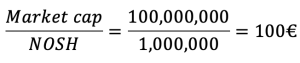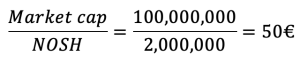Stock split
In this article, Raphaël ROERO DE CORTANZE (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2018-2022) introduces the specificities of stock splits.
Stock split
What a stock split?
A stock split is a decision by a company’s board of directors to increase the total number of shares by issuing more shares to current shareholders. The effect is to divide the existing shares into multiple new shares.

For instance, a company with 1 million shares launches a 2-for-1 stock split. Post-stock split, the Number of Outstanding Shares (NOSH) will be 2 million, thus, the company has to issue 1 million new shares. Each existing shareholder will receive an additional issued share for each share he/she already has.
During a stock split, the market capitalization of the company remains the same. In effect, the company has simply issued new shares to existing shareholders, it has not sold those shares (it would have been the case during a capital increase for instance). As the market cap remained the same and the Number of Outstanding Shares doubled during this stock split, the adjusting variable is the stock price. In this case it is divided by 2.
Before the operation, the per share price amounted to:
After the stock split, the per share price amounts to:
In other words, a stock split does not add any real value, because the issued shares are not bought.
Why do companies split their stock?
Stock splits are far from being uncommon. Apple has undergone two stock splits in the last 10 years: the first in 2014 (7-for-1 stock split) and the second in 2020 (4-for-1 stock split, where the share price decreases from $460 to $115). In 2020, Tesla has also decided to go with a 5-for-1 stock split, which reduced the share price from $1,875 to $375. But why do companies resort to stock-splits?
Two main reasons can explain why companies go through splitting their stock:
- Decrease the stock price: when to stock price is too high, it can be quite expensive to acquire “lots” of shares (lot in the sense of bundle). Splitting the stock reduces the prices, thus allowing more investors to buy the company’s stock.
- Increase the stock liquidity on the market: a higher number of shares outstanding can result into a higher liquidity for the stock, which makes the stock more attractive for buyers and sellers. Indeed, it allows more flexibility, and provide buying and selling movements from having too much of an impact on the company’s stock price.
Many companies exceed later the price level at which they had previously split their stock, causing them to go through another stock split. For instance, Walmart has split its stock 9 times between 1975 and 1999.
Stock exchanges publish regularly a Stock Splits Calendar, which notifies the market when to expect a split and at what ratio.
Stock split signaling
As we have seen in our example above, a stock-split is supposed to not influence the stock price (besides dividing its price by the stock-split ratio). In reality, a stock-split usually sends a positive signal to the market, as stock-splitting announces higher liquidity and decreased prices. Stock splits also allow companies such as Apple or Tesla to prevent their stock from breaking through the ceiling and make the stock unaffordable.
Reverse stock-split
What is a reverse stock-split
As for a traditional stock split, a reverse stock split is a decision made by a company’s board of directors. Nonetheless, like its name indicates, a reverse stock-split is the opposite of a traditional stock split. The goal is to decrease the total number of shares.
Before the reverse stock split After the reverse stock split
In this example, the reverse stock split ratio is 1-for-2 (i.e., 1 new share for 2 existing shares). From the 1 million shares of the company, 0.5 million are destroyed. The Number of Outstanding Shares post-reverse stock-split is thus 0.5 million. As for a traditional stock split, no real value is created or destroyed, the market capitalization remains the same. The adjusting variable is the stock price. In this case, the stock price is multiplied by 2.
Why do companies go through reverse stock-split?
The reverse stock-split procedure is usually used by companies which have a low share price and would like to increase it. Indeed, companies can be delisted from stock exchanges if their stock falls below a certain price per share.
In addition, a reverse stock split can be used to eliminate shareholders that hold fewer than a certain number of shares. For instance, in 2011, Citigroup launched a reverse 1-for-10 split in order to reduce its share volatility and discourage speculator trading.
Useful resources
CNN Why it’s time for Amazon and other quadruple-digit stocks to split
Nasdaq Stock Splits Calendar
The Economic Times What is ‘Stock Split’
About the author
Article written in June 2021 by Raphaël ROERO DE CORTANZE (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management, 2019-2022).