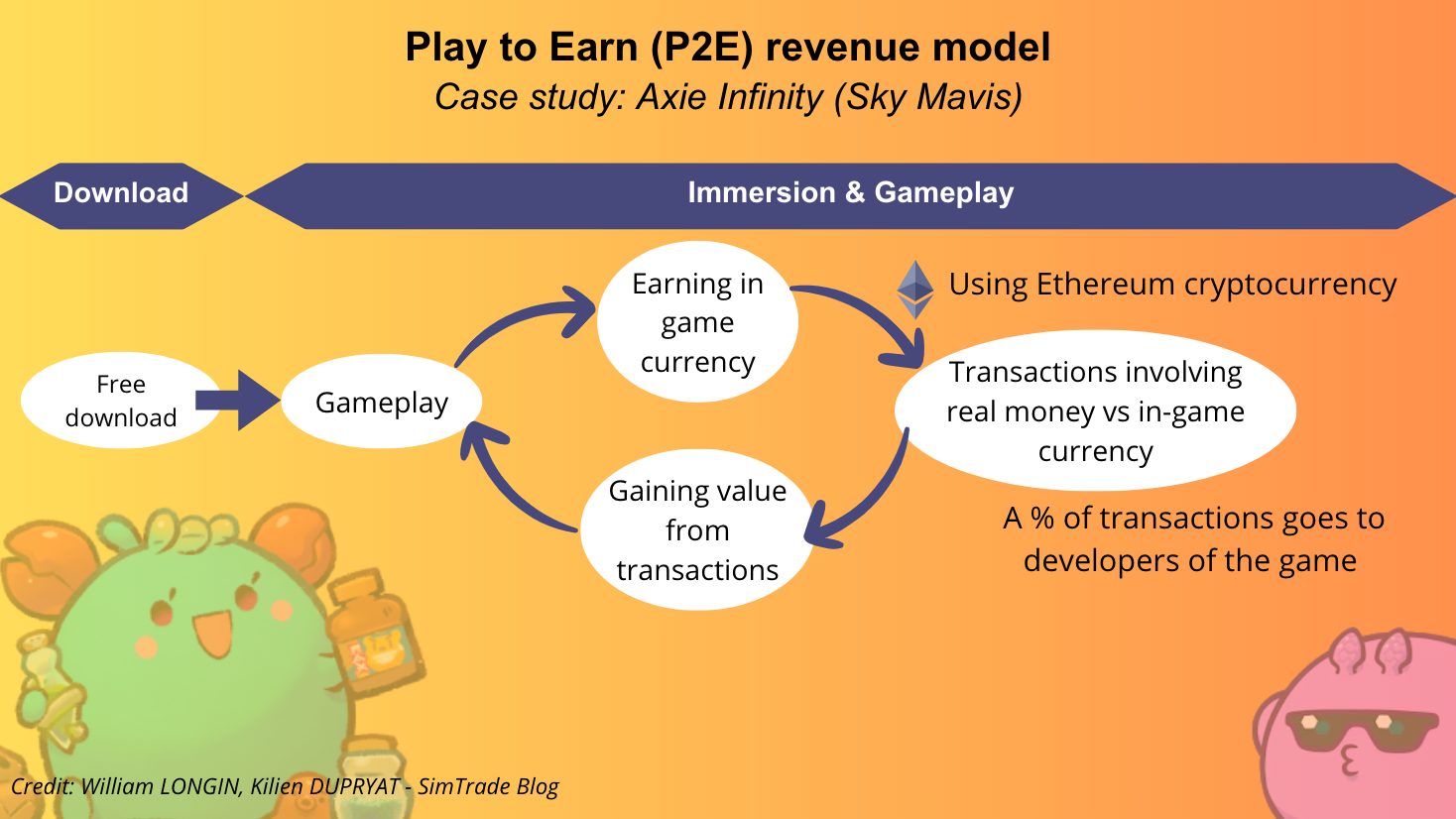
Source: the authors.
The flow chart above illustrates the play-to-earn (P2E) revenue model, using Axie Infinity as an example. The process begins with a free download, allowing players to access the game without an initial purchase. Once immersed in gameplay, players engage in activities—such as battles, breeding, or quests—that reward them with in-game currency. What sets P2E apart is that these virtual assets have real-world value, often tied to cryptocurrencies like Ethereum. Players can trade, sell, or convert their earned in-game currency and items into real money, effectively monetizing their skill, time, and investment in the game. Every transaction, from buying and selling digital creatures (Axies) to acquiring special items, passes through a decentralized marketplace, with a percentage of each trade returning to the game developers. This cycle creates an ecosystem where both players and creators benefit financially, as gameplay activities drive the value of the in-game economy and sustain the platform’s growth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the “Free-to-Play”, “Freemium”, and “Play-to-Earn” revenue models have revolutionized the way video games generate revenue, each presenting distinct strategies to engage and monetize players while having their games freely downloadable to players. These revenue models are also used in different sectors such as dating applications, social media and music streaming companies.
From a data analysis perspective, both models provide a wealth of information on user preferences and behaviors, allowing for increased personalization and optimization of gaming experiences. However, this also raises ethical questions, particularly concerning the management of gaming addiction and impulsive spending, especially among young or vulnerable players. In terms of performance, statistics often show that the Free-to-Play model can reach a broader user base, while the Freemium model can generate higher revenue per active user due to the need to unlock content, and Play-to-Earn models gain revenue when the gamer user base is active and growing. Each business model has its merits and drawbacks, and the choice of model largely depends on the type of game and the target audience.
Why Should I Be Interested in This Post?
You should be interested in this post because it gives insights on the revenue models companies in the video game industry have adopted. There a section on “blockchain” video games that are very recent and could hold a prevalent space in the years to come. Indeed, by mixing real currency and in-game currency and creating a virtual economy it can become even more addictive and meaningful for players. In the light of the new technologies developed in the augmented reality and virtual reality spaces these types of video games could be the future.
Related Posts on the SimTrade Blog
▶ Raphaël ROERO DE CORTANZE Gamestop: how a group of nostalgic nerds overturned a short-selling strategy
Useful resources
Access Creative College How much is the gaming industry worth?
Techquickie (YouTube channel) Blockchain Games Are Here – What You Should Know
Wikipedia Axie Infinity
About the authors
The article was written in December 2024 by William LONGIN (Sorbonne School of Economics, Master in Money Banking Finance Insurance, 2024-2026) and Kilien DUPAYRAT (IESEG School of Management, Grande Ecole Program, Entrepreneurship, 2022-2027).
▶ Read all articles by William LONGIN.
