
In this article, Nithisha CHALLA (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management (MiM), 2021-2024) delves into the Herfindahl-Hirschmann Index(HHI).
History of the Herfindahl-Hirschmann Index(HHI)
The Herfindahl–Hirschman Index (HHI) originated in the mid-20th century as a measure of market concentration. Its roots trace back to Albert O. Hirschman, who in 1945 introduced a squaring-based method to assess trade concentration in his book “National Power and the Structure of Foreign Trade.” A few years later, Orris C. Herfindahl independently applied a similar concept in his 1950 doctoral dissertation on the U.S. steel industry, formalizing the formula that sums the squares of firms’ market shares to capture dominance. Over time, economists combined their contributions, naming it the Herfindahl–Hirschman Index.
During the 1970s and 1980s, the measure gained prominence in industrial organization and competition economics. In 1982, the U.S. Department of Justice and the Federal Trade Commission officially adopted the HHI in their Merger Guidelines to evaluate market concentration and the impact of mergers, establishing it as a global standard. Since then, competition authorities worldwide, including the European Commission and the OECD, have incorporated HHI into their antitrust frameworks, and it remains widely used today to assess competition across various industries, such as banking, telecommunications, and energy.
The Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI) is a widely used measure of market concentration and competition in various industries. The HHI has become a crucial tool for finance professionals, policymakers, and regulatory bodies to assess the level of competition in a market. In this article, we will delve into the basics of the HHI, its calculation, interpretation, and advanced applications, including recent statistics and news.
What is the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI)?
The HHI is a numerical measure that calculates the market concentration of a particular industry by considering the market share of each firm. The index ranges from 0 to 10,000, where higher values indicate greater market concentration and reduced competition. For example, a market comprising four firms with market shares of 30%, 30%, 20%, and 20% would have an HHI of 2,600 (30² + 30² + 20² + 20² = 2,600).
Calculation of the HHI
The HHI is calculated by summing the squares of the market shares of each firm in the industry. The market share is typically expressed as a percentage of the total market size. The formula for calculating the HHI is:
Formula for the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI).
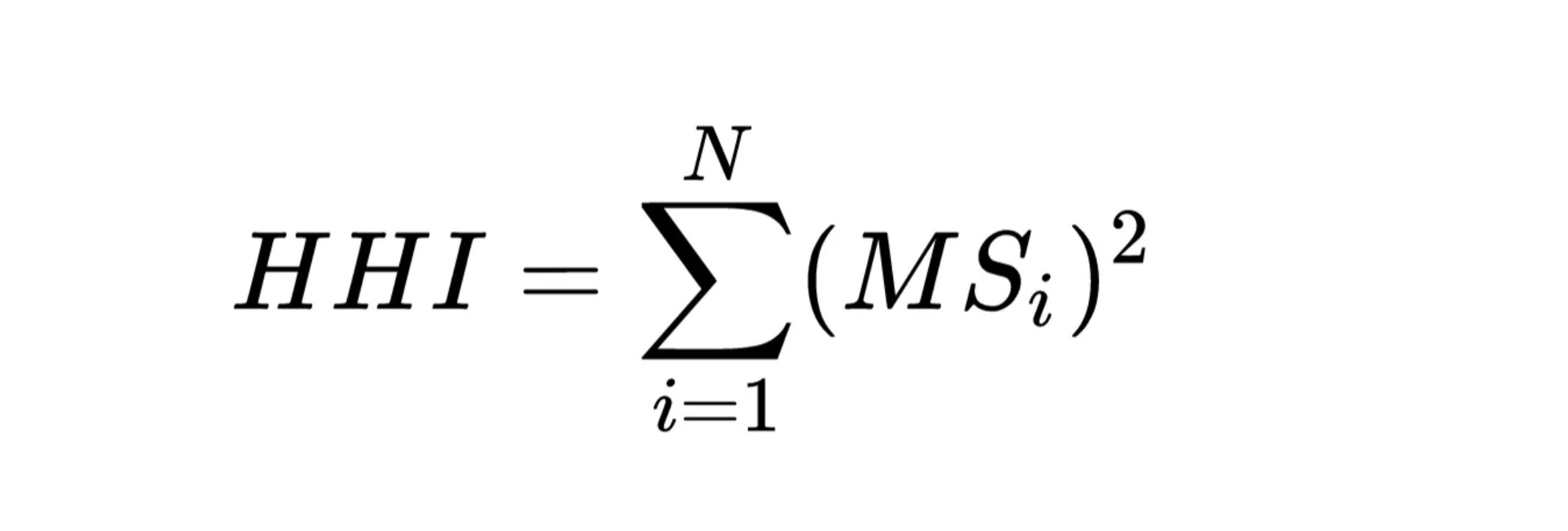
Source: the author.
where MSi is the market share of firm i, and N the number of firms.
The HHI ranges from 0 (perfect competition) to 10,000 (monopoly).
Interpretation of the HHI
According to the HHI, the concentration of sectors can be categorized as low, moderate and high:
- Low concentration (HHI < 1,500): Indicates a highly competitive market with many firms.
- Moderate concentration (1,500 ≤ HHI < 2,500): Suggests a moderately competitive market with some dominant firms.
- High concentration (HHI ≥ 2,500): Indicates a highly concentrated market with limited competition.
I built an Excel file to illustrate the three cases: low, moderate, and high concentration.
Low concentration: HHI < 1,500
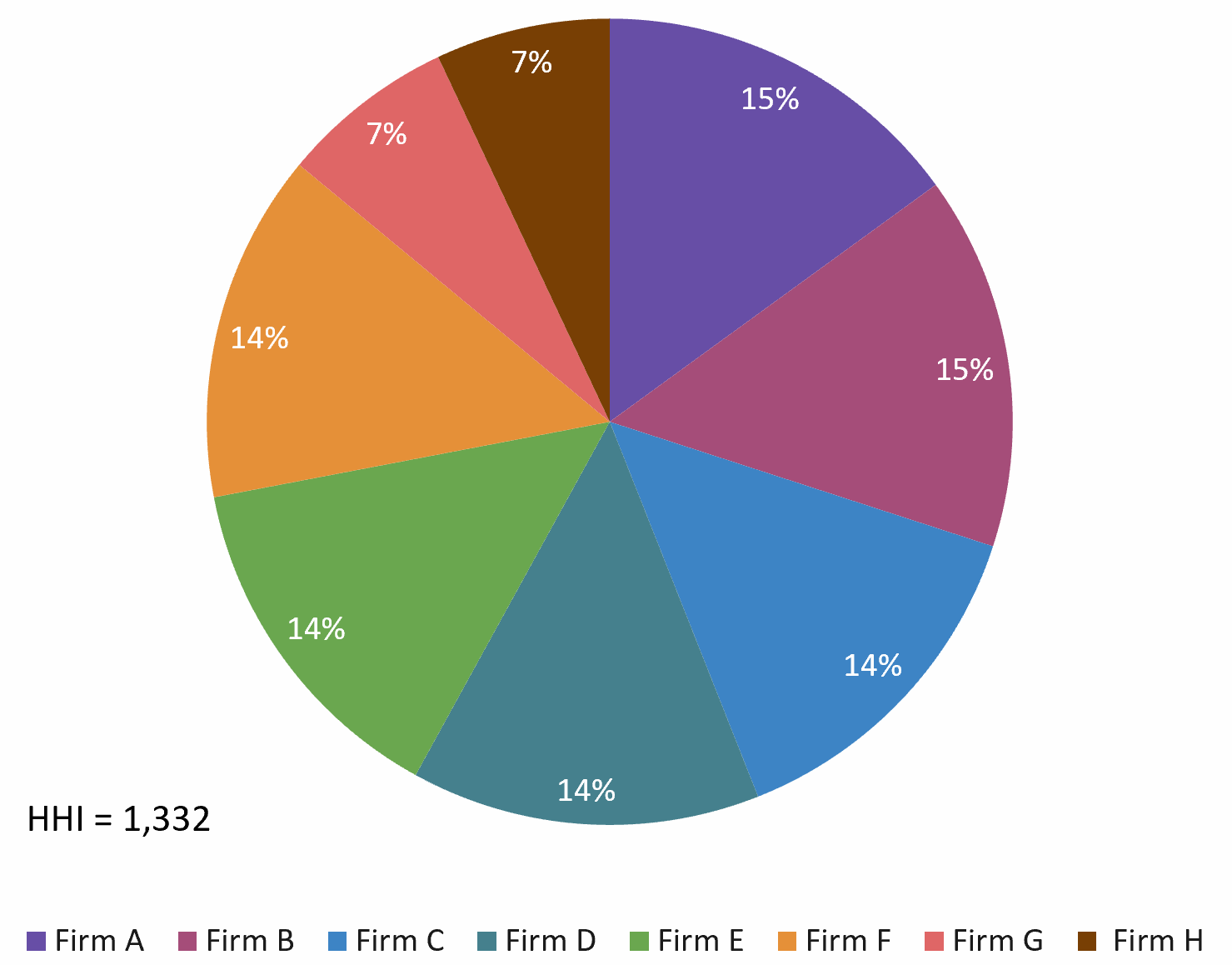
Source: the author.
Moderate concentration: 1,500 < HHI < 2,500
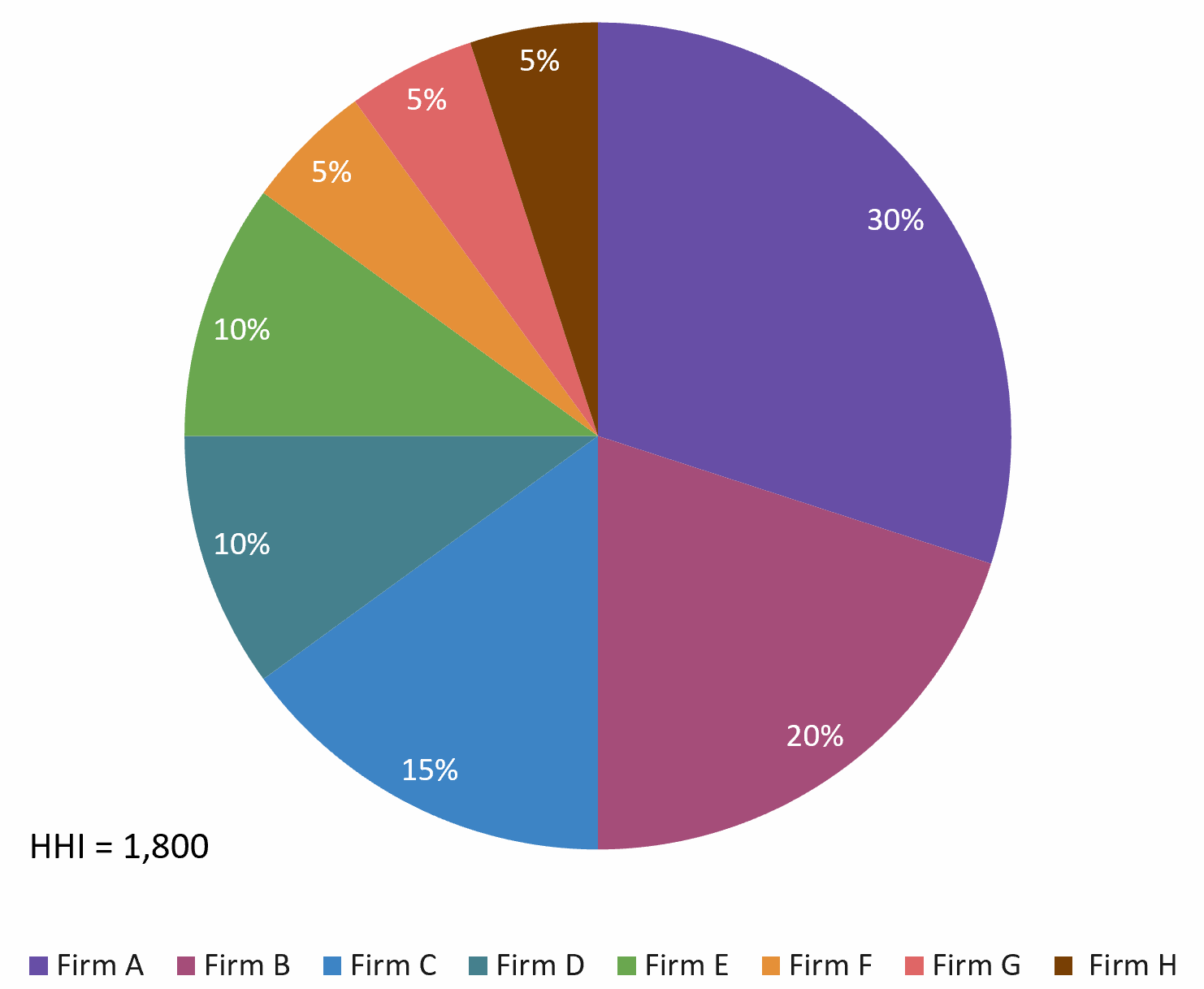
Source: the author.
High concentration: HHI > 2,500
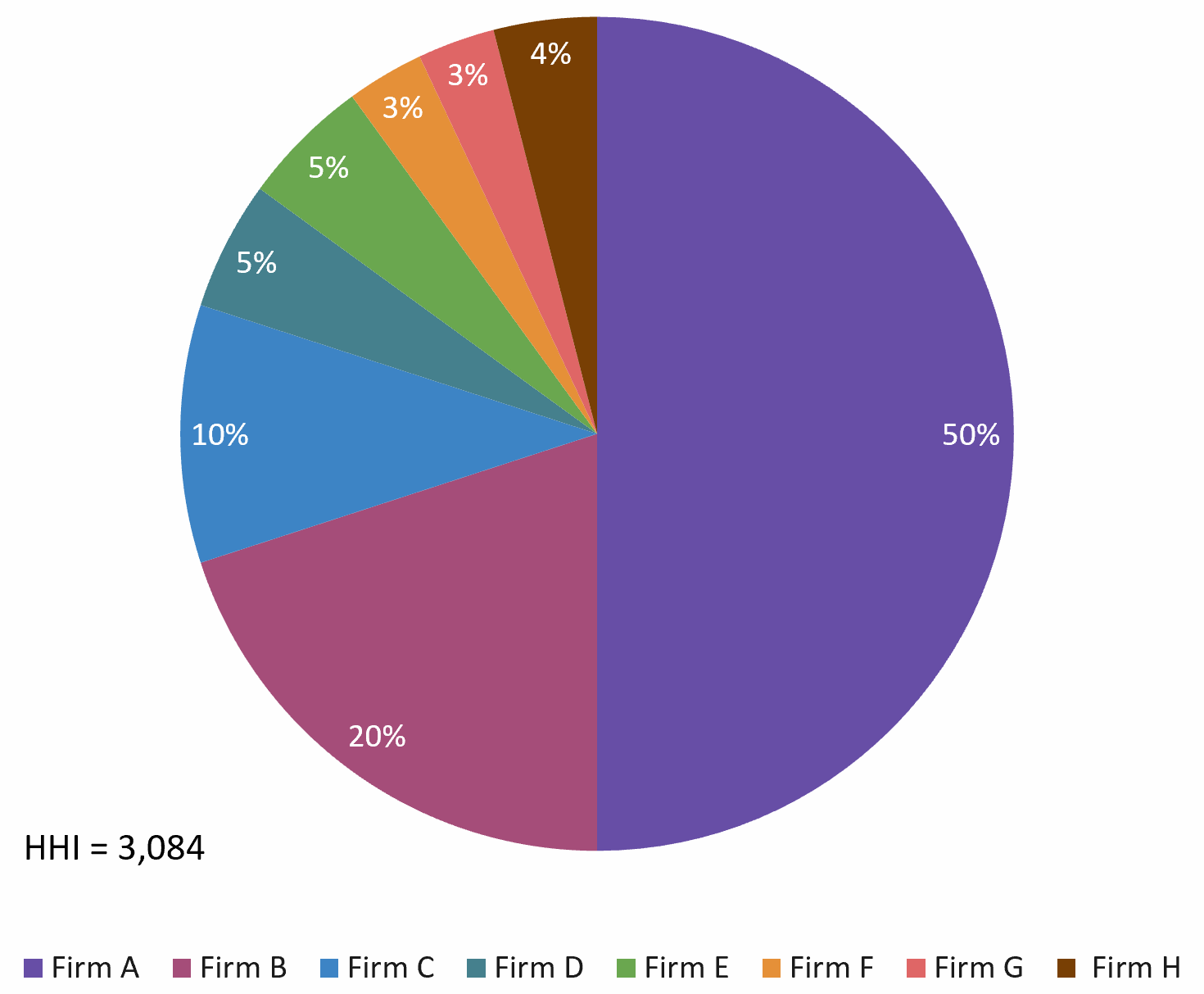
Source: the author.
You can download below the Excel file for the data used to build the figure for the HH index.
Advanced Applications of the HHI
The HHI has several advanced applications in finance, economics, and regulatory frameworks. Some of these applications include:
- Merger analysis: Regulatory bodies, such as the US Federal Trade Commission (FTC), use the HHI to assess the potential impact of mergers and acquisitions on market competition.
- Industry analysis: Finance professionals use the HHI to analyze the competitive landscape of an industry and identify potential investment opportunities.
- Antitrust policy: The HHI is used to inform antitrust policy and enforcement, helping to prevent anti-competitive practices and promote competition.
- Market structure analysis: The HHI is used to analyze the market structure of an industry, including the number of firms, market shares, and barriers to entry.
Criticisms and Limitations of the HHI
While the HHI is a widely used and useful measure of market concentration, it has several criticisms and limitations. Some of these include:
- Simplistic assumption: The HHI assumes that market shares are a good proxy for market power, which may not always be the case.
- Ignorance of other factors: The HHI ignores other factors that can affect market competition, such as barriers to entry, product differentiation, and firm conduct.
- Sensitive to market definition: The HHI is sensitive to the definition of the market, which can affect the calculation of market shares and the resulting HHI value.
Real-World Examples
US Airline Industry: The HHI for the US airline industry has increased significantly over the past two decades, indicating growing market concentration. According to a 2020 report by the US Government Accountability Office, the HHI for the US airline industry increased from 1,041 in 2000 to 2,041 in 2020.
US Technology Industry: The HHI for the US technology industry has also increased significantly over the past decade, indicating growing market concentration. According to a 2022 report by the US FTC, the HHI for the US technology industry increased from 1,500 in 2010 to 3,000 in 2020.
Recent Statistics and News
- A 2021 FTC staff report on acquisitions by major technology firms highlighted a “systemic nature of their acquisition strategies,” indicating a clear trend toward market concentration as they frequently acquired startups and potential competitors.
- A 2020 article by the American Enterprise Institute noted that while the HHI for the US airline industry had increased by 41% since the early 2000s, inflation-adjusted ticket prices had actually fallen.
- In its 2019 antitrust lawsuit to block the T-Mobile and Sprint merger, the US Department of Justice argued the deal was “presumptively anticompetitive,” citing HHI calculations that showed the merger would substantially increase concentration in the mobile wireless market.
- Recent studies have utilized the HHI to analyze hospital market concentrations. For example, research on New Jersey’s hospital markets revealed increasing consolidation, with several regions classified as “highly concentrated” based on HHI scores. This information is crucial for understanding the implications of market concentration on healthcare accessibility and pricing
Regulatory Framework
The HHI is widely used by regulatory bodies around the world to assess market competition and concentration. In the US, the FTC and the Department of Justice use the HHI to evaluate mergers and acquisitions and to enforce antitrust laws. Similarly, in the European Union, the European Commission uses the HHI to assess market competition and concentration in various industries.
Conclusion
The Herfindahl-Hirschman Index remains a fundamental instrument for assessing market concentration and competition. Its applications have evolved across various sectors, providing valuable insights into market structures. However, practitioners should be mindful of its limitations and consider complementing the HHI with other analytical tools for a comprehensive market assessment.
Why should I be interested in this post?
The Herfindahl-Hirschman Index is a powerful tool for analyzing market structure and assessing competitive dynamics. As markets continue to evolve, the HHI will remain an essential tool for navigating the complexities of competition in the modern economy. So as business and finance students, it is necessary to know such an important index to keep up with the evolving world around us.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ Nithisha CHALLADatastream
Useful resources
United states Department of Justice Herfindahl–Hirschman index
Eurostat Glossary:Herfindahl Hirschman Index (HHI)
United States Census Bureau Herfindahl–Hirschman index
Academic articles
Bach, G. D. (2020, March 18). Strong Competition Among US Airlines Before COVID-19 Pandemic. American Enterprise Institute.
Federal Trade Commission. (2021, September). FTC Staff Presents Report on Nearly a Decade of Unreported Acquisitions by the Biggest Technology Companies. Federal Trade Commission
United States Department of Justice. (2019, June 11). Complaint, United States of America et al. v. Deutsche Telekom AG et al. (Case 1:19-cv-01713). United States District Court for the District of Columbia
About the author
The article was written in October 2025 by Nithisha CHALLA (ESSEC Business School, Grande Ecole Program – Master in Management (MiM), 2021-2024).

