Free Cash Flow: A Critical Metric in Finance
In this article, Lou PERRONE (ESSEC Business School, Global BBA, 2019-2023) explains the concept of Free Cash Flow and its importance in financial analysis.
What is Free Cash Flow?
Free Cash Flow (FCF) is a critical financial metric used to determine the amount of cash generated by a business after accounting for capital expenditures. It represents the cash available for distribution among all the securities holders of a company (equity holders and debt holders) and provides insight into a company’s financial health and its ability to pursue opportunities without external financing.
How is Free Cash Flow Calculated?
The general formula for calculating Free Cash Flow:
Free Cash Flow = Operating Cash Flow – Capital Expenditures
Operating Cash Flow refers to the total amount of cash generated by a company’s core operating activities. It reflects the cash generated from the actual business operations of selling goods and services.
Capital Expenditures (CapEx) are funds used by the company to purchase, upgrade, and maintain physical assets. This could include expenditures on property, plant, equipment, and technology.
Example of FCF
The Excel document provided as an exemple is a critical financial tool that enables an in-depth analysis of ABC Limited’s Free Cash Flow (FCF). By meticulously tracking the inflows and outflows of cash, the spreadsheet highlights the company’s capacity to generate cash after covering all its capital expenditures. Observing the ‘Net Cash Flow’ row, we can discern the periods where the company has successfully managed its resources to produce a positive FCF, which indicates surplus cash availability that can be used for debt repayment, reinvestment in the business, dividends to shareholders, or as a reserve for future growth opportunities. Conversely, any negative FCF would warrant a closer investigation into the company’s spending on assets or its operational efficiency. The ability to forecast and analyze FCF is crucial for business sustainability and strategic financial planning, as it provides a clearer picture of financial health beyond simple profitability metrics.
Example of computation of free cash flows.
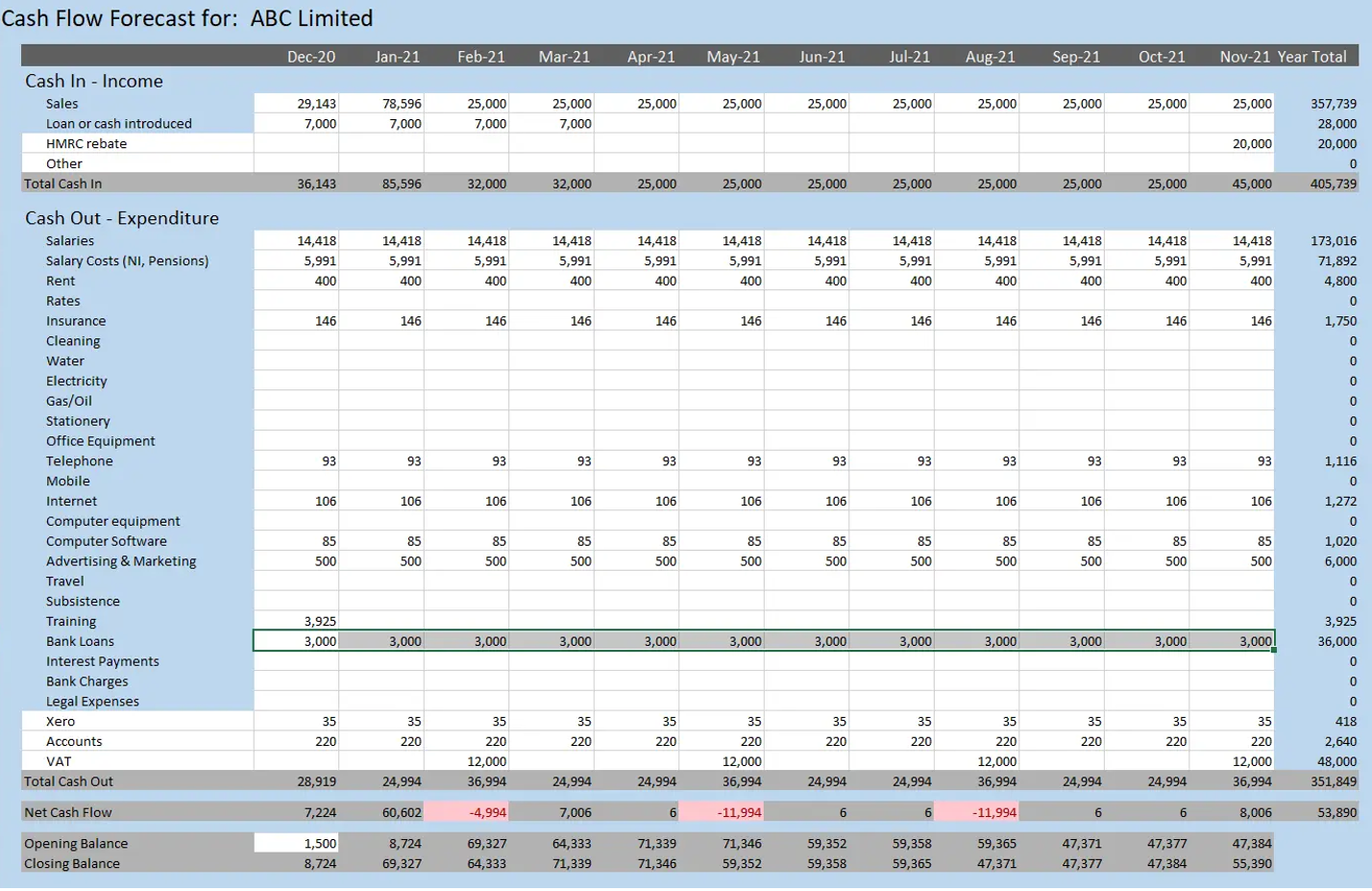
Source: the author.
Why is Free Cash Flow Significant?
FCF is an important indicator of a company’s financial strength. It shows how efficient a company is at generating cash and is often used by analysts and investors to assess whether a company has the financial flexibility to invest in its business, pay down debt, return money to shareholders, or weather economic downturns.
Factors Impacting Free Cash Flow
While many elements can impact the calculation of FCF, some key influencers include:
- Revenue Growth: Increases in sales can lead to higher operating cash flows.
- Operating Margins: Efficiency in managing operational costs can lead to better margins and in turn affect FCF positively.
- Capital Efficiency: Companies that manage their capital expenses efficiently can have higher free cash flows, as they spend less on fixed assets relative to the cash they generate.
The Dual Nature of FCF
A consistently positive FCF indicates a company’s ability to generate surplus cash after meeting all its operational and capital requirements. On the other hand, consistently negative FCF might suggest that the company is investing heavily for future growth or struggling to generate enough cash.
Interpreting Free Cash Flow
It’s crucial to contextualize FCF within the industry and the specific company’s growth stage. High-growth firms might have lower FCF due to heavy investments, while mature companies might generate more consistent free cash flows.
Why should I be interested in this post?
Understanding Free Cash Flow is indispensable for management students. It not only measures a company’s profitability but also its liquidity, solvency, and the overall health of its business model. By assessing FCF in conjunction with other financial metrics, students can gain a comprehensive view of a company’s financial health, aiding them in making informed investment or management decisions. Whether it’s for investment appraisal or corporate financial analysis, understanding the nuances of FCF is fundamental for anyone in the realm of finance and business.
Related posts on the SimTrade blog
▶ All posts about Financial Techniques
Useful resources
Damodaran A. (2012) Investment Valuation: Tools and Techniques for Determining the Value of Any Asset 3rd ed. New York: Wiley.
Brealey R.A., Myers S.C., and Allen F. (2011) Principles of Corporate Finance 11th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill/Irwin.
Ross S.A., Westerfield R.W., and Jaffe J. (2016) Corporate Finance 11th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill/Irwin.
About the author
The article was written in December 2023 by Lou PERRONE (ESSEC Business School, Global BBA, 2019-2023).

