Covid-19 and its effect around hospital
This article written by Subhasish CHATTERJEE (ESSEC Business School, Master in Strategy & Management of International Business (SMIB), 2020-2021) discusses the financial impact of the Covid-19 crisis on the healthcare sector in India and especially for hospitals.
Impact of the Covid-19 crisis on hospital operations
For any organization, a positive operating margin is essential for long-term Financial stability. Few organizations can maintain themselves for a long period when total operating expenses are greater than total operating revenues. A positive operating margin allows the organisation to develop its business by financing new projects with internal financial resources along with external financial resources such as debt and equity.
For hospitals, a positive operating margin allows them to invest in new treatment services for enhancing patient satisfaction, building of new facilities, and researching on new drugs.
Before Covid-19
Compared with other sectors, healthcare margins typically have been very low. Even before the appearance of Covid-19, a number of Indian hospitals struggled with poor or even negative margins—in other words, they were losing money on their operations. In fact, the median hospital margin was around 4.7 percent. This situation has been perilous to the future viability of many of Indian hospitals.
My experience during my internship
When the Covid-19 pandemic emerged, hospitals had to renounce the non-Covid treatment. The result was a drastic slowdown in volume of patients and in revenue, but the expenses remained high. To date, nobody can assure when and to what degree these non-Covid patients will return in the hospital. The result has been an uncertain future about the ability of hospitals to serve their communities and remain financially viable. My experience was in India but if you follow the statistics, the hospitals are suffering from same consequences anywhere in the world.
As indicated in Figure 1, during the year 2020, because of the Covid-19 crisis, 39.4% of hospitals lost more than 50% of their revenue compared to last year. Hospital Systems are Data from Hospital Centre Compiled Together.
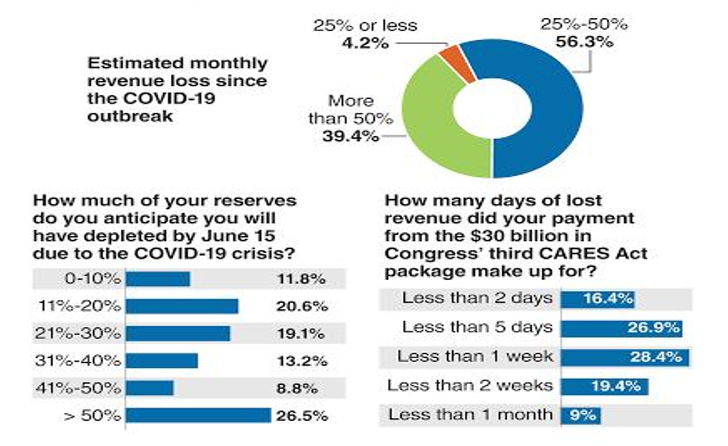
Source: AMGA surveys.
As indicated in Figure 2, during the year 2020, because of the Covid-19 crisis, 47.6% of independent medical groups lost more than 50% revenue as clinics couldn’t treat and provide bed to patients on a larger scale like hospitals. Independent Medical group are the private clinics run by physicians.
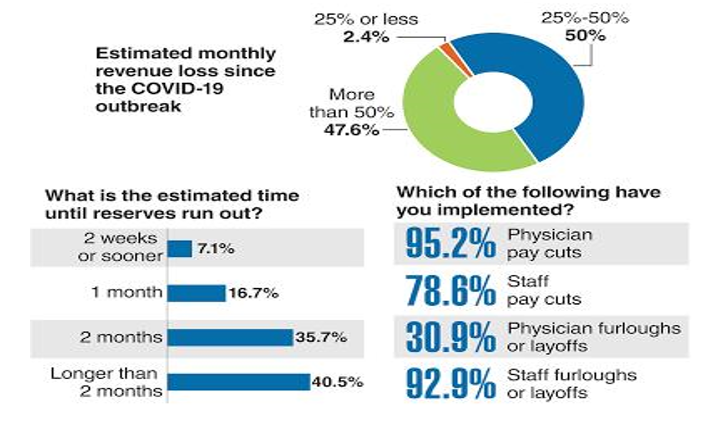
Source: AMGA surveys.
The possible long-term impact of Covid-19 in hospitals
To date, the financial impact of Covid-19 has been significant, even with Government funding, the financial damage is likely to continue. Adding to this is the unpredictable nature of Covid-19. Now more than ever, hospitals will need support from governments, and will need to rethink their strategic–financial plans for what is likely to be a highly challenging environment even as Covid-19 cases diminish.
Key concepts
I present below key concepts to understand the financial situation of a business.
Ebitda
Ebitda = Revenue – Operating expense – Employee expense – Administrative & other expense
Some expenses of hospitals:
- Wages and benefits
- Professional fees
- Food for patients
- Medical equipment
- Prescription drugs
- Professional liability insurance
- Utilities
- Nursing, general and other professional services.
Some revenue of hospitals:
- Patient service revenue
- Research revenue
- Academic revenue
Profit before and after tax
Profit before tax = Ebitda – Depreciation – Amortization – Interest on debt
Profit after tax = Profit Before Tax – Tax rate ✖ Profit Before Tax
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ All posts about Professional experiences
About the author
Article written by Subhasish CHATTERJEE (ESSEC Business School, Master in Strategy & Management of International Business (SMIB), 2020-2021).

